You can pick from many top moldable plastic materials for vacuum casting. These include urethane resins, ABS-like materials, polycarbonate-like materials, silicone rubber, and epoxy materials. Each moldable plastic material helps you make high-quality prototypes and end-use parts. Many engineers use vacuum casting to test design and function before using plastic injection molding resins. Studies show that picking the right materials for vacuum casting affects the quality of prototypes, casting performance, and product design. The common materials used in vacuum casting help you get accurate casting results for many uses.
Key Takeaways
Vacuum casting uses plastics like urethane, ABS-like, polycarbonate-like, silicone rubber, and epoxy. These materials help make detailed and high-quality parts fast and at a low cost.
Picking the best material depends on what your part needs. You must think about strength, flexibility, looks, and where it will be used. This helps you get strong and correct prototypes or small batches.
Urethane resins are flexible and tough. ABS-like materials are strong and have smooth surfaces. Polycarbonate-like plastics are clear and do not break easily.
Silicone rubber works well for soft parts and flexible molds. Epoxy materials make strong parts that can handle heat and tough jobs.
Vacuum casting saves time and money for small groups of parts. It helps test new designs quickly. It is good for car, medical, and consumer product industries.
Vacuum Casting Overview
Process Basics
Vacuum casting helps make plastic parts that are very detailed. First, you need a master model. You can make this with 3D printing or CNC machining. Put the master model in a container. Pour liquid silicone over it. Wait for the silicone to harden. Take out the master model. Now you have a mold that matches your design.
Next, mix a moldable plastic material like polyurethane or silicone rubber. Pour this into the silicone mold. Use a vacuum to pull out air bubbles. This makes the part smooth and precise. Put the mold in an oven so the part can cure. When it is done, take out the part. Trim it and check if it looks right.
Here is a table that shows the main steps and how long each takes:
Step | Description | Timing Data |
|---|---|---|
Master Model Creating | Make a detailed model with 3D printing or CNC machining. | N/A |
Silicone Mold Making | Pour silicone over the model and cure it in an oven at 40°C. | 8-16 hours |
Casting the Parts Under Vacuum | Mix and remove air from the moldable plastic, then pour it into the mold using a vacuum. | Degassing: 50-60 sec |
Resin Curing | Let the part cure in the mold, usually in an oven. | About 1 hour |
Demolding the Cast Parts | Take out the part and finish it. | N/A |
Why Use Moldable Plastic Material
Vacuum casting is helpful when you need prototypes or just a few parts. You can use many types of moldable plastic material, like polyurethane, silicone rubber, and epoxy. These materials help you make parts that look and feel like real plastic injection molding resins. This lets you test your design before making lots of parts.
Vacuum casting gives you smooth and accurate parts. You can change your design or switch materials fast. This makes it good for rapid prototyping and for making parts for cars, medical devices, and consumer products.
Tip: Silicone molds for vacuum casting do not last as long as molds for plastic injection molding. You can use a silicone mold about 20-30 times before you need a new one.
Vacuum casting saves money for small batches. It is faster and cheaper than plastic injection molding because you do not need expensive metal molds. But the best process depends on what you need. If you want parts fast, with high precision, and want to try different moldable plastic material options, vacuum casting is a smart choice. If you need to make a lot of parts, injection molding materials are better because they last longer.
