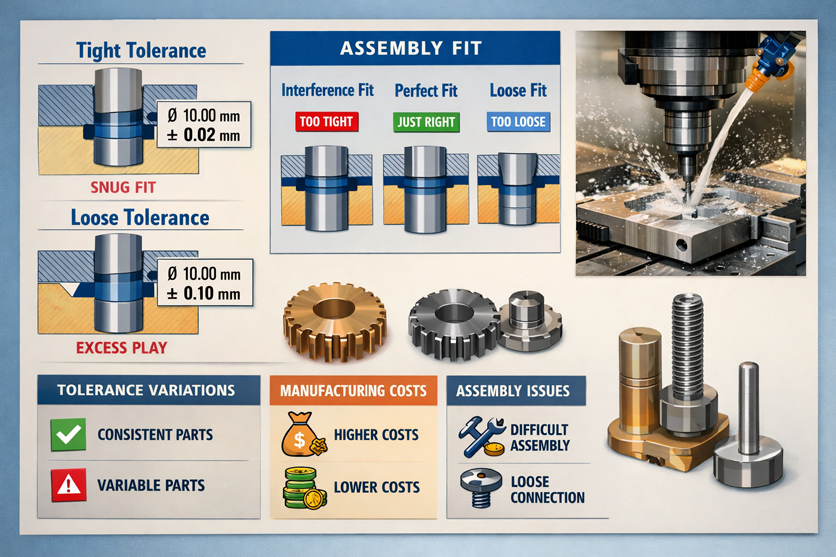
CNC machining tolerances for assembly fit are important. They help parts line up and work well. They also make sure parts last a long time. When you set tolerances, you pick the size range that is okay. This keeps parts steady and accurate. Bad tolerances can cause parts to not fit right. They can make parts wear out too fast. Parts may shake or even break during assembly.
Tolerances help stop things from breaking or being unsafe.
Wrong tolerances can mess up the whole assembly. This can make products not last as long.
If you ignore tolerances, you may spend more money. You might waste time and materials.
Getting the right mix of fit, accuracy, and cost helps your assemblies work the way you want.
Key Takeaways
Pick tolerances that match what each part needs to do. This helps the parts fit and work well.
Use normal tolerances for parts that are not very important. This can save time and money.
Think about how tolerances add up in assemblies. This helps stop problems with how parts fit together.
Talk clearly with your CNC supplier about what tolerances you need before making parts.
Try out tolerances with prototypes first. This helps you find and fix problems early.
How CNC Machining Tolerances Affect Assembly Fit (Quick Answer)
Why CNC Tolerances Directly Determine Assembly Success
CNC machining tolerances are very important for assembly. They decide if parts fit together the right way. When you pick good tolerances, each part lines up as planned. This makes assembly easy and helps products work well. If you do not use the right cnc machining tolerances, your assembly might not work.
Problems can happen when tolerances add up and cause parts to not fit.
If tolerances stack up in the worst way, you might not be able to put parts together or they could break.
Advanced machining services can control many features at once. This lowers the chance of problems.
Tighter cnc machining tolerances can make manufacturing take longer because more steps are needed.
Higher tolerances can also mean more scrap and more checks.
In big assemblies, small changes in each part can add up. This can make parts not fit if the total change is too much.
You must balance cnc machining tolerances to get the best fit and make your assembly work well.
What Happens When Tolerances Are Too Tight or Too Loose
If you choose tolerances that are too tight, you can have problems. You might need extra steps like grinding or EDM. This makes things cost more and take longer. Tight cnc machining tolerances can mean longer machine times and special tools for checking. This can make your parts cost a lot more than normal tolerances. Machines must go slower to keep tight limits. This can also make more scrap.
But if you pick tolerances that are too loose, parts may not fit at all. Loose tolerances can make parts line up wrong. You might need to fix them or throw them away. Sometimes, the final product cannot be used. You need to find the right balance so your assembly fits well and does not waste time or money.
What Are CNC Machining Tolerances?
Definition of Machining Tolerances in CNC Manufacturing
You can find machining tolerances on most engineering drawings. Machining tolerances show how much a part’s size can change from the exact size you want. These limits help you check the quality of your parts. When you set machining tolerances, you decide how much bigger or smaller a part can be and still work well.
