Rapid prototyping (RP) will transform manufacturing by providing a faster tool for product development at cheaper costs while offering more flexibility in design. Working mainly in the auto and aerospace industries, Supply Chain Management enhances the delivery of goods and services and ensures that the company operates in a technologically innovative world.
Rapid Prototyping is the creation of form or function physical models with the most applicable manufacturing processes comprising 3D rapid prototyping, CNC machining services, and laser rapid prototyping. It can decrease lead times and improve the cyclic design and common in some industries requiring speed and accuracy.
Evolution of Prototyping in Manufacturing
Traditional Prototyping:
In traditional methods, the models are built manually or using machines, which are time-consuming and involve a lot of resources. These processes were manual making repetitive changes both hefty and expensive.
The Rise of Rapid Prototyping:
The 1980s marked the beginning of the formation and development of stereo lithography and other technologies belonging to rapid prototyping. In contrast to traditional models of modeling, rapid prototypes satisfy the need for modeling, enable concurrent working, and are sparing in the amount of physical material. Rapid prototyping market surges from $2.5B to $15B by 2031. Its versatility in the materials and industries ensures it has revolutionized product design.
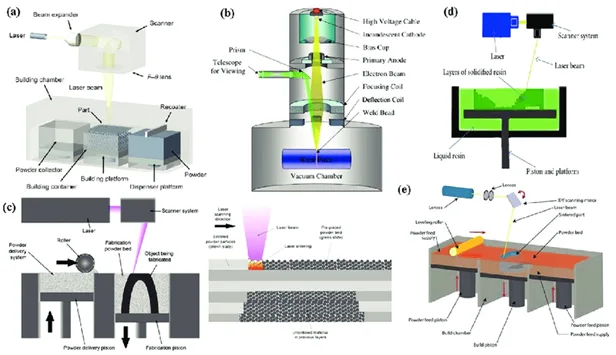
Key Technologies in Rapid Prototyping
3D Printing/ Additive Manufacturing
3D printing also known as additive manufacturing is the process of manufacturing a digital model by building it in a successive layer by layer. It can handle complex topographies and all kinds of material viz. polymer and metal; hence, it can be used extensively in sectors of healthcare and electronics.
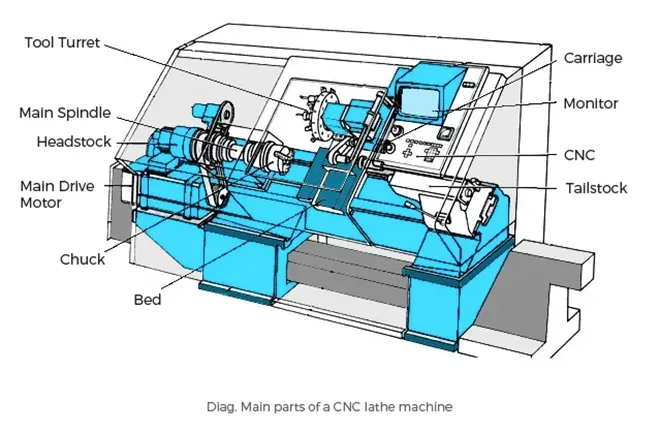
CNC Milling & Lathe Operations
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Milling is a part of CNC Manufacturing that involves the automated shaping of material using computer-controlled tools. CNC technologies achieve high levels of accuracy for prototypes that need to possess great mechanical strength. These are best suited for use in components of aerospace as well as automotive industries.
Laser Sintering & Laser Stereolithography
They both are 3D printing techniques that use lasers to build parts in layers. Laser-based techniques employ powdery materials or photopolymers to generate intricate components with intricate surface quality and dimension. This precision is especially important in the medical applications of the material as well as in designing complex models of clothes and accessories.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twins technology allows manufacturers to test performance and other designs before physical production by stimulating prototypes virtually due to massive development time and cost savings. Digital twin enables the creation of a prototype quickly which can be tested without worrying about the physical implications.

Key Benefits of Rapid Prototyping in Manufacturing
Faster Time-to-Market:
Traditional manufacturing processes are slow; making any alterations in the design or structure of the product time and energy-consuming. Rapid prototyping minimizes development cycles due to making several iterations within a short time and immediate testing. Technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining enable the creation of prototypes within hours and ensure businesses stand out from their competition.
Cost Reduction:
Traditional prototyping often involves the use of costly molds and materials in the making of prototypes. Rapid prototyping cuts these costs through a process called additive manufacturing. It helps in cutting down the expenses of the project since extra materials are not produced in the process and design errors are easily pointed out.
Design Flexibility and Customization:
Rapid prototyping is the most flexible process and designers can test and modify as they wish without going through all steps again. The iterations of designs are necessary for the proper development of the product since all the concepts have to be improved considering feedback. CAD software facilitates incremental progression as each design can be adapted to a customer or market's requirements.
