
When deciding between silicone mold vs injection mold prototypes, there are several key factors to consider. First, determine how many parts you need. Next, evaluate your budget and how quickly you require the parts. It’s also important to identify the materials you plan to use and assess the complexity of your part design.
Factor | Silicone Mold (Vacuum Casting) | Injection Mold (Injection Molding) |
|---|---|---|
Production Volume | Small runs (up to ~100 units) | Large volumes (hundreds of thousands) |
Cost | Lower tooling cost for small batches | High initial cost, better for high volume |
Speed | Mold in 5-7 days, slower per-part speed | Mold takes weeks, fast per-part speed |
Material Compatibility | Polyurethane resins, limited options | Wide range of plastics, high resistance |
Part Complexity | Good for simple parts, less precision | Best for complex, precise parts |
Choosing between silicone mold vs injection mold prototypes depends on your project needs. Silicone molds are ideal for small to medium quantities and quick design changes, while injection molds are better suited for producing large volumes of high-quality, precise parts.
Key Takeaways
Use silicone molds if you need less than 100 parts. They are good for quick changes in design. This helps save time and money.
Pick injection molding if you need many parts. It is best when you want high accuracy and the same quality every time. You can use many types of materials with it.
Silicone molds are made fast and are good for testing rubber-like parts. They do not last long and you cannot use many materials with them.
Injection molds take more time and cost more at first. But they make many exact parts fast and last a long time.
Think about how many parts you need, your budget, how hard your part is to make, what materials you want, and your timeline. This will help you choose the best way to make your prototype.
Quick Comparison – Silicone Mold vs Injection Mold Prototypes

Cost Differences
When you look at silicone mold and injection mold prototypes, you might think the prices are very different. But the cost to make each mold is often about the same. Making one mold can cost between $500 and $5,000. Bigger or more detailed molds can cost up to $20,000. The biggest difference is how many parts you want to make. Silicone molds cost a lot at first and do not last long. They are best if you only need a small number of parts. Injection molds cost more at the start, but if you make thousands of parts, each part gets much cheaper.
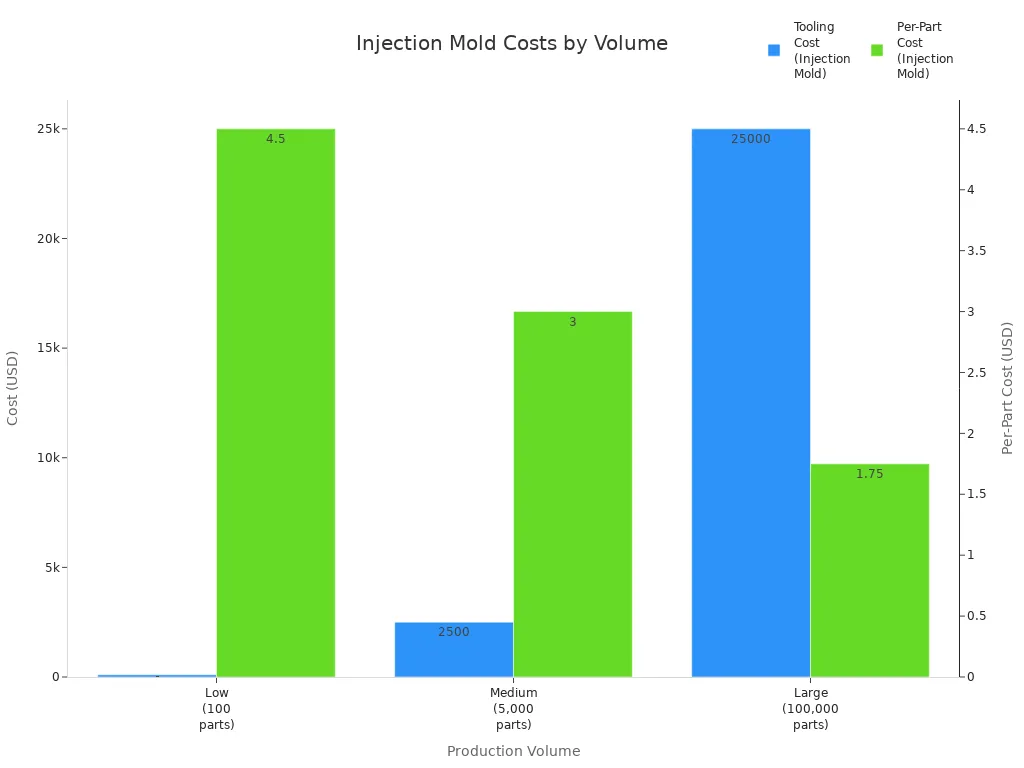
Tip: If you only need a few parts, silicone molds can save you money. If you need a lot of parts, injection molding is cheaper in the long run.