Machining tolerances tell you how much a part’s size can change from the number you want.
Engineers use tolerances to make sure parts work together in assemblies.
Manufacturers use tolerances to check quality during production.
ISO 2768 gives rules for machining tolerances. It has levels like fine, medium, coarse, and very coarse.
Machining tolerances help every part fit and work as planned. It is hard to make every part perfect, so tolerances give clear rules. These rules help machinists and inspectors during production. If you follow machining tolerances, you make fewer mistakes and keep your assembly strong.
Tip: Always check what machining tolerances your project needs. The right machining tolerances save time and money.
Why Tolerances Matter for Mechanical Assembly
Tolerances are important for how parts fit and work together. Machining tolerances set the limits for how much parts can change in size. This is important for how they fit and work in assemblies. You need to pick machining tolerances that match your product. If you work in aerospace or medical devices, tight machining tolerances are very important. Even small changes can cause big problems or safety issues.
Tolerances are not always easy to see but can change how parts work and fit.
They are made to handle changes in how things are made but still work right.
Knowing about the cost of tolerances helps engineers make better choices.
You need to think about material properties, how you make parts, and how you check them to get the right machining tolerances. Tolerances are important in engineering drawings because they show the limits for how much parts can change. This matters because no part is perfect, and tolerances make sure parts still work even if they are a little different. Good machining tolerances help you stop assembly problems, waste less, and make better products.
Impact of CNC Machining Tolerances on Assembly Fit
How Tolerances Influence Part Alignment and Function
You need to control tolerances so your parts fit right. Tolerances tell you how much a part’s size can change and still work. When you pick the right tolerances, your parts line up and move well. This lowers the chance of problems when you put things together.
Tolerances change how parts fit and work in assemblies.
Good tolerances stop parts from being crooked or too tight.
Clear tolerances make assembly easier and cut down on fixing parts.
You should always think about how tolerances will change how your part works. If you do not, parts might not line up or move smoothly. Tolerance stack-up can make these problems worse, especially with lots of parts. You need to plan for tolerance stack-up early so you do not get surprised.
Risks of Poor Tolerance Control in Assemblies
If you do not control tolerances, you can have many problems. Small mistakes in tolerances can hurt how things work and make them unsafe. This is very important in aerospace or medical devices. You might need to fix parts, which costs more money and time.
Bad tolerances can make parts not fit and cause assembly to fail.
Misalignment from bad tolerances can be unsafe and cause problems.
You might waste more and spend more if parts do not meet tolerances.
If tolerances are not steady, parts can wear out fast or move wrong.
Big changes from set tolerances can slow down making parts and cost more.
You should always check for tolerance stack-up when you design. This helps you stop problems before you make parts. Good tolerance control keeps your assemblies safe, strong, and saves money.
Types of Fits in Mechanical Assembly
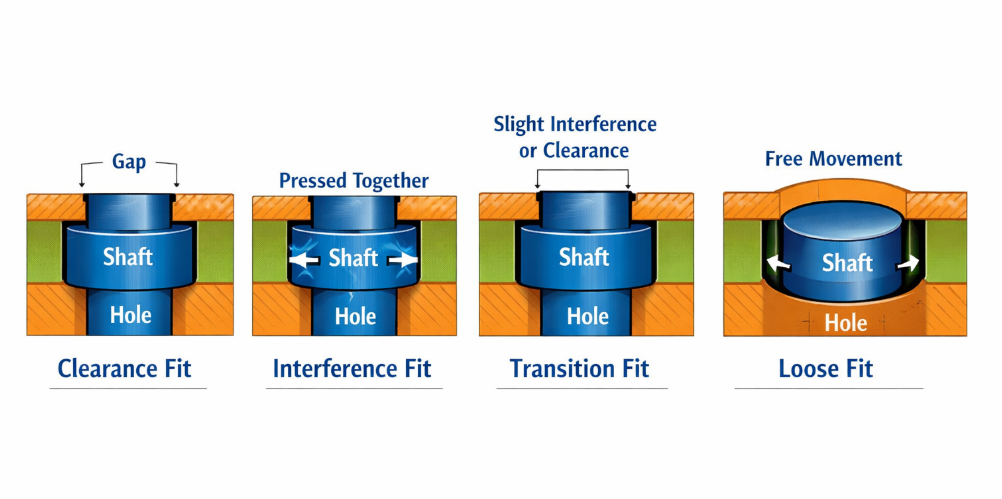
Clearance Fit and Typical CNC Tolerance Ranges
Clearance fits let two parts move or slide easily. There is a small gap between the parts. You see clearance fits in shafts and holes. These fits help parts turn smoothly or go together without trouble. The smallest shaft is always smaller than the biggest hole. This stops jamming and lets you put parts together without force.
