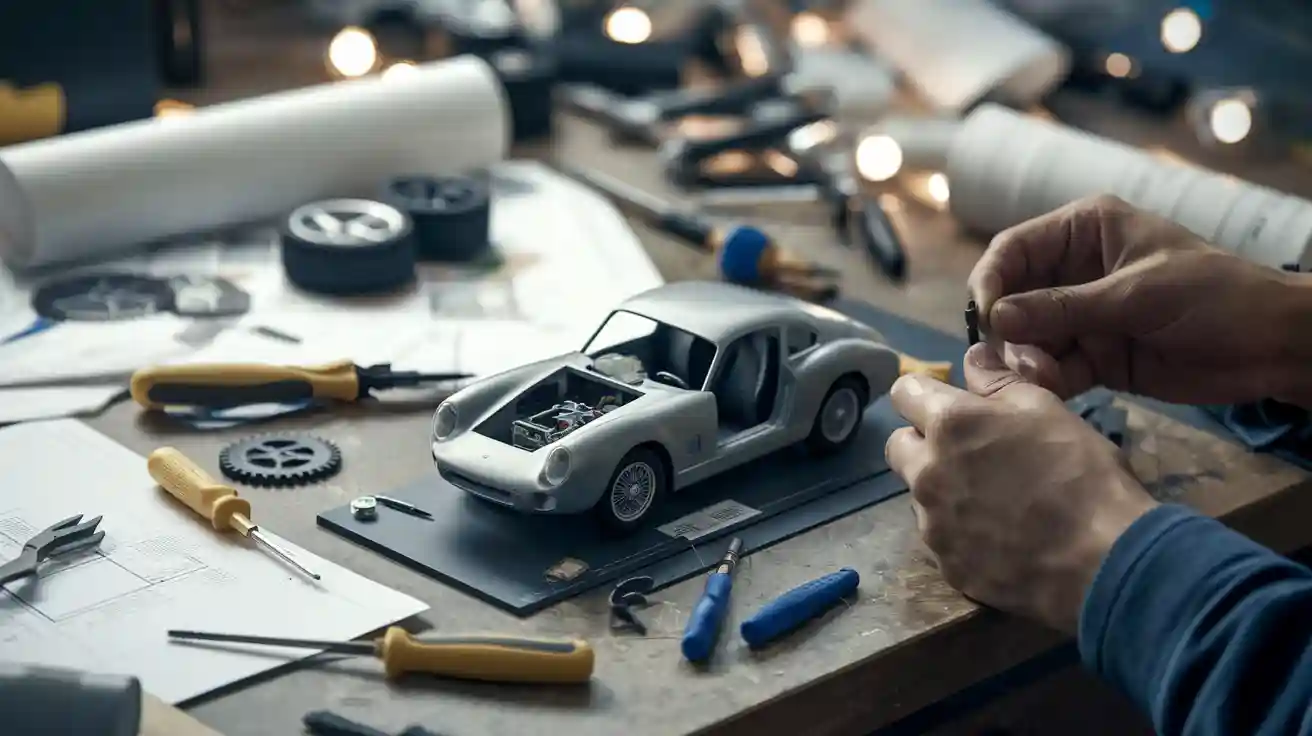
Prototyping car models play a crucial role in car design, enabling the testing of ideas, enhancement of features, and early resolution of safety concerns. Throughout the car development process, prototyping car models allow engineers to evaluate vehicle performance effectively. For instance, advanced simulation tools have significantly improved car safety and saved countless lives. Rigorous testing during the initial stages ensures vehicles operate more efficiently and comply with safety regulations, resulting in innovative and reliable automobiles.
Key Takeaways
Begin by thinking of ideas and drawing simple sketches. This helps find design problems early.
Use CAD software to make precise 3D models. These let you adjust quickly and build prototypes easily.
Ask stakeholders for feedback to improve the design. This ensures it works well for users.
Concept and Design in the Automotive Prototyping Process

Coming Up with Ideas and Drawing Basic Designs
The first step in car prototyping is brainstorming ideas. Look at current designs, trends, and what customers like. Drawing helps you see your ideas and try out options. Keep your drawings simple, focusing on the car's shape and purpose. This step helps spot problems and improve your idea before moving ahead.