The vacuum casting market is getting bigger. In 2024, it is worth about $3.82 billion. Many people want precise parts and fast prototypes. Different regions help the market grow:
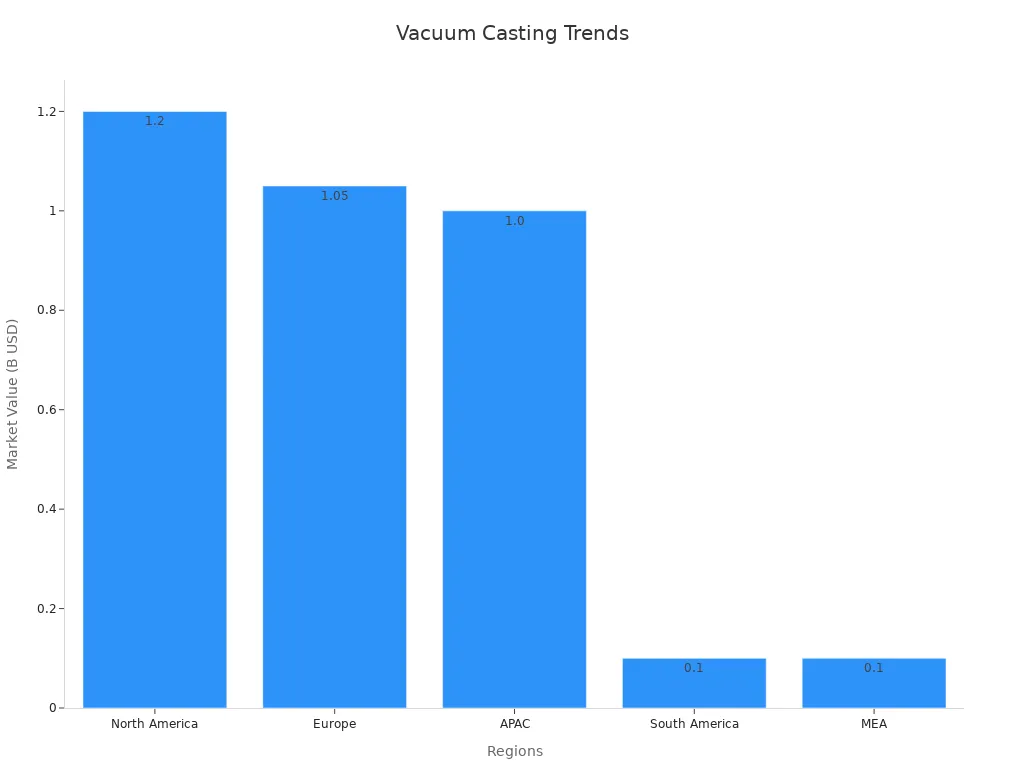
Vacuum casting keeps getting better with new materials and more accuracy. It is now an important way to make things in modern design and manufacturing.
Material Requirements
Key Properties
When you pick a moldable plastic material, you need to think about some important things. These things help you make good parts. Flexibility, strength, and how well it handles heat are very important. You should also check if the material is clear, how tough it is, and if it stays strong when hot. Each thing changes how your part works in real life.
There are rules like ASTM D790-17 and ASTM D955-12(2017) to help you test these things. ASTM D790-17 checks how much a material bends before breaking. ASTM D955-12(2017) looks for warping, so you know if your part will keep its shape. You should also look at how hard the resin is. Rigid polyurethane resins are pretty hard, with Shore D between 78 and 86. Elastomeric grades can stretch a lot, sometimes over 250%. Silicone molds with Shore A of 40–50 are flexible and last a long time.
Here is a table that shows the main physical properties for vacuum casting materials:
Property | Typical Range/Benchmark |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Rigid to highly flexible |
Strength | Moderate to high |
Impact Strength | Moderate to high |
Temperature Resistance | Up to 120°C |
Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.15% of nominal size |
Hardness | Shore D 78–86 (rigid), Shore A 40–50 (mold) |
Note: Try to keep wall thickness between 1.5 and 4 mm. This helps you avoid problems and get better prototypes.
Suitability for Prototypes
Vacuum casting is great for making prototypes. You can test your ideas before making lots of parts. Many companies, like Mahle, use vacuum casting to make car parts for testing. These prototypes help you see if things fit, work, and look right.
You can pick different materials to match the final part’s properties. This helps you make prototypes that feel like the real thing. Vacuum casting gives you good accuracy, with tolerances around ±0.15%. This is good enough for most prototypes and small batches. You can also check how strong your prototypes are and how well they handle hits.
Vacuum casting saves time and money. You can make many prototypes quickly. This lets you try new ideas and fix your design before spending a lot on tools.