Speed and Turnaround
Silicone molds are much faster to set up. You can make a silicone mold in just a few hours or days. This is good if you need to test your design quickly or change it fast. Injection molds take longer to make because they are made from metal. It can take weeks to finish one. But once the mold is ready, injection molding makes parts very fast, especially if you need a lot.
Method / Part Size | Typical Turnaround Time |
|---|---|
Injection Molding - Small Parts | ~7 days |
Injection Molding - Standard Parts | ~15 days |
Injection Molding - Large Parts | ~20 days |
Silicone Mold (LSR) | ~9 days (often faster for simple parts) |
Volume and Durability
Silicone molds are good for making up to 100 parts. They wear out quickly and are not good for making lots of parts. Injection molds are made to last a long time. They can make hundreds of thousands of parts that all look the same. If you want your mold to last and make many parts, injection molding is better.
Material Compatibility
Silicone molds use materials like liquid silicone rubber (LSR) and high consistency rubber (HCR). These are soft, safe for the body, and good for medical or food parts. Injection molds can use many kinds of plastics, like thermoplastics and thermosets. This means you have more choices for how strong, colorful, or smooth your parts are.
Precision and Detail
Injection molds make parts with very exact shapes and smooth surfaces. They keep the size and fit of parts very close to what you want. This is important for parts that must fit together well. Silicone molds can show good detail, but the material can shrink more, about 5-7%. This makes it harder to get the exact size you want. You might see more changes in size and finish with silicone molds. If you need parts to be very exact, injection molding is the best choice.
When to Use Silicone Mold

Advantages of Silicone Mold
Silicone molds have many good points for making prototypes and small batches. They cost less, are quick to make, and let you change designs easily. The table below shows the main benefits:
Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
Cost | Silicone molds need less money to start and are cheaper than injection molds. |
Speed | You can make silicone molds fast, sometimes in just a few days, so you get prototypes quickly. |
Design Flexibility | Silicone molds show small details, allow tricky shapes, and make it easy to take out parts without breaking them. |
You can change your design and test new ideas fast with silicone molds. This helps you make better prototypes quickly. Silicone molds give you better material and surface quality for rubber-like parts than 3d printing.
Tip: If you want to try different designs or need rubber-like prototypes, silicone molds help you go from idea to part in just days.
Best Applications
Silicone molds are best when you need a small or medium number of parts, want to change designs fast, or need special materials. You can use these molds for many rubber-like parts. Here are some common uses:
Industry | Common Applications of Silicone Mold Prototyping | Key Material Properties Leveraged |
|---|---|---|
Consumer Products | Soft grips, wearable parts, kitchen tools safe for food | Flexibility, safe to touch, safe for food |
Medical Devices | Implants, fake body parts, tubes, surgery tools | Safe for the body, strong, safe with chemicals |
Automotive | Gaskets that handle heat, seals, bendy parts | Handles heat, safe with chemicals, stands up to weather |
You will see silicone molds used for quick prototypes in electronics, medical, and car parts. For example, you can make soft grips, bands you can wear, or gaskets that handle heat. These molds are also cheap for small batches, especially if you want to test rubber-like parts before making lots of them.