You can pick how much space you want by changing tolerances. Loose clearance fits are good when you do not need high accuracy. Tight clearance fits are better when you want more control but still need easy movement. In CNC machining, clearance fit tolerances are usually from 0.01 mm to 0.05 mm for most metals. You should check your design and pick tolerances that fit your needs and budget.
Transition Fit in Precision Assemblies
Transition fits are between clearance and interference fits. These fits help parts line up well but still let you move or remove them. Transition fits are important for precision assemblies. They help you put bushings in place, mount bearings, and build gear parts.
Transition fits balance clearance and interference for precision.
They let you position parts well and take them apart if needed.
You use them for bushings, bearings, and gear assemblies.
Tolerances for transition fits can give a small gap or a tiny overlap. This makes assembly easier and keeps things accurate. You need to check tolerances closely to stop problems with lining up or moving parts.
Interference Fit and Press-Fit Considerations
Interference fits, or press fits, join parts by making one part a bit bigger. You push the parts together, and the tight fit holds them. This fit type helps put parts in place, but it is harder to do. You must figure out tolerances for both strength and accuracy. Machinists find this hard because small mistakes can cause big trouble.
Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Cold Temperature | Enough interference stops slipping when cold. |
Hot Temperature | Too much interference can break parts when hot. |
You need to think about how pressing parts many times can hurt them. It can make the material weak and change the size. Sometimes, the pressure you plan for does not come back after you take parts apart and put them together again. Moving parts, like with vibration, can make the fit weaker and cause damage. Spinning forces can also change how strong the fit is, so you need to think about more than just still loads.
Remember how lubrication can change your design.
Think about what the part does, the load, the material, how you make it, cost, and tolerances.
You must set tolerances carefully for interference fits. This helps you stop assembly problems and keeps your product strong and safe.
How Fit Types Determine CNC Tolerances for Assembly
Matching Fit Type to Functional Requirements
You need to pick the right fit type for your assembly. Each fit type needs its own tolerances to work well. If you want parts to move easily, use a clearance fit. This fit has bigger tolerances so parts can slide or turn. If you want parts to line up but still move a little, use a transition fit. Here, tolerances are smaller to control the gap or overlap. If you want parts to stay together tightly, use an interference fit. This fit needs the smallest tolerances because parts press together and do not move.
Tip: Always think about how your assembly works before picking tolerances. The wrong fit type can make things break or cost more.
You should talk with your machinist or engineer about which fit type is best. They can help you choose tolerances that fit your needs and budget. Good planning makes your assembly strong and safe.
Common Fit and Tolerance Mismatches in CNC Parts
Many problems happen when fit types and tolerances do not match. If you use loose tolerances for a tight fit, parts can shake or make noise. If you use tight tolerances for moving parts, they can jam or wear out. You need to check what each part does and pick the right tolerances.
Here are some common mistakes:
Using clearance fit tolerances for press-fit parts
Setting interference fit tolerances on moving joints
Forgetting to adjust tolerances for material changes
Fit Type | Common Mistake | Result |
|---|---|---|
Clearance | Tolerances too tight | Parts jam or seize |
Interference | Tolerances too loose | Parts slip or fail |
Transition | Wrong tolerances for alignment | Poor assembly quality |
You can stop these problems by checking your design and tolerances for every fit type. Careful planning helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your assemblies working right.
CNC Machining Tolerance Standards and Capabilities
ISO and ANSI Tolerance Systems Explained
You need to know about the main standards for tolerances in CNC machining. The two most common systems are ISO and ANSI. These standards help you set clear dimensional tolerances for your parts. They also make sure your parts work with others from different suppliers.