Top Moldable Plastic Materials

Vacuum casting lets you pick from many materials. You can choose what works best for your part. Each material has special features that help you get good results. Here are some common materials and why people use them.
Urethane Resins
Urethane resins are very popular for vacuum casting. They come in soft, bendy types and hard, stiff types. These resins make parts that look and feel like real plastic. You can use them for testing or for real products.
Urethane resins are flexible in how you use them. You can pick the hardness, bendiness, or color you want. Some types can handle sunlight, water, and chemicals. This makes them good for things used outside, in hospitals, or in cars. Some types work well in hot or cold places.
Here is a table that lists the main features of urethane resins in vacuum casting:
Property / Aspect | Description / Values | Application / Notes |
|---|---|---|
UV Stability | UV-stabilized, prevents yellowing and cracking. | Outdoor parts, light housings, models. |
Outdoor Suitability | Water and abrasion resistance, color stability. | Weatherproof enclosures, vehicle parts. |
Temperature Range | Stable up to ~120°C, flexible at low temps. | Parts near heat or cold. |
Hardness (Durometer) | Shore A 5 (soft) to Shore D 85 (rigid). | Gaskets, bushings, structural parts. |
Tensile Strength | 500–5,000 psi; reinforced up to 14,000 psi. | Parts under stress. |
Impact Resistance | High elasticity, prevents cracks. | Enclosures, bumpers, vibration-damping. |
Abrasion Resistance | Excellent, resists friction. | Moving parts, grips, packaging. |
Specialty Formulations | Heat, chemical, UV, moisture resistance. | Industrial, automotive, aerospace. |
Limitations | Heat resistance limit (~120°C), slower curing, sensitive to humidity. | Plan for production and mold care. |
You can use urethane resins for many jobs. They help you make smooth and exact parts. Foam and castable urethanes are good for light or soft parts. Urethane resins make vacuum casting easy and not too expensive.
ABS-like Materials
ABS-like materials are also a great choice for vacuum casting. Use them when you want parts that act like real ABS plastic. These materials are tough and do not break easily. They give you smooth parts with sharp edges.
You can use ABS-like materials for test parts, covers, and cases. They are good for parts that snap together or need to be strong. You get good quality and exact shapes with these materials. They are easy to paint and finish, so your parts look nice.
ABS-like resins help you check your design before making lots of parts. You can see if things fit and work right. This saves you time and money. Many engineers use ABS-like materials because they work well and are reliable.
Polycarbonate-like Materials
Polycarbonate-like materials make strong and clear parts. Use them when you need parts that can take a hit and stay clear. These materials are good for parts that must be tough and see-through.
Polycarbonate-like urethane is stiff and does not break easily. It can handle heat and keeps its shape.
You can add ribs to make your parts even stronger. This helps your parts be as strong as injection molded or 3D printed ones.
Vacuum casting with polycarbonate-like materials is fast and costs less than other ways.
You get nice finishes and strong parts. This is good for test parts and some real products.
Using these materials is a smart way to make small batches.
You can use polycarbonate-like materials for lenses, covers, and clear cases. They help you get the quality you need for hard jobs.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is a top pick when you need soft and bendy parts. You can use silicone to make both molds and finished parts. Silicone rubber stretches and does not tear easily. It also stays strong with chemicals and heat.
Property / Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Flexibility and Tear Resistance | Silicone rubber is flexible and tear-resistant, suitable for high-fidelity molds. |
Curing Time | Solidifies in 7 hours; dries in 12 hours. |
Mixing Ratio | 1:1 ratio (base to catalyst) ensures proper curing and elasticity. |
Curing Conditions | Room temperature for 8-12 hours or up to 50°C for faster curing. |
Mold Quality | Produces flexible, elastic molds that reproduce details and are reusable. |
Chemical Stability | Silicone rubber has strong chemical stability. |
Safety and Handling | Use PPE and good ventilation for safety and material quality. |
Silicone rubber is great for making molds that show tiny details. Use it for parts that need to bend, stretch, or touch chemicals. Silicone molds last a long time and keep their shape. You get exact and high-quality parts every time.
