You may see two ways to spell this word: molding or moulding. In the United States, people use "molding" for most manufacturing words. In the United Kingdom and other places, "moulding" is the usual spelling. This difference is important at work. Studies show that spelling mistakes can make people think you are less skilled. They may also think you do not pay close attention, even in manufacturing jobs. In manufacturing, molding or moulding means shaping things like plastic or metal. You do this by pressing the material into a mold. This process helps make many parts and products.
Key Takeaways
In American English, use "molding." In British English, use "moulding." This shows you are professional and helps people not get confused.
Molding changes materials like plastic, metal, rubber, and silicone. It does this by pressing them into molds. This makes many different products.
Injection, compression, rotational, and transfer molding work best for different materials. They also work for different product shapes. This helps get the best results.
Pick materials like plastics, metals, or rubber. Think about what the product needs, how much it costs, and if it can be recycled.
Good mold design, checking quality, and using the right tools help make better products. They also save money and help factories do well.
Molding or Moulding: Spelling
American and British Usage
People spell this word in two ways. In the United States, "molding" is used in books, websites, and factories. In the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia, people use "moulding." This difference happened because American and British English changed over time.
Tip: Use "molding" for American companies. Use "moulding" for British or international readers.
You may see both spellings in big companies. Always check which spelling your company or client wants. This small step can help you look more professional.
Industry Preferences
The spelling you use can depend on your job or where you live. Most American factories, manuals, and schools use "molding or moulding" for shaping materials. British and European companies almost always use "moulding."
Here is a table to help you remember:
Region | Common Spelling |
|---|---|
United States | molding |
United Kingdom | moulding |
Canada | moulding |
Australia | moulding |
Some jobs, like plastics or construction, have their own rules. Always follow the rules for your job. Using the right spelling shows you care about details. It also helps you avoid confusion with people from other places.
Definition
What Is Molding or Moulding?
Molding or moulding means shaping materials into certain forms. In manufacturing, you take a raw material like plastic or metal. You press it into a mold. The mold shapes the material. This process helps make many things, like car parts and toys. Molding is used in almost every industry.
When you do molding, you use different molds and materials. For example, injection molding makes plastic parts. A machine pushes melted plastic into a mold. The plastic cools and you take out the part. Injection molding is very common in manufacturing. It lets you make many parts fast and with good accuracy.
There are other types of molding too. Some are compression molding and rotational molding. Each type works best for certain things. The right process depends on what you want to make and what you need in the product.
Note: Molding or moulding is not just for plastic. You can use it for metals, rubber, and glass. The process always shapes a material using a mold.
Key Terms
You will see many special words when learning about molding. These words help you know how the process works. They also help you talk to others in manufacturing and fix problems.
Here is a table that explains some important terms you will find in molding:
Term Category | Examples/Terms | Significance |
|---|---|---|
Molding Techniques | Injection molding, Blow molding, Compression molding | Describe specific molding methods essential for manufacturing processes. |
Mold Components | Insert, Cavity, Knockout Pin | Define parts of molds critical for mold design and operation. |
Process Phenomena | Jetting, Laminar Flow, Breathing | Explain flow behaviors and mold operation phenomena affecting product quality. |
Material Properties | Melt Index, Molecular Weight, Plasticizer | Clarify material characteristics that influence molding behavior and final product properties. |
Operational Parameters | Clamping Force, Molding Shrinkage, Mold Release | Detail process control factors important for ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and quality in molding. |
You will use these words often if you work with molding. For example, in injection molding, you need to know about clamping force and molding shrinkage. These help you make sure your parts are correct. If you work with plastic, you check the melt index. This shows how the plastic will flow in the mold.
You will also hear about different types of molding. Each type uses its own way and has its own good points. Injection molding is good for making many small plastic parts. Compression molding is better for bigger or thicker items. When you know the key terms, you can pick the best process for your job.
Tip: If you want to get better at manufacturing, start by learning these key terms. They help you understand the steps, fix problems, and talk with other workers.
Main Processes

In manufacturing, there are many ways to shape materials. Each molding process shapes things in its own way. You pick a molding technique based on what you want to make. The material and the final shape also matter. Here, you will learn about the main molding processes used in factories everywhere.
Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a very common way to make parts. In this process, melted material goes into a mold. Most of the time, the material is plastic. The material cools and gets hard inside the mold. Then you take out the finished part. You can use injection molding to make car bumpers, toys, and medical devices.
Injection molding is good for making lots of the same part. This process gives you very exact and repeatable results. You can make shapes with small details that other processes cannot do. Many industries use injection molding to make many products.
Tip: Injection molding helps save energy and cut waste. It uses about 38% less energy than some other molding techniques like FDM. It also makes less carbon pollution for each kilogram of material.
Industry studies use special tests to check different settings in injection molding. These tests help you find the best temperature, pressure, and cooling time. Cooling time is important to stop plastic parts from shrinking. High injection pressure can make the finished part stronger. These methods help you make better products and spend less money.
Here is a table that shows what studies found about injection molding:
Study Focus | Material(s) | Process Parameters Investigated | Industry/Application | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Energy and carbon emission modeling in FDM and PIM | PLA | Energy consumption, carbon emissions | Sustainable PLA production | Injection molding uses ~38.2% less energy than FDM; lower CO2 emissions per kg PLA molded |
Injection molding parameter effects on LDPE | Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | Cylinder temperature, mold temperature | Packaging, medical, automotive | Mold temperature significantly affects crystallinity; interaction of temperatures affects spherulite size |
Shrinkage optimization in LDPE injection molding | LDPE | Melting temperature, injection pressure, filling pressure, cooling time | General manufacturing | Cooling time most critical for minimizing shrinkage; injection pressure least effective |
Parameter optimization for recycled HDPE | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | Melting temperature, clamping pressure, injection time, holding time | Recycled product manufacturing | Optimal parameters identified for improved product quality using Gray’s relational analysis |
Effect of injection pressure on PE molecular weight variants | Low and high molecular weight PE | Injection pressure | Mechanical property optimization | High injection pressure improves mechanical properties in HDPE |
Overview of injection molding technology and applications | Various plastics including polyethylene, polystyrene, PLA | Temperature, pressure, cooling time, injection speed | Automotive, medical, packaging, consumer goods | Injection molding is widely used for complex shapes, mass production, and high precision; advanced methods include water-assisted, gas-assisted, microcellular, and rapid thermal cycling molding |
You can use special types of injection molding too. Water-assisted and gas-assisted molding help make hollow parts or lighter products. These techniques let you make strong things with less material.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is another way to shape materials. You put the material in a hot mold. Then you press it with a top plate. The heat and pressure push the material into the mold shape. When it cools, you take out the finished part.
You often use compression molding for rubber, thermosetting plastics, and composites. This process is good for big, flat, or thick parts. You can make car hoods, electrical panels, and appliance covers. Compression molding is used in cars and airplanes too.
Compression molding makes strong parts with a nice surface. You can use it for small or big batches. It is slower than injection molding, but better for some shapes and materials. You can use it for parts that need to handle heat or pressure.
Note: If you need parts with special fibers or layers, use compression molding. You can add things like fiberglass or carbon fiber to make the part stronger.
Sometimes, compression molding is used with other techniques like transfer molding. You can also mix it with extrusion molding or thermoforming for special products.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding, or rotomolding, is a special way to make hollow parts. You put powder inside a mold. The mold spins slowly in an oven. The heat melts the powder. The melted material sticks to the inside and forms a hollow shape. When it cools, you take out the part.
You use rotational molding for big, hollow things like tanks, playground slides, and kayaks. This process makes parts with even walls and no seams. You can also add colors or textures during the process.
Rotational molding is slower than injection or compression molding. But it is great for making large, strong, and light products. You can use many kinds of plastics. Rotational molding is good for custom or small batches.
Tip: If you want a part with no seams or joints, use rotational molding. This process makes one-piece parts that are strong and do not leak.
You can use rotational molding with other techniques like blow molding or thermoforming. You may see it in building and boat making too.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding mixes ideas from compression and injection molding. You put the material in a chamber. A plunger pushes it into a closed mold. The material fills the mold and hardens with heat and pressure. Then you take out the finished part.
You use transfer molding for parts with metal pieces inside, like electrical parts or connectors. This process works well for thermosetting plastics and rubber. Transfer molding lets you control the shape and quality.
Transfer molding is faster than compression molding but slower than injection molding. You use it for medium-sized batches. This process is common in electronics, cars, and airplanes.