Error Reduction & Better Testing:
Rapid prototyping helps businesses to create prototypes that are similar to the final product and allows realistic market testing. Since functional models can be made, then product tests can be run to find out areas that require improvement before actual production. Such consecutive testing helps to produce better products with less probability of costly modifications.
Sustainability Benefits:
Rapid prototyping supports sustainable development using only the necessary materials and encouraging efficient production. It cuts out the expenses involved in the disposal of waste products and energy used in the production process aligning with eco-friendly production processes.
How Rapid Prototyping is changing the Manufacturing Process?
Collaborative Design and Development:
The use of the different prototypes helps to improve communication between engineers and designers. As the process of design is inclusive of cross-functional teams and other stakeholders, the team is always sure that what is being developed will address user or customer needs while fitting organizational strategies and objectives.
Prototyping for Mass Customization:
Another approach is prototyping for mass customization through integration of the Rapid prototyping technologies. Technologies such as 3D Printing and CAD systems enable organizations to design products based on preferences, yet can be scaled. This approach is unique but relatively affordable and has been applied across different sectors.
Prototyping in the Era of Industry 4.0:
Prototyping in Industry 4.0 combines digitization and physical models in product development thus changing the traditional processes. Digital twins can be used to digitally recreate real-world situations thus lowering cost and time through the elimination of the physical prototypes. Techniques such as 3D printing and CNC machines turn virtual designs into highly tangible products.
Supply Chain Optimization:
The supply chain benefits from rapid prototyping because it speeds up product development, and reduces lead-time and procedures. The use of technology and 3D printing breaks the dependency of business with the traditional supplier thus making it easy to meet market challenges. This makes it more efficient, and cost-effective and enhances the overall supply chain responsiveness.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping parts
Automotive Industry:
Rapid prototyping revitalizes the automotive industry by cutting development time in half from five years to three. SL prototyping is currently applied regularly in parts such as interiors, engines, and assemblies. Companies like Chrysler and GM in the US benefit from reduced development time cuts and cost cuts to deliver better upgrades more quickly.
Aerospace Industry:
Rapid prototyping is critically important to aerospace as it is capable of delivering superior surface finish and accuracy. It is used by almost all North American firms in the aerospace industry for creating detailed systems and parts. This technology facilitates greater testing, providing lightweight, high-strength parts important for the safety and performance of aerospace vehicles.
Consumer Electronics:
Rapid prototyping is especially important in the electronics industry. Modern technologies allow identifying design issues and prevent major changes late in the production cycle. By using these techniques, global electronics leaders gain the freedom of time and cost, coupled with elegant and reliably functional appearances of a smartphone, laptop, or wearable device.
Healthcare/Medical Devices:
It has been used from simulating surgery operations to preparing implants by changing the health sector dramatically. Techniques such as 3D printing include CT imaging for specific configurations and customized implants. Fields include neurosurgery, orthopedics, and orthodontic applications, in which distinct approaches can be better considered and potential problems minimized before implementation.
Fashion & Footwear:
Rapid prototyping such as 3D printing drives creativity in fashion, enabling sophistication and sustainability. Nike and Adidas are some brands that utilize it for smart shoes, and custom geometries. This technology increases the speed, creativity, and utilization of materials in creating better fabrics, in fashion and footwear especially.
Challenges and Limitations of Rapid Prototyping in Manufacturing
Material Limitations:
Rapid prototyping faces a restricted set of materials such as plastics or low-quality metal. This is good for some uses, but in industries such as aerospace or healthcare, more hard-wearing materials are needed. The availability of a vast range of materials is also limited which may restrict RP’s ability to expand its applications.
· Accuracy & Precision:
Achieving high accuracy and precision in RP is difficult. Some prototypes may not be perfect replicas of their respective digital models therefore posing problems in terms of fit, function, and quality. This is a problem in applications such as medical devices, where the error difference can have serious ramifications on product safety.
Cost of Advanced RP Technologies:
Advanced RP technologies, for instance, metal 3D printing or multi-material systems can be expensive. These technologies involve large capital investments in terms of acquisition, require higher initial outlay in the form of sophisticated machinery, and have recurring costs for maintenance thus reducing their attractiveness to either small firms or start-ups.
Scalability Issues:
Another limitation of RP is scalability; although it is brilliant at producing prototypes, it provides a challenge in mass manufacturing. Unlike traditional processes such as injection molding, RP is not always efficient or cost-effective for large-scale production. This makes it rather impractical especially for businesses that require large quantities of product.
Conclusion
The LK Prototype involves strength in the area of the development of rapid prototyping solutions that can design and provide the necessary solutions that can support customer requirements in terms of speed, cost, and flexibility. A combination of advanced tech, in product design, development, differentiation, and operation helps give the company an edge.
 LKprototype
LKprototype