
Estimated reading time: 22 分钟 You use the vacuum casting process to make exact parts from a master model. This method lets you change your design and use cheap tools. It is great for making prototypes and small batches. You get high-quality prototypes with smooth surfaces and tricky shapes. This happens because there are fewer air bubbles and you can use more materials. AdvantageDescriptionReduced Porosity and DefectsGets rid of air pockets so parts are stronger.Superior Surface FinishMakes smoother surfaces, so you do not need much extra work.Complex GeometriesLets you make detailed designs that other ways cannot do.Material VersatilityWorks with many…

You use epoxy resin casting moulds to shape resin for projects. Sometimes, resin gets stuck in a mould. You may also see bad details on finished pieces. This can happen if you choose the wrong mould type or material. Silicone moulds help stop these problems. They are flexible and have non-stick surfaces. Many crafters use special moulds for casting resin. Some use deep pour moulds or custom moulds. You should match your mould to your resin and project needs. This helps you get the best results. Key Takeaways Pick silicone moulds if you want smooth resin pieces. They bend easily…

You might ask how much vacuum casting costs in 2026. The usual mold price is between $200 and $1000. Each part often costs from $10 to $100. Many things can change the price. These include the material you pick, how complex your part is, and what finishing you want. Vacuum casting is a good choice for making a few items. It costs less per part than injection molding for small batches. Silicone molds are quicker and cheaper to make than using machines. Making a small number of parts works best for prototypes and working pieces. This vacuum casting price guide…
Image Source: pexels Vacuum casting is the quickest and most cost-effective way to produce parts through low volume manufacturing in China. If you need high-quality parts for testing or launching new products, this method helps you save both time and money. With low volume manufacturing China services, you get your molds much faster than in other regions, typically within just 5 to 7 days. SourceAverage Lead TimeTop 10 Vacuum Mold Casting Manufacturers in China5–10 working daysVacuum Casting/Silicone Molding/Urethane Casting Services7-12 Business DaysVacuum Casting for Rapid Prototyping7 to 15 days You don’t have to invest in expensive tooling. With low volume…

You can get optical clarity in clear vacuum casting parts by picking the right transparent resin, controlling the casting steps, and using good finishing methods. Transparent resins like water-clear polyurethane and VC-8744 Transparent give high optical clarity. Water-clear polyurethane also blocks UV light, so it works well for medical and prototype uses. The table below lists common resins and their properties: Resin TypeOptical ClarityUV ResistanceApplicationsWater-Clear PolyurethaneHighYesPrototyping, Medical DevicesVC - 8744 TransparentHighN/AConsumer Goods, Automotive Components Finishing steps like polishing help you get the best results. Key Takeaways Pick a good clear resin, like water-clear polyurethane, to get high optical clarity in…

If you want to make silicone parts with vacuum casting in China, you should know the steps to do it well. This vacuum casting china guide shows why picking the right supplier and design is important. Vacuum casting lets you make a prototype or small batch fast and without spending a lot. You can make cheap prototypes and get good silicone parts quickly. Tip: A simple guide helps you not make mistakes and get what you want. Key Takeaways Vacuum casting in China helps you save money. It costs less than in Europe or the USA. You can make prototypes…
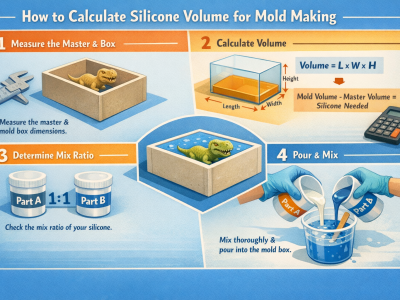
Accurate measurements stop you from wasting silicone and help you calculate silicone volume for mold effectively. They also ensure your mold works correctly. You can find silicone volume using a simple formula: Required Material Volume equals Mold Container Volume minus Model Volume. For regular shapes, use these formulas: ShapeFormulaSquare/RectangleVolume equals length times width times heightCylinderVolume equals π (3.14) times radius squared times height Follow these steps to get the right amount of silicone each time. Key Takeaways It is very important to measure carefully. Measure your mold container and model two times so you do not make mistakes. Use the…
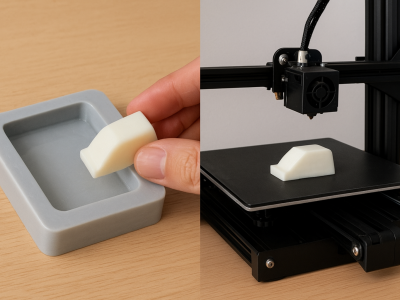
You may wonder if silicone vacuum casting and 3D printing costs are more favorable for your project. This is crucial when you require silicone molds or prototypes. The true answer hinges on the quantity of parts you need and their intended functionality. If you only need one or two pieces, 3D printing is typically the more economical option, and it also delivers your parts more quickly. However, if you require a larger number of parts, the silicone vacuum casting and 3D printing costs will vary. Here’s a quick comparison to help you understand how they stack up: FactorVacuum Casting3D PrintingTooling…

When you pick the best silicone for prototype molds, Shore A hardness is important. Shore A shows how soft or hard the silicone feels. It goes from very bendy to very stiff. This scale helps you choose a silicone that fits your project. Softer silicone is good for tiny details. Harder silicone lasts longer when used a lot. Here is a quick look at common Shore A values: Shore A HardnessDescription10°Very bendy, for special uses20°Soft, like a rubber band40°Bendy, like a pencil eraser60°Good for tubes and gaskets70°Tough, like tire tread80°Hard, can take the place of plastic You can find top…

If you want to outsource vacuum casting China in 2025, you should first decide what your project needs. You also need to get your CAD files ready. Good 3D drawings help suppliers give you fast and correct quotes. You should check the newest cost ranges before you choose. For example, mold costs are often between $200 and $1,000. Per-part costs are usually between $10 and $100. Cost TypeCost RangeMold Costs$200 - $1,000Per-Part Costs$10 - $100 Picking the right supplier is very important for quality and delivery. If you know each step of the process, you can avoid mistakes. This also…
Want to convert your CAD design into a sample prototype or small-batch production? Upload your files and get a fast and accurate quote.