Aspect | ISO Tolerance System | ANSI Tolerance System |
|---|---|---|
Usage | Used in cars, planes, and medical devices | Used mostly in North America |
Symbols | Uses special symbols for tolerance callouts | Uses different symbols for tolerance callouts |
Standardization | Makes parts work together across industries | Like ISO but made for North American standards |
You should pick the right system for your project. This helps you avoid mistakes with dimensional tolerances and keeps your assembly process smooth.
Typical CNC Machining Tolerances by Process
Different CNC processes can reach different tolerances. You must know what each process can do before you set your dimensional tolerances. Most milling and turning machines can hold tolerances of ±0.005 inches. Grinding can reach even tighter tolerances, sometimes down to ±0.0005 inches.
Processes | Tolerance Standards |
|---|---|
Milling (3-axis) | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Milling (5-axis) | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Lathe | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Router | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Router (Gasket Cutting Tools) | ± 0.762 mm or 0.030” |
Engraving | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Screw Machining | ± 0.13 mm or 0.005” |
Steel Rule Die Cutting | ± 0.381 mm or 0.015” |
Rail Cutting Tolerances | ± 0.762 mm or 0.030” |
Surface Finish | 125RA |
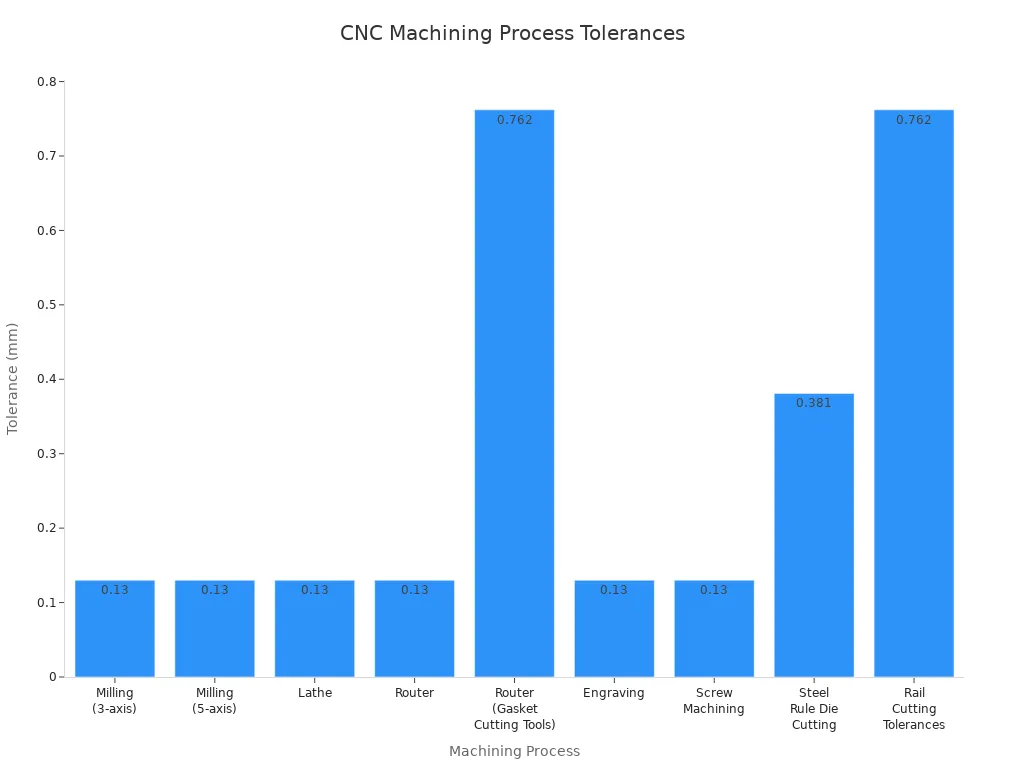
You should always check the process limits before you set your dimensional tolerances. This helps you avoid costly mistakes and keeps your parts within the right tolerances.
How Material and Geometry Affect Achievable Tolerances
Material and part shape can change what tolerances you can get. Harder materials can wear out tools faster, which makes it harder to keep tight dimensional tolerances. Some materials, like soft metals or plastics, can bend or get rough edges. This makes it tough to hold close tolerances.