Prototyping at this stage has many advantages:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Spotting Problems Early | Prototypes show design mistakes or technical issues quickly. |
Faster Decisions | Clear prototypes help decide on features and designs faster. |
Better Teamwork | Prototypes give teams a shared idea to discuss and improve. |
Reducing Risks | Early prototypes catch problems before they become expensive. |
Saving Money | Spending on prototypes can save a lot of money later. |
Making Digital Models with CAD Tools
After finishing your sketches, use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) tools. CAD software helps you make exact 3D models of your car design. These models show details and let you test if the design works. You can also check how it performs in real-world conditions.
Digital models make prototyping faster by allowing quick changes. They are also used to create physical models with 3D printing or CNC machines. CAD tools ensure accuracy and save time during development.
Important Design Points: Usefulness, Looks, and Practicality
When designing prototype cars, balance usefulness, looks, and practicality. Usefulness means the car works well and meets needs. Looks focus on how attractive the car is to buyers. Practicality checks if the design can be made within time and budget limits.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Usefulness | The car must work well and be practical for users. |
Looks | The car's appearance should attract buyers based on their tastes. |
Practicality | The design must be realistic to make within time and budget. |
To balance these points, try these tips:
Know your audience to decide if looks or function matter more.
Use designs that can change looks without affecting performance.
Try rapid prototyping to make quick changes and improvements.
By focusing on these points, you can design a car that works well and appeals to buyers.
From Virtual Models to Physical Prototyping Car Models
Ways to Make Scale Models (e.g., 3D Printing, Clay Modelling)
Making scale models connects digital designs to real prototypes. Two common methods are 3D printing and clay modelling. Each has its own benefits based on project needs.
3D printing has changed how car prototypes are made. It cuts the time from design to model, reducing it from 20 weeks to just 2 weeks. This method also saves up to 90% of costs by using plastic instead of metal. Additionally, 3D printing creates detailed shapes that hands cannot make.
Clay modelling is still popular for its hands-on and creative process. Designers shape and adjust the model by hand, exploring forms and looks. However, it takes more time and resources because it is done manually.
Metric | 3D Printing | Clay Modelling |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Cuts design-to-model time from 20 weeks to 2 weeks | Slower due to manual work |
Cost | Saves up to 90% with plastic instead of metal | Higher due to materials and labour |
Design Flexibility | Easily makes complex shapes | Limited by hand-sculpting skills |
Making Working Prototypes: Tools and Materials
To build a working prototype, you need proper tools and materials. Start by finalising your design with CAD software. Then, use fast prototyping methods like CNC machining or vacuum casting to create your model. CNC machining ensures accuracy, while vacuum casting makes high-quality models with smooth finishes.
Materials are very important at this stage. Plastics are lightweight and cheap, while metals are strong for testing. Polyurethane resin, used in vacuum casting, gives a smooth finish like injection-moulded parts. These tools and materials help make prototypes that look good and work well.
Solving Problems in Physical Prototyping
Making physical prototypes can be tricky, but smart solutions can help. For example, advanced simulation tools let you test designs digitally before making real models. This reduces mistakes and saves time. Companies like PacMar Technologies use simulations to speed up testing and create better designs.
Common problems include bad data, old systems, and team resistance. To fix these, check data when collecting it, use software to connect systems, and show benefits through small projects. These steps make it easier to move from digital designs to real prototypes.
Tip: Always test your prototype in real-world settings to find and fix problems early.
Testing and Improving the Prototype Car Model
Checking Safety and Performance
Safety checks are very important for improving your car model. They make sure the car is safe and works well in different situations. You can test crash scenarios to see how the car protects people inside. Testing brakes, steering, and suspension shows if the car is reliable.
Using smart tools like regression analysis helps predict problems early. For example, you can study how materials affect crash safety. These tests ensure the car meets safety rules and works as planned.
Testing in Tough Conditions and Durability
Environmental tests check how the car works in extreme weather. These tests look at materials and make sure the car is reliable in tough conditions. Accelerated life testing is another method. It quickly shows how parts might fail after years of use. This helps find weak spots and improve strength.