Silicone molds help you change your design quickly. You can make a new mold in a few days, test your part, and change your design if you need to. This helps you make better prototypes and get feedback fast. The chart below shows how silicone mold prototyping is faster and cheaper than other ways:
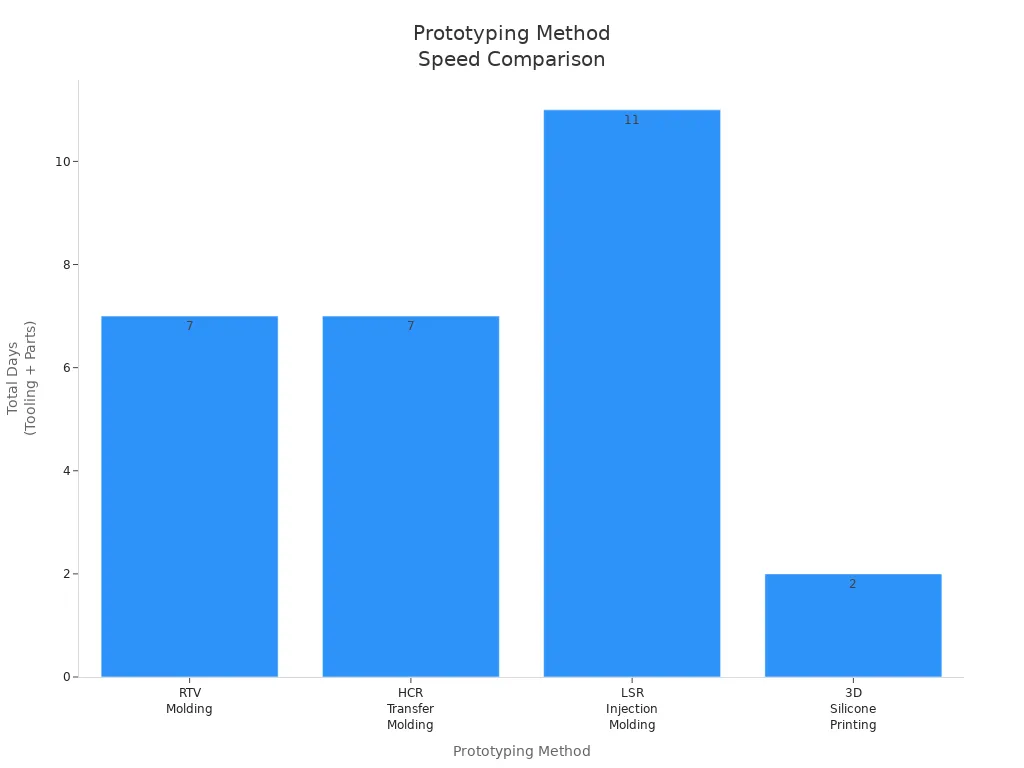
You can see that silicone mold methods like RTV and HCR are quick and accurate. They are faster than injection molding and give better material results than 3d printing. If you need rubber-like parts to test how they work, silicone molds are a smart pick.
Limitations
Silicone molds have some downsides too. These molds do not last as long as metal molds. Most silicone molds can make 10 to 200 parts, depending on the material and how you care for them. If you use them with polyurethane or epoxy, they last only 10 to 50 times. Keeping molds away from sun and water can help them last up to 30% longer.
Silicone molds cannot use as many materials as injection molds. You can use them for bendy, clear, or food-safe stuff, but not every kind of plastic. Picking the wrong silicone can make your part unsafe, especially for food or medical uses.
Getting the exact size is also harder. Silicone molds can show small details, but you might see more shrinking or small size changes than with injection molding. Things like mold shape, how long it cures, and care affect how close your part is to the right size. If you need parts that are very exact or always the same, you may want to use another method.
Note: Silicone molds are great for fast prototypes, rubber-like parts, and small batches. They are not good for making lots of parts or parts that must be super exact.
When to Use Injection Mold
Benefits of Injection Mold
Injection molding is great for making lots of parts. It gives you high quality and very exact shapes. You can use it to make thousands or even millions of the same part. This is good when you need every part to be just right.
Some main benefits of injection molding are:
You can make many parts fast. This helps if you need a lot of parts.
Every part looks and works the same. You can trust the quality each time.
You save money when you make big batches. The first mold costs a lot, but each part gets cheaper as you make more.
You can pick from many plastics. Some are strong, some have bright colors, and some are smooth.
You do not waste much material. You only use what you need, and you can recycle extra plastic.
You get very exact parts. Injection molds can make parts that fit together perfectly.
Many industries use injection molding. For example, electronics companies use it for cases that must look good and work well. Car makers use it for strong and tricky parts. Medical companies use it to make safe and high-quality tools.