Note: If you need to put wires or metal inside a part, use transfer molding. The process keeps the metal in place and covers it with plastic or rubber.
You can use transfer molding with other techniques like blow molding or extrusion molding. This makes it useful for many special jobs.
Now you know about the main molding processes: injection molding, compression molding, rotational molding, and transfer molding. Each one has its own best uses. By learning these techniques, you can pick the right process for your needs.
Materials
Plastics and Polymers
Plastics and polymers are the most used materials in molding. They are cheap, flexible, and easy to shape. You can make many shapes and sizes with plastic. Plastics are used for toys, bottles, car parts, and packaging. There are many types of plastic, like PET, HDPE, and PP. Each type is good for different things.
The molded plastics market is growing quickly. More people buy plastic products because they earn more money and find new uses.
Companies use more recycled and biodegradable plastics now. This helps the planet and follows new rules.
Since 2023, factories have made 8.3 billion metric tons of new plastics.
Blow molding is a common way to make bottles and containers. It saves money and makes complex shapes.
PET is often used for packaging. It is strong and easy to recycle.
Asia Pacific makes the most plastic. This is because the area is growing fast and gets help from the government.
Molded plastics are needed for drinks, personal care, and medical items.
The blow molding market is also changing. Companies use more recycled polymers to follow new laws. HDPE is the main plastic for bottles and home goods. PP is important for food and personal care packaging. Big brands want to use less new plastic and make recycling easier.
Tip: When you pick materials for molding, think about how the product will be used, how much it costs, and if it can be recycled.
Metals
Metals are strong and used in molding when you need tough parts. You see metals in car engines, tools, and electronics. Metal injection molding (MIM) makes small, strong, and detailed parts. Stainless steel, aluminum, and chromium are common metals.
Metric/Category | Value/Statistic | Year/Period | Notes/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
Global MIM Market Size | USD 4.76 billion | 2024 | Growing fast |
Forecasted Market Size | USD 13.26 billion | 2037 | 8.2% CAGR |
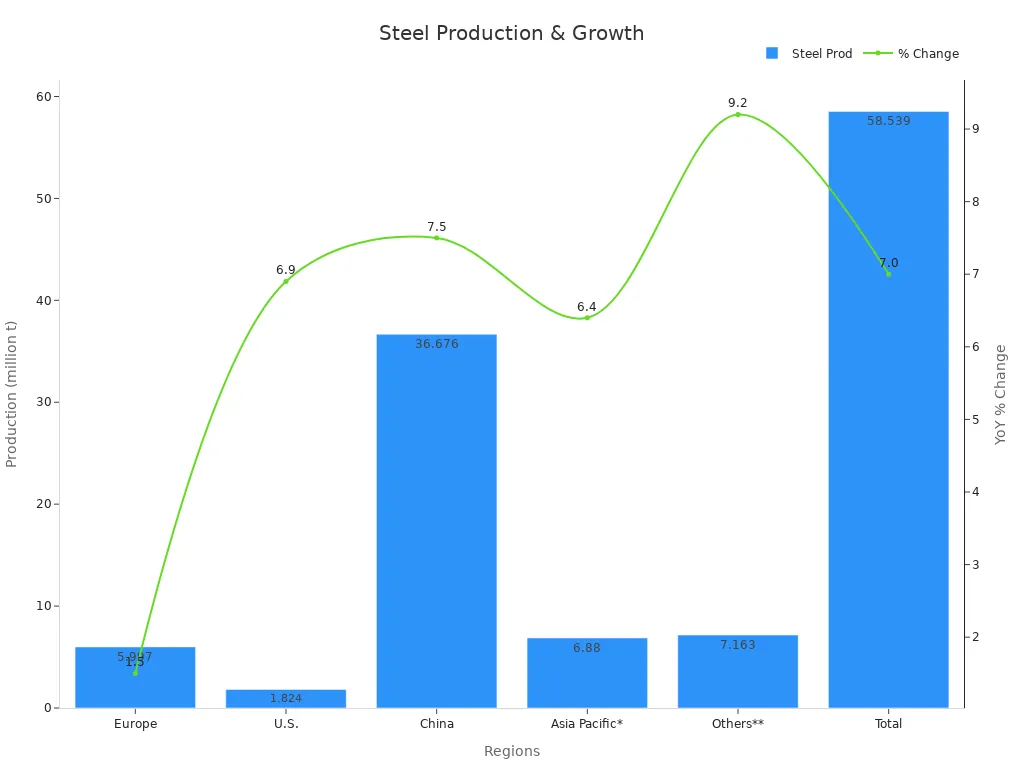
Stainless Steel Production | 62.6 million metric t. | 2024 | 7% global increase |
Asia Pacific Market Share | 38% | 2037 | Largest share |
North America Market Share | 25% | 2037 | Second largest |
Asia Pacific makes the most metal, mostly for cars and electronics. Stainless steel production is going up in China and the U.S. Here is a chart that shows stainless steel production by region:
When you pick metals for molding, you get parts that can handle heat, pressure, and wear. Metal molding is important for cars, military tools, and electronics.