Silicone rubber is good for medical tools, seals, and gaskets. It is safe, strong, and simple to use. You can count on silicone for detailed vacuum casting jobs.
Epoxy Materials
Epoxy materials are strong and last a long time. Use them in vacuum casting when you need tough parts that stick well. Epoxy resins harden into strong parts that can take heat and chemicals.
Studies show epoxy composites made by vacuum casting are very strong. Adding fillers or tiny particles makes them even better. Use epoxy for parts that must handle stress, heat, or chemicals.
Epoxy materials are good for tools, strong parts, and glue joints. You get exact and high-quality parts every time. Epoxy resins help you make parts that last and stay strong in hard places.
Note: Thermoset materials like epoxy are stronger and more stable than most thermoplastics. They keep their strength even when it is hot, so they are good for tough jobs.
Vacuum casting lets you pick from many materials. You can match what you need for your project. Each material gives you something special, like bendiness, strength, or clearness. By knowing your choices, you can get the best parts for your vacuum casting work.
Applications
Prototypes
Vacuum casting helps you make prototypes fast and easy. You can test your ideas before making lots of parts. Many companies use vacuum casting for prototypes. The parts look and feel like the real thing. You can pick urethane resins, ABS-like, or polycarbonate-like materials. These materials help you check if parts fit and work well. You can also see if they look right. Vacuum casting lets you change your design quickly. You do not have to wait a long time. Making prototypes this way helps you avoid big mistakes later.
Use vacuum casting for prototypes when you want:
Fast results
Real testing
Saving money on small batches
Automotive
Vacuum casting is used a lot for car parts. You can make bumpers, grilles, panels, and covers. Urethane resins and ABS-like materials are strong and tough. They help parts last and not break easily. Polycarbonate-like materials are good for clear parts like headlight covers. Vacuum casting lets you make shapes that are hard to make other ways. The parts are light, so cars use less fuel. You can test new ideas and fix them fast. This process is good for both test parts and small runs in cars.
Automotive Parts | Common Materials Used | Why Use Vacuum Casting? |
|---|---|---|
Bumpers, panels, covers | Urethane, ABS-like, PC-like | Fast changes, detail, cost savings |
Headlight pods, grilles | Polycarbonate-like | Clarity, strength, design flexibility |
Tip: Vacuum casting helps you make plastic parts instead of metal or glass. This makes parts lighter and cheaper.
Medical Devices
Vacuum casting is important for making medical devices. You can use special plastics that are safe for people. Silicone rubber and ABS-like materials are good choices. These materials are safe, easy to clean, and can be made germ-free. Vacuum casting gives you detailed parts for testing and real use. The process follows rules like ISO 13485 for safety and quality. You can make parts for devices, covers, and even tools for surgery. Vacuum casting helps you make new things fast and follow the rules.
Consumer Products
Vacuum casting is used to make many things people buy. This includes electronics, things for the home, and sports gear. ABS-like and urethane resins are strong and last a long time. Vacuum casting lets you make parts with lots of detail and color. You can keep costs low, especially for small amounts or new products. The process gives you good, high-quality parts. Many companies use vacuum casting to test ideas and sell new products faster.
Product Type | Material Choice | Key Benefits of Vacuum Casting |
|---|---|---|
Electronics cases | ABS-like, urethane | Detail, color, cost efficiency |
Household goods | Urethane, silicone | Durability, flexibility, quick changes |
Sporting equipment | Polycarbonate-like | Impact resistance, clarity |
Note: Vacuum casting is good for many uses. It helps you get parts fast, with good quality, and saves money.
Material Selection
Picking the right material for vacuum casting is important. It helps you get the best part for your project. You should think about how strong the part needs to be. You also need to look at how it looks, how much it costs, and if it will last in different places. Here are some steps to help you choose well:
Mechanical Properties
First, think about how strong your part should be. Vacuum casting lets you use many kinds of resins. Some are ABS-like, nylon, or glass-filled types. Each resin has its own strength and flexibility. Some are better at taking hits. You can test resins to see if they are strong enough. Use tests like tensile, flexural, and impact tests. If you need a part that is very strong, glass-filled nylon-like materials are good. Polyurethane and silicone resins are good if you want parts that bend or are tough. Always pick a resin that matches what your part needs to do.