Factor | Impact on Tolerances |
|---|---|
Hardness | Changes tool wear and machining speed |
Thermal Stability | Affects how well tight tolerances stay |
Ductility | Changes how exact the final part is |
Part Complexity | Decides which CNC machine and method to use |
Material Machinability | Shows how easy it is to get needed tolerances |
You also need to think about part geometry. Complex shapes may need special machines to keep dimensional tolerances tight. Simple shapes are easier to hold within tolerances. Always match your design to the right material and process for the best results.
Tip: When you plan your parts, always think about how material and shape will affect your tolerances. This helps you get the best fit and function for your assembly.
Key Factors in Selecting Tolerances for Assembly Fit
Material Compatibility and Thermal Expansion
You must think about material compatibility when picking tolerances. The hardness, elasticity, and thermal expansion of each part are important. If one part is much softer, it can bend or change shape. This can happen during assembly or when the part is used. If this happens, the fit can get ruined and the joint might fail. Materials get bigger when they get hot and smaller when they cool down. If your assembly faces hot and cold, the fit can change. If parts have different thermal expansion, their sizes can change unevenly. This can make the assembly not hold together well.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Material compatibility is essential. | You need to study the thermal and mechanical properties of materials, like thermal expansion and hardness. |
Use materials with low thermal expansion. | You can design assemblies to handle temperature changes so the fit stays good. |
Materials get bigger when hot and smaller when cold, which changes the fit.
Big temperature changes can make parts change size and hurt the joint.
If parts expand differently, their sizes can shift and change the fit.
You should always check if parts work well together and plan for temperature changes. This keeps your assembly strong.
Part Geometry and Feature Sensitivity
The shape of a part changes how easy it is to keep tight tolerances. Thin walls and tiny features are hard to machine just right. Complicated shapes can bend or twist during machining. You should not use designs that make it hard to keep tolerances steady. Simple and even shapes help you get better results.
Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) gives you more control. It helps you show how parts should line up and fit together. GD&T uses symbols to tell machinists what is needed. This system helps you keep tolerances in tricky designs and makes sure parts work as planned.
The shape of a part is important for tight tolerances, especially with thin walls and small features.
Designers should not use complex shapes that can bend during machining.
Simple and even shapes help keep tolerances steady.
Assembly Method and Installation Process
How you put parts together changes the tolerances you need. Press fits, slip fits, and bolted joints all need different tolerances. Press fits need very tight tolerances so parts stay together. Slip fits can use looser tolerances so parts move easily. How you install parts, like heating or cooling them, can also change the fit. You should always match your tolerances to how you put parts together. This helps you avoid problems when building your assembly.
Tip: Always look at your assembly steps before you pick tolerances. This helps you stop mistakes and keeps your work easy.
Balancing Cost vs Precision in CNC Machining
Tighter tolerances cost more money. The price does not go up in a straight line. When you make tolerances tighter, the cost goes up much faster. You need better machines, slower speeds, and more checks. For example, a normal aluminum bracket might cost $50. If you need ±0.001" precision, the price can jump to $150 or more. Sometimes, the cost can be 24 times higher for super tight tolerances.
Tolerance Level | Cost Increase Factor |
|---|---|
±0.005" | 2x |
±0.001" | 4x |
±0.0001" | Up to 24x |
You should only use tight tolerances where they are really needed. For parts that are not important, normal tolerances save money and time. Always balance how exact you need your parts with your budget. This helps you get the best value from CNC machining.