Rubber and Silicone
Rubber and silicone are bendy materials used in molding for things that need to stretch. You find them in car parts, medical tools, and kitchen items. Silicone rubber is special because it can take heat and comes out of molds easily.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Market Size (2025) | $2.5 billion |
Projected Market Size (2033) | $4–4.5 billion |
CAGR (2025-2033) | 6% to 7.6% |
Key Growth Drivers | Automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer goods, dental, 3D printing |
Major Players | Shin-Etsu Chemical, Dow, Smooth-On, regional manufacturers |
Regional Growth | Strong in North America and Asia-Pacific |
Competitive Advantages | Heat resistance, flexibility, release properties |
The market for silicone rubber is getting bigger. More industries use these materials because they last long and work in hard places. New trends include eco-friendly silicone and smart molds with sensors.
Note: If you need a part that bends, stretches, or takes heat, rubber and silicone are great choices for molding.
Mold Manufacturing
Mold Materials
When you start mold manufacturing, you need to pick the right materials for your molds. The choice depends on what you want to make, how many parts you need, and your budget. For plastic molds, you often use steel or aluminum. Steel lasts longer and handles high-volume jobs. Aluminum costs less and works well for small batches.
You should think about these points when choosing mold materials:
Durability: Some materials resist chemicals, heat, and wear better than others. If you need molds for harsh environments, pick materials with high resistance.
Cost: Look at the price of raw materials, tooling, and waste. Check if you can recycle or reuse the mold.
Production volume: For low-volume jobs, you might use cheaper materials. For high-volume runs, you need strong materials that last.
Mold complexity: Complex molds with grooves or special shapes cost more to make.
Testing: Always test your mold with a prototype before full production.
Here is a table to help you see how production volume affects cost:
Production Volume | Approximate Number of Parts | Mold Cost (USD) | Material Cost per Part (USD) | Labor Cost per Part (USD) | Approximate Cost per Part (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Low Volume | ~100 | Low (~$100) | Moderate (~$0.50) | High (~$3.00) | High (~$4.50) |
Medium Volume | ~5,000 | Moderate (~$2,500) | Moderate (~$0.50) | Moderate (~$2.00) | Moderate (~$3.00) |
High Volume | ~100,000 | High (~$25,000) | Moderate (~$0.50) | Low (~$1.00) | Low (~$1.75) |
You can lower costs by using simple mold designs, picking cost-effective materials, and working with your suppliers. For plastic molds, always check the melt flow and shrinkage rates to avoid problems during production.
Mold Design
Good mold design helps you make better products faster. When you design plastic molds, you need to plan for the shape, size, and features of each part. You also need to think about how the material will flow and cool inside the mold.
Studies show that using smart mold design can cut production time by 12%, save 2% on raw materials, and lower energy use by 16%. You can use computer tools and simulations to test your mold design before making it. This helps you find the best spot for gates and vents, which lets air out and stops defects.
In plastic molds, the placement of gates and vents is very important. If you put them in the right place, you get better quality and fewer problems like air bubbles. You can use special software to run tests and find the best mold design for your needs.
Tip: Always check your mold design with a prototype or a small test run. This step helps you catch mistakes early and save money.
When you focus on good mold design, you make stronger, more reliable parts. You also use less energy and materials, which helps your business and the environment.