Tip: If you need thousands of parts that are all the same and very exact, injection molding is the best way.
Prototype Injection Molding
Prototype injection molding lets you test your ideas before making lots of parts. These molds are made from softer metals like aluminum. They are quicker and cheaper to make than regular molds. You can make test parts that are just like the real thing.
Here is how prototype injection molding helps you:
You use the same plastic as the final part. This lets you see how your part will work.
You can check how your part looks and feels.
You can test if your part is strong and fits well.
You can change your design fast. These molds are easy to fix if you need to.
You get your test parts in one or two weeks. This is much faster than waiting for full molds.
You can try different ideas with this method. You can test many designs at the same time. This helps you find the best one. You can also use this to test soft or bendy parts.
Aspect | Prototype Injection Molding | Production Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Tooling Material | Aluminum or soft steel, quick to machine | Hardened steel, built for long-term use |
Mold Cavities | Single cavity, easy to change | Multiple cavities for high-volume production |
Process Speed | Fast turnaround, simple tooling | Longer lead time, complex tooling |
Automation | Manual or basic automation | Advanced automation for complex parts |
Cycle Time | Longer per part | Shorter per part |
Cost | Lower upfront cost, good for small runs | Higher upfront cost, lower per-part cost at scale |
Output Quality | Matches production parts, good for testing | High-quality, consistent parts for mass production |
Flexibility | Easy to modify for design changes | Hard to change, costly to modify |
Production Volume | Best for small runs and prototypes | Best for high-volume production |
This table shows how prototype and production molding are different. Prototype molding is fast and easy to change. Production molding is best for making lots of parts.
Production Injection Molding
Production injection molding is used when you need many parts for a long time. These molds are made from hard steel. They can make hundreds of thousands or even millions of parts. The more you make, the cheaper each part gets.
Production injection molding uses machines that work by themselves. The machines put in the plastic, shape it, and take out the part. This makes the process fast and keeps the quality high. You can add special shapes, like threads or undercuts, with special molds.
You also get very exact and repeatable parts. Every part matches your design, even after making thousands. This is important for cars, electronics, and medical tools, where every part must be just right.
Note: Production injection molding is best for making lots of parts, long projects, and parts that must be very exact and always the same.
Drawbacks
Injection molding has some downsides you should know:
The first mold costs a lot of money. This is not good if you only need a few parts.
You have to wait longer for your first parts. Making the mold can take weeks.
It is hard to change your design. Every change means making a new mold, which takes time and money.
Prototype molds cannot always make very tricky or super exact parts. This can make it hard to test every detail.
Injection molding works best when your design will not change much and you need lots of parts. If you think you will change your design a lot, you may want to try other ways first.
Alert: Make sure your design is ready before you start injection molding. Changing things after you start can cost a lot and take more time.
Decision Factors
Quantity Needed
Think about how many parts you want. If you only need a few, silicone molds are a good pick. These molds can make up to 100 parts before they wear out. If you need hundreds or thousands, injection molding is better. Production molds can make the same part over and over. The quality stays high for every piece.
Use silicone molds for small batches, up to 100 parts.
Pick injection molding for big batches, hundreds or thousands of parts.
Budget
Your budget helps you decide what to use. Silicone molds cost less at the start. You pay less for the mold, which is good if you only need a few parts. Injection molding costs more at first because the molds are metal and take longer to make. But if you need lots of parts, each part costs less, and the quality is better.
Tip: For small projects, silicone molds save money. For big projects, injection molding is a better deal over time.
Part Complexity
Check your part’s shape and details. Silicone molds work for simple shapes and some tricky features. If your part needs to be very exact or has tiny details, injection molding is best. Production molds can make complex parts with high quality every time.
Silicone molds are good for simple or bendy parts.
Injection molding is best for complex, exact parts.
Material Needs
The material you pick is important. Silicone molds use materials that can handle heat and chemicals. These are great for medical, baby, and food parts. You can test rubber-like materials and see how they work. Injection molding uses many types of plastics, from strong to bendy, and makes lots of parts that are always the same.