Tolerance Stack-Up in CNC Machined Assemblies
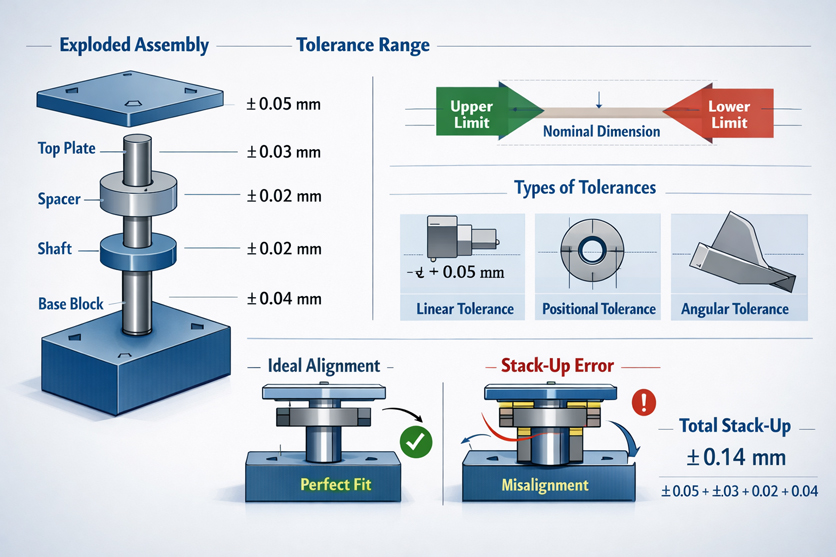
What Is Tolerance Stack-Up and Why It Causes Assembly Issues
You need to know how tolerances add up in assemblies. Tolerance stack-up is when all the part tolerances combine. Each part has a size range it can be. When you put parts together, these ranges add up. If the total is too big, the assembly might not fit or work. Tolerances help control part sizes, but you must watch how they add up. If you ignore this, you can have big problems. Sometimes, every part is okay by itself, but the whole thing fails. This happens when the total change is too much. Many engineers make mistakes by adding tolerances wrong. This can make you guess too high or too low for the final size. If you do not check the total, your assembly might not fit.
Note: Tolerance stack-up can make parts not fit, even if each part is within its own limits.
Simple Examples of Linear Tolerance Stack-Up
You can see tolerance stack-up in simple assemblies. Here are some examples that show how tolerances change fit and function:
Tolerance Stack Name | Description | Potential Failure(s) |
|---|---|---|
TR-1 | Top rail groove width to chassis base guide fin width | Fin too wide—cannot fit in groove; grinding on rail; fin too narrow—n/a |
TR-2 | Top rail center thread to screw | Screw will not fit or thread |
TR-3 | Top rail wheel bevel surface width to chassis bevel wheel spacing | Too narrow—chassis can fall off track; too wide—chassis will not move smoothly |
TR-4 | Top rail wheel bevel surface width to chassis bevel wheel height | Too narrow—chassis will not move smoothly; too wide—chassis sits lower than expected |
TR-5 | Top rail inner center beam surface to bottom of chassis fin clearance | Fin too tall—chassis will not move smoothly; fin too short—n/a |
You can see that small changes in tolerances can cause big problems with fit.
How to Reduce Stack-Up Risk in Assembly Design
You can lower the risk of tolerance stack-up by using smart design steps. Try these ideas:
Use worst-case analysis. Add all the biggest tolerances to see the largest change. This keeps your assembly safe but may need tighter tolerances.
Try statistical analysis, like root-sum-square (RSS). This lets you use looser tolerances and still have most assemblies work.
Learn what your manufacturing process can do. Know the limits so you do not ask for impossible tolerances.
Use geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T). This helps you control how parts line up and fit.
Tip: Always plan for how tolerances add up in your design. This helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your assemblies working well.
How to Specify CNC Machining Tolerances for Reliable Assembly
Defining Functional Requirements First
You need to know what your assembly must do. Figure out the job of each part before picking tolerances. If a part needs to move, spin, or hold weight, decide how much it can change. Tolerances tell you how much a size can be off and still work. Focus on the parts that matter most for how things work. For important parts, use tighter tolerances to make them last. For less important parts, looser tolerances save money and time.
Tip: Always ask, “What does this part do?” before you pick tolerances.
Avoiding Over-Tolerancing in Non-Critical Features
Making tolerances too tight can cause problems when making parts. It costs more and takes longer but does not always help. Use normal tolerance charts for parts that are not important. Using ISO 2768-m as a default keeps things simple. If you forget to add tolerances, people can get confused and make mistakes. Too many tight tolerances make machining harder and slow everything down. You need to find a good balance between being exact and being practical.
Tight tolerances cost more and slow things down.
No tolerances can confuse people and cause errors.
