If you want to make your medical device idea a reality quickly and affordably, medical device prototypeing development is the way to go. Vacuum casting for medical devices offers a great solution for creating precise models. You don’t have to wait long or spend a lot of money. By using 3D-printed molds and patterns, you can test new designs rapidly and make changes easily. When planning medical device prototypeing development, consider how this process can help you achieve your project goals efficiently. Key Takeaways Vacuum casting helps make medical device prototypes faster. You can make many prototypes in a short…
Vacuum casting lets you make a prototype that is strong and accurate, with a vacuum casting lead time that is shorter than many other methods. You can pick from many materials to fit your needs. The process uses silicone molds, so it costs less for small amounts. You get results fast, allowing you to test parts sooner. Vacuum casting lead time is a significant advantage, making it a preferred choice for many engineers. The table below shows why many engineers like casting for working prototypes. AdvantageDescriptionPrecisionCan copy complex shapes and small details very well.Cost EfficiencyCheaper for small batches because silicone…

You might wonder how long vacuum casting takes. For most projects, you can expect a typical lead time of 7 to 15 days. If you need parts quickly, some suppliers offer rush options in as little as 2 to 3 days. When you order up to 20 parts, the process may take up to 15 days. Knowing the vacuum casting lead time matters for your project planning because: Efficient lead times let you respond quickly to market demands. You can reduce total manufacturing costs. You improve collaboration with your suppliers, which leads to better results. Key Takeaways Most projects take…

You can pick from many vacuum casting surface finishes. These include painting, polishing, texturing, manual sanding, vapor smoothing, dyeing, plating, clear coating, pad printing, silk screening, laser etching, custom color matching, and soft touch coatings. Each finish helps with different things. Some finishes stop rust or make parts last longer. Others help block electricity, lower outgassing, make surfaces smoother, or make parts look nicer. Picking the right finish helps your part work better and look how you want. Key Takeaways Look at different vacuum casting surface finishes like painting, polishing, and plating. These finishes can make your parts look better…

You can usually get 20 to 25 parts from a silicone vacuum casting mold, but the vacuum casting mold lifespan can vary depending on the part design. Most vacuum casting jobs focus on small or medium batches, making this method ideal for those seeking fast results. It also aids in creating accurate prototypes. Many manufacturers choose vacuum casting for quick production runs, as other methods are not as fast or efficient. Key Takeaways You can usually make 20 to 25 parts with one silicone vacuum casting mold. Pick the right materials to help your mold last longer. Keep your part…
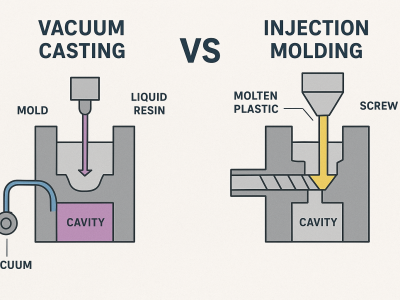
If you want to make a few parts or test ideas, vacuum casting is fast and costs less at the start. However, if you need to make many parts, injection molding is cheaper for each part and can produce millions. When considering your options, think about factors like price, the quality of the parts, how quickly you need them, the materials you want, and the complexity of the parts. Below is a comparison of Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding: FactorVacuum CastingInjection MoldingTooling Cost$200–$1,000$10,000+Per-Part Cost$10–$100<$1 (at scale)Lead Time10–20 days4–12 weeksProduction Volume50 prototypes2 million unitsMaterial OptionsLimited resinsWide range of plastics This chart…

Image Source: unsplash Vacuum casting is a highly cost-effective prototyping process—but how precise can it really be? In this guide, we dive into the typical tolerances achievable with urethane/a cast parts, the key factors that influence dimensional accuracy, and the quality control strategies you should use to minimize variation. Whether you’re designing for tight-fitting assemblies or functional prototypes, this page gives you a clear engineering-level understanding of what to expect, and how to design for optimal accuracy in vacuum cast components. You can expect vacuum casting tolerance to be about ±0.3 mm or ±0.3% for most parts. This accuracy depends…

Image Source: pexels Vacuum casting is a versatile method for producing prototypes and low-volume production parts using polyurethane (PU) or epoxy resins. One of the most critical factors for part quality is wall thickness. Proper wall thickness ensures consistent resin flow, minimal shrinkage, and dimensional stability, while poor design can lead to warping, sink marks, or incomplete casting. This guide provides minimum and recommended wall thickness ranges, practical design tips, and engineering considerations for vacuum-cast parts. 1. Minimum and Recommended Wall Thickness The optimal wall thickness depends on part size, geometry, and resin type. Below are general guidelines: FeatureMinimum ThicknessRecommended…

You should expect about 0.15% shrinkage with Vacuum Casting Material. This is common with polyurethane resins and elastomers. If you do not think about shrinkage, your parts may not fit. They might also not work as you want. Plan for shrinkage before you start making parts. This helps you get accurate results. Polyurethane resins and elastomers are popular. They have shrinkage rates you can predict. Key FactorImpact on Dimensional Accuracy and FitShrinkage during curingPart size changes; it depends on the resin type.Geometry of the partThicker parts shrink more and may bend.Temperature controlCareful curing keeps sizes correct. Key Takeaways Vacuum casting…

If you want to learn how to make mold 3d model for vacuum casting, you can follow some simple steps and guidelines. Start by creating a 3d model, as this is the foundation for how to make mold 3d model. Pay close attention to the mold design to ensure you can easily remove the finished part. The process of how to make mold 3d model involves having a precise model, careful mold making, and proper casting techniques. Many people achieve consistent and repeatable results by using this method. For instance, silicone molds made from a 3d model can be reused…
Want to convert your CAD design into a sample prototype or small-batch production? Upload your files and get a fast and accurate quote.