Applications of Using Molding

Molding changes many things you use every day. You see molding in cars, toys, and even in hospitals. These uses help make things lighter, stronger, and cheaper. The table below shows how different industries use molding and how much of the market they have:
Application Sector | Market Share (%) | Growth Drivers and Notes |
|---|---|---|
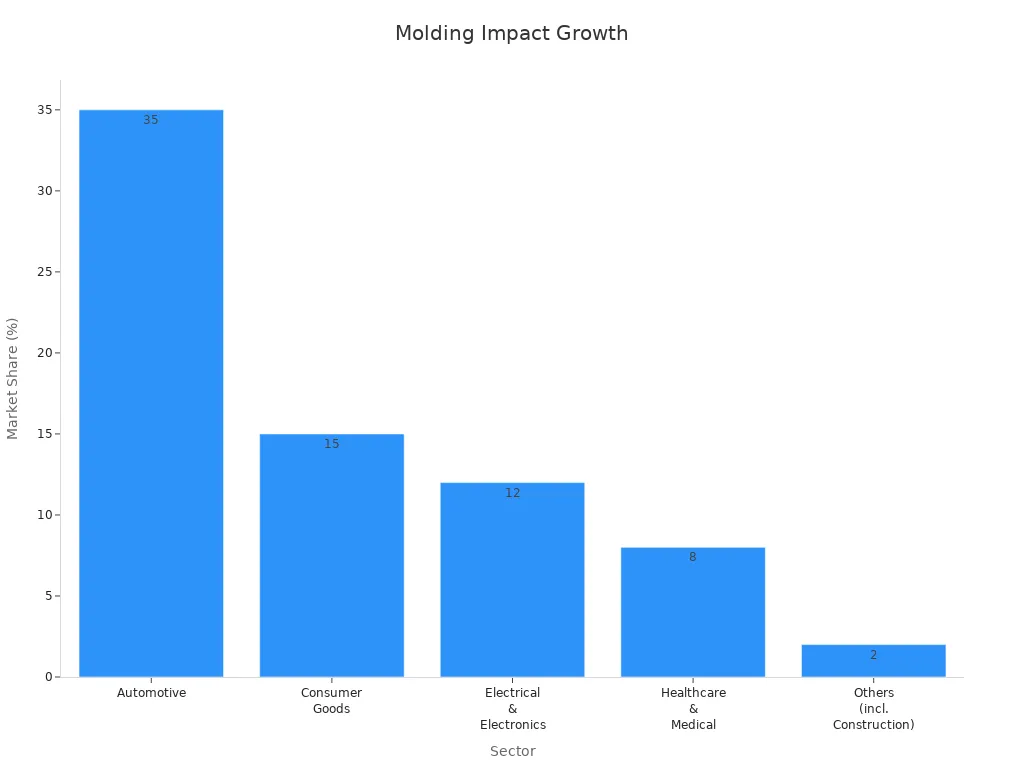
Automotive | ~35% | Largest segment; demand for lightweight interior and under-the-hood components; machine upgrades +28%. |
Consumer Goods | ~15% | Customized small-batch manufacturing; 22% increase enabled by electric machines. |
Electrical & Electronics | ~12% | 25% rise in electric machine adoption due to miniaturization and component density. |
Healthcare & Medical | ~8% | Over 30% of medical manufacturers switching to all-electric systems for contamination control. |
Construction & Others | ~2% | Moderate growth driven by innovation and lightweight design demand. |
Automotive
Most molding is used in making cars. Car companies use molding for dashboards and bumpers. They also use it for engine parts. These parts need to be light and strong. Lighter cars use less gas. Blow molding makes fuel tanks and air ducts. New machines help make more parts, up 28%. Molding lets car makers try new shapes and safety ideas.
Consumer Products
You use molded things at home every day. Toys, kitchen tools, and chairs are made with molding. Companies use molding to make many shapes and colors. Electric machines help make small batches and custom items. This has made production go up by 22%. Blow molding is used for bottles and containers. You get safe and fun products because of molding.
Medical Devices
Hospitals need molding for safe tools. Syringes and IV parts are made this way. Surgical devices use molding too. Micro molding makes tiny parts for gentle treatments. Over 30% of medical factories now use all-electric machines. This keeps tools clean. You get safer and better care because of molding.