Standard charts make things easier and cut down on mistakes.
Best Practices for Tolerance Documentation and Drawings
Clear drawings help you share tolerances with your supplier. Use rules like ISO 2768 or ASME Y14.5. Only put tolerances where they are needed. Do not add too many numbers to your drawings. Make sure the tolerances match what CNC machines can do. Use GD&T for parts that must be very exact. Tolerances can be two-sided or one-sided, so pick what works best. Good drawings mean fewer rejected parts and faster production.
Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
Makes manufacturing easier | |
Apply GD&T | Keeps key parts very exact |
Saves money and time |
Note: Tolerances tell the maker how much a part can change. Tight tolerances need more checks, but loose tolerances give more freedom.
Common Tolerance Mistakes That Cause Assembly Failures
Overly Tight Tolerances and Unnecessary Cost
Some people think the tightest tolerances are always best. But this is not true. Using very tight tolerances can make your parts cost a lot more. Shops need special machines and tools to meet these limits. This means they spend more money at the start and later on. Workers must check parts more often, which takes extra time. Machines slow down because tools wear out faster and need changing. More parts get thrown away, so you waste materials. All these things make your parts cost more, but your assembly may not work better.
More checks mean higher labor costs.
Special tools add to the price.
Changing tools slows down making parts.
More scrap means more waste.
You might need extra material because of bad parts.
Loose Tolerances Leading to Poor Fit or Vibration
Loose tolerances can also cause problems. If you let parts change size too much, they might not fit together. Car doors might not close right. Engine parts may not line up, so they do not work well. Devices can break because parts do not fit or are not straight. You need to control tolerances to stop these problems. Checking quality helps you find mistakes before customers get the parts.
Tolerance stack-up analysis helps stop assembly problems. If you do not control how sizes add up, many parts together can cause big issues.
Ignoring Assembly Sequence and Real-World Conditions
You need to think about how you put parts together. If you ignore the order, small changes can add up and cause failures. These changes can make parts not fit as planned. If you do not use the right tolerances and GD&T, you can have problems in mass production. Real-life things, like heat or how you handle parts, can also change how tolerances work. Always plan for these things to keep your assembly strong.
These mistakes can make assemblies fail.
Using the right tolerances and GD&T stops fit problems in production.
Best Practices for Achieving Consistent Assembly Fit
Designing with Manufacturing and Assembly in Mind
You should design parts so they are easy to make and put together. When you plan your assembly, pick tolerances that CNC machines can do. Using the right tolerances helps machinists make parts that fit well. Try not to use shapes that are hard to control. Simple shapes make it easier to keep tolerances steady and stop mistakes. You can make a CNC prototype part to test your design first. This lets you see if your tolerances work before making lots of parts.
Tip: Always talk about your tolerances with your CNC supplier before you start making parts.
Using Datum Structures Effectively
Datum structures help you control tolerances in your assembly. You set a special point or surface on each part. This makes it easier to measure and check tolerances. Use datums to help parts fit and line up the right way. If you use clear datums, you keep tolerances the same for all parts. You can use tables to show which datums control which tolerances.
Datum Feature | Controls Tolerances For |
|---|---|
Hole Center | Shaft alignment |
Flat Surface | Assembly base |
Edge | Part location |
Pick datums that match what your assembly needs. This helps you stop mistakes and keep tolerances tight.
Validating Tolerances with Prototypes and Test Fits
You need to check tolerances before making lots of parts. You can use CNC prototype machining to make test parts. This lets you see if tolerances work in real assemblies. Put the parts together and look for gaps, parts that do not line up, or spots that are too tight. If you find problems, you can change tolerances before making more parts. Write down your test results and share them with your team. This helps you keep tolerances steady and avoid wasting money.
Note: Testing tolerances with prototypes saves money and helps assembly fit better.
Working with CNC Machining Suppliers on Assembly Tolerances
Communicating Design Intent Clearly
You need to tell your CNC machining supplier what you want. Explain why you picked certain tolerances for your parts. This helps the supplier know what is most important for your assembly. Use clear drawings and notes to show which features need tight tolerances. Show which features can be more flexible. If you want a CNC prototype part, add a link to the CNC part machining service page. This helps your supplier know what you expect and how to make the right fit.