Test Type | What It Measures | Example Standard |
|---|---|---|
Tensile Strength | How much force it can take | ASTM D638 |
Flexural Strength | How much it bends before breaking | ASTM D790 |
Impact Strength | How well it resists sudden hits | ASTM D1822 |
Appearance and Finish
Vacuum casting makes parts with nice surfaces. You can pick resins that look clear, shiny, or dull. Silicone molds help make smooth parts with sharp details. If you want a special color or feel, choose a resin that fits your idea. Some resins can even look like glass or metal.
Cost and Volume
Vacuum casting is cheaper for small numbers of parts. Silicone molds cost less than metal molds. If you need 20-50 parts, vacuum casting saves money. If you need more parts, each part costs more. Think about how many parts you want and your budget. New machines and materials can help lower costs and make more parts.
Environmental Resistance
Check if your part needs to handle sun, water, or chemicals. Some resins have things added to help them last longer. Silicone and polyurethane resins can take heat and chemicals. There are tests like UL 746C and ASTM G154 to check if materials last outside. Pick a resin that will stay good in your part’s environment.
Selection Checklist
What strength or flexibility do you need?
What should the part look or feel like?
How many parts do you want to make?
How much money can you spend?
Will the part face heat, sun, or chemicals?
Does your part need special features or different materials?
Tip: Always make and test one part first. This helps you check if it fits and works well.
Vacuum casting gives you lots of choices. If you match the resin to your needs, you get strong and good-looking parts. Think about what is good and bad about vacuum casting for your project. This helps you pick the best material for your design.
Comparison Table

Properties and Uses
When you pick a material for vacuum casting, you want to know how it works. Tables and charts help you compare different materials. These tools make it easier to choose the best one for your project. You can check things like strength, how well it resists wearing out, and how exact the part will be. You can also see how each material acts in different casting jobs.
Here is a table that shows how three dental impression materials work in vacuum casting. All three materials give about the same precision. This means you can trust any of them to make accurate parts.
Material Group | Mean Height (mm) | Standard Deviation | ANOVA p-value | Pairwise Comparison p-values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Control | 8.05 | 0.03 | 0.99 | Control vs Polyether: 0.88 |
Polyether | 8.08 | 0.03 | Control vs Silicone: 0.399 | |
Addition Silicone | 8.06 | 0.05 | Polyether vs Silicone: 0.349 |
You can see that vacuum casting gives you very exact results for dental parts, no matter which material you use.
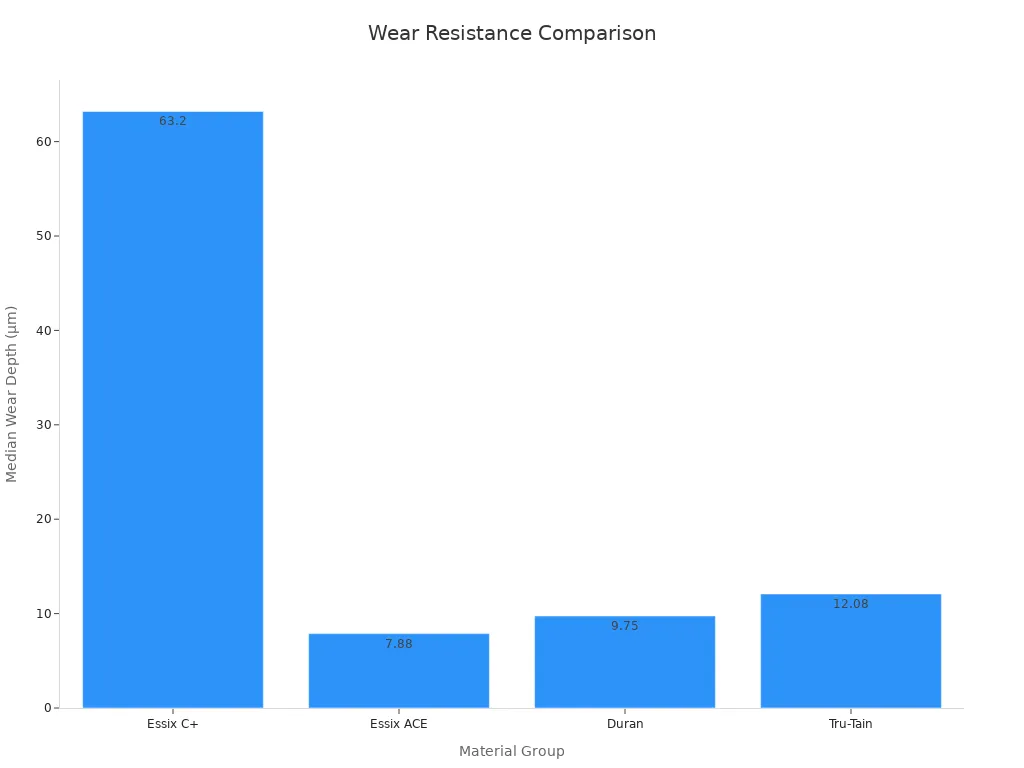
You also want to know how long materials last before they wear out. The next table compares four plastics used in vacuum casting. You can see which ones last longer and which ones wear down faster.