Electronics
You use electronics like phones and computers every day. Molding makes cases, connectors, and switches. These parts must be made very carefully. Smaller parts and more details mean more electric machines are used, up 25%. Blow molding helps make some electronic covers. You get smaller and smarter devices thanks to molding.
Construction
Builders use molding for pipes and panels. They also use it for insulation. These parts make buildings lighter and stronger. New designs and materials help the construction industry grow. You see safer and more energy-saving homes because of molding.
Tip: Molding helps every industry make new and better products. You see more choices and cool designs because of molding.
Design Considerations
Part Design
When you design a part for molding, you must think about how the shape and size will affect the process. Simple shapes make it easier to use different molding techniques. If you want to use injection molding, you should avoid sharp corners and thick sections. These features can cause problems like warping or uneven cooling. You need to plan for the way the material flows inside the mold. This helps you avoid air pockets and weak spots.
Draft angles help you remove the part from the mold. You should add these angles to every side that touches the mold. Ribs and bosses give your part strength without adding too much weight. You also need to think about shrinkage. Every material shrinks a little when it cools. You must adjust your design to get the right size after molding.
Tip: Always make a prototype before full production. This step helps you find design problems early.
Tooling
Tooling is one of the key design considerations in molding. The mold must match your part’s shape and size exactly. If you use injection molding, you need strong molds made from steel or aluminum. Hardened steel molds last longer and work well for high-volume jobs. Aluminum molds cost less and suit small batches.
You should invest in quality tooling with tight tolerances. This means the mold parts fit together very closely. Good tooling helps you keep the right shape and size for every part. You must also add cooling channels to control the mold temperature. This step is important for injection molding because it affects how fast you can make parts.
Part geometry and complexity change how you design the mold.
The material you choose affects how long the tooling lasts.
Production volume tells you if you need a simple or complex mold.
Tight tolerances help you get the right size every time.
You must watch for problems like shrinkage and thermal changes.
Statistical methods like Response Surface Methodology help you test different settings. You can use these tools to find the best temperature, pressure, and cycle time for injection molding. Studies show that polyurethane molds shrink less than silicone molds. This fact helps you pick the right material for your tooling.
Note: Regular maintenance and inspections keep your molds working well and save you money on repairs.
Quality Control
Quality control is another key design consideration in molding. You want every part to meet your standards. You should track key metrics like reject rates and on-time delivery. Statistical Process Control methods, such as X-bar charts, help you spot problems early. These tools show you if your injection molding process stays within limits.
You can use automation to inspect parts. Machines do not get tired and can check many parts quickly. Machine learning models, like neural networks and random forests, help you find defects faster. Some studies show these tools can cut inspection time by 73% in injection molding.
Use 100% inspection for complex parts.
Try periodic or automated checks for large batches.
Keep your workspace clean to avoid defects.
Train your team so everyone knows how to spot problems.
Methods like Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing help you improve your process. Supplier quality management ensures you get good raw materials. These steps help you make better products with fewer defects.
Tip: Good quality control in injection molding saves you time and money. It also keeps your customers happy.
Now you know how "molding" and "moulding" are different. Pick the right spelling for where you live or work. This is very important in American factories. Molding uses many ways and materials to make strong things. It helps you build products for many jobs. Car makers, hospitals, and food companies all use molding. They need it to make safe and fast products. Good molds help you get better quality and save money.
Molded parts are used in lots of things, like car doors, toys, and medical tools.
Safety rules, good training, and taking care of machines help your work go well.
If you need fast help, look at the FAQ section.
FAQ
What is the difference between "molding" and "moulding"?
You use "molding" in American English. You use "moulding" in British English. Both words mean the same thing in manufacturing. Always check which spelling your company or client prefers.
Which materials can you use for molding?
You can use plastics, metals, rubber, and silicone for molding. Each material works best for certain products. For example, plastics make toys and bottles. Metals make strong machine parts.
How do you choose the right molding process?
You look at the product shape, size, and material. Injection molding works for small, detailed parts. Compression molding fits large or thick items. Rotational molding makes hollow shapes. Transfer molding helps with parts that need metal inserts.
What should you do if your molded part has defects?
Check the mold for damage or dirt.
Review your process settings like temperature and pressure.
Try using better materials or adjusting cooling time.
Ask your team for advice if you cannot find the problem.
 LKprototype
LKprototype