Tip: Always use simple words and mark important tolerances on your drawings. This makes things less confusing and helps parts get made faster.
Reviewing Tolerance Feasibility Before Production
You must check if your tolerances match what CNC machines can do. Ask your supplier to look at your tolerances before making parts. Suppliers know which tolerances are easy or hard to reach. They can tell you if your tolerances are too tight or too loose. If you use CNC prototype machining, you can test your tolerances before making lots of parts. This step helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your assembly fit working well.
Check tolerances with your supplier early.
Test tolerances using CNC prototype machining.
Change tolerances if your supplier gives feedback.
Step | Action |
|---|---|
Review | Check if tolerances will work |
Prototype | Test tolerances with sample parts |
Adjust | Change tolerances if needed |
Inspection, Measurement, and Quality Control for Assembly Fit
You must check parts to see if they meet your tolerances. Use tools like calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to measure sizes. Your supplier should follow quality control steps to keep tolerances steady. If you find parts that do not meet your tolerances, ask for fixes. Good checking stops problems and keeps your products strong.
Note: Always ask your supplier for inspection reports. These reports show if your tolerances are met and help you trust your parts.
You can use a table to keep track of inspection results:
Feature | Tolerance Specified | Measured Value | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
Shaft Diameter | ±0.005" | 0.504" | Pass |
Hole Location | ±0.01" | 0.009" | Pass |
Groove Width | ±0.002" | 0.003" | Fail |
If you keep checking tolerances, you make sure your assembly fits every time.
Conclusion: CNC Machining Tolerances as a Competitive Advantage
Key Takeaways for Engineers and Product Designers
You can use tolerances to make your designs better. Setting the right tolerances helps parts fit and work as planned. This lowers the chance of assembly problems. You also save time and money when making parts. Here are some important things to remember:
Always pick tolerances based on what the part does.
Use standard tolerances for features that do not change assembly.
Check how tolerances add up in your assembly.
Talk with your CNC supplier about tolerances before making parts.
Test tolerances with prototypes to find problems early.
Remember: Good tolerances help your assembly go smoothly and make your products more reliable.
How Proper Tolerance Strategy Improves Cost, Quality, and Assembly Reliability
A smart tolerance plan gives you a real advantage. You can control costs by using tight tolerances only where needed. This stops waste and lowers scrap. You also make sure each part meets your quality goals. When you manage tolerances well, your assemblies fit right every time.
Benefit | How Tolerances Help |
|---|---|
Lower Costs | Less fixing and fewer bad parts |
Better Quality | Parts fit and work the same |
Reliable Assembly | Fewer surprises when putting together |
You should always check tolerances as your design changes. You can change tolerances to match new needs or materials. Using tolerances wisely builds trust with your team and customers. It shows you care about every detail.
Tip: Make tolerances part of your design plan from the start. This helps you make better products and stay ahead in your industry.
You can get the best assembly fit by doing a few things. First, figure out what each part needs to do. Next, pick tolerances that fit the job and your budget. Work with your CNC supplier to make sure everything is right. Check and change tolerances if your design changes.
Remember: If you balance accuracy, how things work, and cost, your products will be better. If you want to learn more, look at information from groups like ASME or ISO.
FAQ
What is the most common CNC machining tolerance for general parts?
Most CNC parts use ±0.005 inches (±0.13 mm). This tolerance works for many assemblies. It also helps keep costs low.
How do I choose the right tolerance for my assembly?
Think about how your parts fit together. Use tighter tolerances for important fits. Use standard tolerances for less important features. Always ask your CNC supplier for help.
Can tight tolerances increase production costs?
Yes, tight tolerances cost more. Machines must go slower and get checked more. Special tools are needed. You pay extra for these steps. Only use tight tolerances when you really need them.
What happens if I ignore tolerance stack-up?
If you ignore stack-up, your assembly might not fit. Small mistakes in each part can add up. Always check how tolerances add together in your design.
Do different materials affect CNC tolerances?
Yes, different materials can change how easy tight tolerances are. Hard or soft materials can make it harder to hold tolerances. Some materials get bigger or smaller with heat. Always think about material properties when you set tolerances.
 LKprototype
LKprototype