Test Type | Details |
|---|---|
Testing Range | |
Environmental Testing | Checks how materials and parts work in harsh conditions. |
Accelerated Life Testing | Speeds up durability tests to predict failures and costs. |
These tests give useful information about how long the car will last and how it performs in real life.
Finding and Fixing Design Problems
Design checks help find and fix problems before making the car. Tools like exploratory data analysis (EDA) show patterns and unusual results in tests. For example, scatter plots can show weak areas in the design. Sensitivity analysis is also helpful. It shows how changes, like material thickness, affect the car's performance.
Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
Regression Analysis | Predicts trends and improves designs early. |
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) | Finds patterns and unusual results in test data. |
Sensitivity Analysis | Shows how changes in one part affect safety and performance. |
Fixing these problems early saves time and money. It also ensures the car meets all the needed standards.
Feedback and Iterative Improvements in the Automotive Prototyping Process
Collecting Opinions from Stakeholders
Getting opinions from stakeholders is key to improving your car model. Stakeholders like engineers, designers, and users share ideas that make designs better. Involving them early ensures their needs match the project goals. For example, group discussions can build trust and bring new ideas to improve the prototype.
To manage feedback well, split stakeholders into technical and general groups. This makes their roles clearer and more organised. Audi AG improved feedback by fixing unclear comments through repeated steps. Each step solved problems and matched stakeholder goals with project aims.
Making Changes Using Feedback
Stakeholder feedback helps you make useful changes to the design. Spotting problems early with user and expert input lets you fix flaws quickly. For instance, adding new technology based on feedback can improve the car’s features. Testing changes ensures they meet safety and performance rules.
A clear process for using feedback includes finding problems, fixing them, and checking results. This method not only improves the design but also increases its success. Testing the car yourself gives helpful ideas to improve future designs.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Effectiveness | |
Product Improvement | Feedback adds new features and improves the car’s quality. |
Higher Success Rate | Testing the car gives ideas to make better designs later. |
Getting the Prototype Ready for Final Review
Getting your prototype ready for review needs careful work. Involve stakeholders to get useful feedback. Test how the car works in real-life situations to check its usability. Showing the prototype in its real setting helps get honest opinions. Share only important details to focus feedback on key areas.
Good practices include testing often to check safety and performance. Use advanced tools to test real-world conditions and ensure the car meets all rules. Teamwork between designers, engineers, and builders makes the final product even better. By doing this, you can confidently show a well-prepared prototype for approval.
Tip: Explain that the design is still early to get helpful feedback from stakeholders.
Making a prototype car model has important steps. First, think of ideas and draw sketches. Next, create digital designs and then make physical models using quick prototyping methods. Testing the model checks its safety, performance, and strength. These steps save time, cut costs, and improve efficiency by over 75%. They also reduce testing time by up to 30%.
Learning more about car prototyping can lead to great chances. It helps confirm designs, collect useful data, and work well with others. Begin with small, simple designs and try new ideas. Keep improving with each step. Every prototype helps you get better at this creative process.
FAQ
What materials work best for prototyping car models?
The best material depends on your needs. Plastics like ABS are cheap and light. Metals like aluminium are strong. Polyurethane resin gives a smooth, polished finish.
How do 3D printing and CNC machining compare for prototyping?
Feature | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Quicker for complex designs | Slower for detailed work |
Cost | Cheaper for small projects | More expensive for precise parts |
Accuracy | Good for basic models | Great for exact components |
Can beginners learn CAD software for car prototyping?
Yes, beginners can learn CAD software. Tools like Tinkercad or Fusion 360 are easy to use. They also have tutorials to guide you in making accurate designs.
Tip: Use free CAD tools first to practise before buying advanced ones.

Start your project with LKprototype
LKprototype company simplifies procurement for custom manufacturing, Suitable for making your products or prototypes with a variety of materials, such as metal or plastic, silicone rubber, from 3D Printing to CNC Machined Parts and Vacuum Casting , with a focus on speed and efficiency. Our platform provides instant quotes. With LKprototype, You can connect with the team to communicate your project to ensure quality and on-time delivery.
Start with an instant quote and experience how our technology and expertise can make custom part procurement faster and easier.
 LKprototype
LKprototype