Method | Best For Materials Like... | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
Silicone Mold | Rubber-like, heat-resistant, safe | Medical, food, infant products |
Injection Molding | Many plastics, strong or flexible | Consumer, automotive, electronics |
Timeline
Time matters when picking a method. Silicone molds let you get parts fast. You can make a mold in just a few days and start testing right away. This helps you change your design quickly. Injection molding takes longer to set up because the molds need more work. But once the mold is ready, you can make lots of parts very fast, sometimes in seconds.
If you need parts soon or want to test designs, use silicone molds.
If you want to make lots of parts fast, pick injection molding.
Note: If you want to change your design a lot, silicone molds are more flexible. If you want to make big batches quickly, injection molding is best.
Case Studies
Consumer Products
Many companies use silicone molds to make things like kitchen tools, toys, and sports gear. Brands pick silicone molds when they want to try new designs fast. For example, Casco Bay Molding uses single cavity silicone molds for faucet spray faces and drinking caps. These molds let you change your design quickly and save money. Parts come out smooth, so you do not need much extra work. If you want soft or bendy elastomeric parts, silicone molds are a good choice. They also help the environment because you can recycle the molds and make less waste. Silicone molds give better surface quality and last longer than 3d printing for elastomeric parts. You can use 3d printing for first models, but silicone molds are better for real product tests.
Companies use silicone molds for kitchenware, toys, and sports items.
You can change designs fast and save money.
Elastomeric parts from silicone molds look and feel better than 3d printed ones.
Medical Devices
Medical device makers use both silicone and injection mold prototyping to make new products faster. You can use medical-grade silicone rubber to make elastomeric parts like implants, tubes, or surgery tools. These molds let you test how the part works and feels before making lots of them. You also meet strict quality rules with automated checks and ISO certifications. Some companies use 3d printing for first samples, but silicone molds work better for elastomeric parts. You can also use injection molding for small batches to test and improve your design. This helps you get your product to market faster and with less risk.
Medical device companies use silicone molds for safe, flexible elastomeric parts.
You can test real materials and get feedback fast.
3d printing is good for first models, but silicone molds are better for final tests.
Startups and Iteration
Startups need to test ideas quickly. Silicone molds help you make elastomeric parts fast and change your design without spending too much. You can use 3d printing for the first version of your part. After that, switch to silicone molds for better quality and more real testing. This lets you show your product to investors or customers sooner. You also save money because you do not need to order big batches. Elastomeric parts from silicone molds help you find problems early and fix them before full production.
Tip: Use 3d printing for first prototypes, then switch to silicone molds for elastomeric parts when you want better quality and real-world tests.
Bridge Tooling
Bridge tooling helps you go from prototype to full production. You can use silicone molds or short-run injection molds to make elastomeric parts while waiting for your final tools. This step is important if you want to start selling before your main molds are ready. You might use 3d printing for first samples, then use silicone molds for small batches. This gives you time to test your elastomeric parts in real life. You can also fix design problems before spending money on big production molds. Bridge tooling with silicone molds keeps your project moving and helps you give good parts to your customers.
Bridge tooling uses silicone molds for elastomeric parts before mass production.
You can use both 3d printing and silicone molding for faster results.
This method lowers risk and helps you finish on time.
Picking the best prototyping method depends on what you need. Silicone molds are good if you want quick, cheap, and easy-to-change prototypes. Injection molding is better if you need lots of parts that are strong and exact.
Quick Checklist:
Need less than 100 parts? → Silicone mold
Want to change your design quickly? → Silicone mold
Need thousands of perfect parts? → Injection mold
Need many kinds of plastic? → Injection mold
Not sure what to pick? Ask a prototyping expert for help.
FAQ
What is the main difference between silicone mold and injection mold prototypes?
Silicone molds work best for small batches and quick changes. Injection molds suit large runs and high precision. You should pick based on how many parts you need and how exact your parts must be.
Can I use silicone molds for production parts?
You can use silicone molds for short production runs. They do not last as long as metal molds. If you need hundreds or thousands of parts, injection molding works better.
How fast can I get parts with each method?
You can get silicone mold parts in a few days. Injection molding takes longer to set up, but once ready, it makes parts very quickly.
Which method gives better surface finish and detail?
Injection molding gives you the best surface finish and detail. Silicone molds show good detail, but you may see more shrinkage or small changes in size.
 LKprototype
LKprototype