Material Group | Median Wear Depth (µm) | Significant Difference |
|---|---|---|
Essix C+ | 63.20 | Wears out faster than the others (P < .001) |
Essix ACE | 7.88 | Lasts longer, not much different from Duran |
Duran | 9.75 | Lasts longer, not much different from Essix ACE |
Tru-Tain | 12.08 | Lasts longer than Essix C+ |
Essix ACE, Duran, and Tru-Tain last longer than Essix C+. This helps you pick the best plastic when you need parts that do not wear out quickly.
You can also look at industry reports for vacuum casting. These reports show that how you process the material changes how smooth and exact your parts are. You can use these tables to see which materials give you the best finish and accuracy. Some plastics make smoother parts, while others are stronger.
Tip: Always pick your material based on what your vacuum casting project needs. You get better parts when you focus on accuracy, wear resistance, and the right process.
Tables and charts help you make smart choices for vacuum casting. You get clear facts about how each material works. This helps you get the best quality and precision for your parts.
You now know about the best moldable plastic materials for vacuum casting. Each material has its own special properties for your project. Think about how your part will be used when you pick a material. Vacuum casting helps you make strong test parts and real products. Use the selection guide and table to compare your choices. There are many options for vacuum casting projects. If your project is tricky, ask an expert for help. Vacuum casting lets you try, fix, and finish your parts quickly. This process makes making parts simple and fast. Vacuum casting helps you bring your ideas to life from start to end.
FAQ
What is the best material for vacuum casting prototypes?
Most people use urethane resins for prototypes. These resins are strong and flexible. They also make parts look smooth. If you need something special, try ABS-like or polycarbonate-like materials.
How many parts can I make with one silicone mold?
A silicone mold usually makes 20 to 30 parts. The number depends on your material and part shape. Always check your mold after each use for damage.
Can I use vacuum casting for clear parts?
Yes, you can make clear parts with vacuum casting. Polycarbonate-like and some urethane resins work well for this. These materials give you clear and strong parts. Use them for things like lenses or covers.
How do I choose the right resin for my project?
Make a checklist:
Think about how strong and flexible your part should be.
Pick the color and finish you want.
Count how many parts you will make.
Think about heat, sun, or chemicals. Always test one part before making more.
Is vacuum casting safe for medical devices?
Vacuum casting can be safe for medical devices. You need to use medical-grade materials like silicone rubber or special ABS-like resins. Always follow safety rules and test your parts before using them.
 LKprototype
LKprototype