The manufacturing process does affect the cost factors, time, quality, and size. Both cast urethane and injection molding are common techniques utilized in the making of parts for the automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries. They get to know the best method to use depending on their manufacturing, designing, and engineering requirements.
What is Injection Molding: A Comparison with Cast Urethane?
Cast Urethane is a casting process in which a liquid polymer is delivered in molds to form parts. It is often used for low production volume and initial part making because of the lower manufacturing cost, type of material, and time consumption when compared to injection molding.

Introduction to Cast Urethane
Cast urethane is a versatile and widely used material in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. It is a type of polyurethane that is cast into a mold to create a specific shape or design. Cast urethane is known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and durability. This makes it an ideal material for high-performance applications.
How Cast Urethane Works
· Making a silicone mold
A silicon master pattern must be made. In this process, it can be made from 3D printing or machining. This is used to make an impression of the other half of the mold.
· Pouring liquid urethane
To fill the mold perfectly, the liquid urethane is cast in the silicone mold at the right proportion. This process ensures material conforms easily to the shape and requirements.
· Curing
The urethane cures in the silicone mold and molds to the shape. It ensures that the material gets the right strength, and, most importantly, the right size.
· Finishing
This step serves to improve the overall aesthetic look, functionality as well as readiness to use.
Cast Urethane Materials
Cast urethane materials are available in a wide range of formulations, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. The selection of the right material depends on the specific application and the desired properties of the final product.
· Types of Cast Urethane Materials
There are several types of cast urethane materials, including:
Polyurethane elastomers: These materials are known for their high elasticity and resistance to abrasion and impact.
Polyurethane foams: These materials are lightweight and have excellent insulation properties.
Polyurethane resins: These materials are highly resistant to chemicals and have excellent mechanical properties.
· Material Properties and Selection
When selecting a cast urethane material, it is essential to consider the specific properties required for the application. Some of the key properties to consider include:
Mechanical properties: Tensile strength, compressive strength, and impact resistance.
Chemical resistance: Resistance to chemicals, oils, and fuels.
Thermal properties: Temperature range, thermal conductivity, and thermal stability.
Electrical properties: Dielectric strength, electrical conductivity, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
Typical Applications
· Automotive
In the automotive and electronics industries, cast urethane is applied in the prototyping of dashboard parts and the creation of small-quantity, high-variant auto parts; offering cost-effectiveness, high precision, and a variety of materials.
· Aerospace
As for the aerospace industry, it allows the use of cast urethane in the creation of lightweight yet practical models for final tests, precise and versatile for complex high-level designs.
Medical Devices
For medical applications, cast urethane is used in the manufacturing of custom equipment such as braces, and molds for prostheses; provides accurate, individualized solutions with wide applicability of the material.
· Consumer products
For consumer products, cast urethane is the best for creating a small run of interactive gadgets, toys, specialty items, etc., where achieved results are not just affordable but distinctive.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process with the help of which plastic pieces are formed by injecting molten material into a mold. This injection molding process is ideal for use in large production since it is very efficient and accurate and can duplicate delicate designs.
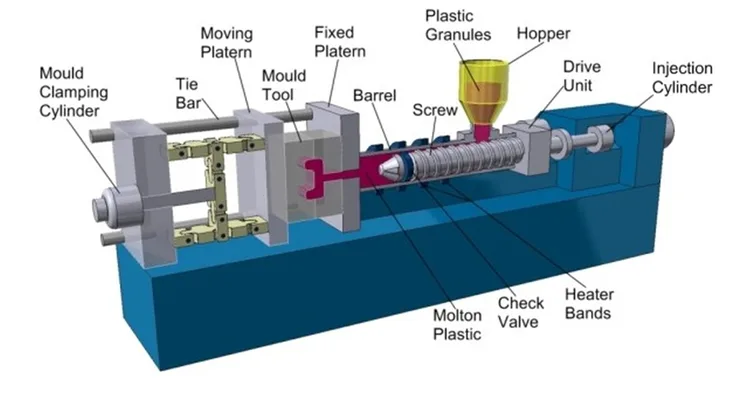
How Injection Molding Works
· Creating molds
Mold making is the process of manufacturing hard-wearing steel or aluminum molds which are accurately engineered according to the part design.
· Injecting molten material
In injection molding, material such as plastic melts. The molten material is then injected into the mold under high injection pressure to make an accurate replica.
· Cooling
The cooling of material to its original shape of the mold strengthens and makes it stable for use or to go through other related processes.
· Ejection
Lastly, when the material has cooled and becomes solid, the part is ejected from the mold. This is followed by a finishing process comprised of trimming, painting, etc.
Typical Applications
· Automotive
In the automotive sector where there is the production of automobiles, there is use of injection molding for large-scale production of automobile parts like bumpers, dashboards, and car interiors, due to high accuracy and high strength.
· Electronics
In the electronics industry, injection molding is used to make long-lasting and highly accurate enclosures for portable communication devices like mobile phones, tablets, and other gadgets.
· Packaging
In packaging, injection molding is employed to devise lidding material, caps, and personalized containers. These have accurate measurements and sturdiness, precisely built to provide stability to seals.
· Consumer goods
In consumer goods, injection molding is used especially for making large numbers of functional articles commonly made of plastic materials. Examples include cooking utensils, storage boxes, household items, etc.
Key Differences between Cast Urethane and Injection Molding
Process Flow Comparison
Cast urethane is made by using versatile silicone molds taken from a master model, where the liquid urethane product is placed by hand. This process is suitable for small-scale production. On the other hand, plastic injection molding entails the use of automated equipment for injecting molten material into permanent steel molds under pressure. This process works well mechanically and while it may not be as accurate as other forms of manufacturing it is more precise and consistent and therefore more economical.
Materials
Cast urethane is accomplished by using mainly polyurethanes which offer a flexible material mainly polyurethane used. This makes it possible to produce properties customized to a particular type of use, particularly for use in prototyping and small-scale production. Injection molding can deal with practically any type of plastic such as ABS, polypropylene, and nylon. These articles contain numerous features especially strength, rigidity, and heat resistance making injection molding very appropriate for the production of a large number of high-quality parts.
Equipment Requirements
Cast urethane only needs a few tools hence it only requires silicone molds, mixing equipment, and a basic structure. This method is for use in low-volume production or for developing prototypes. Injection molding requires hi-tech precision injection units for injecting the material under pressure and metal molds suitable to manufacture components in large quantities. This method provides more opportunities for significant cost savings in high production runs due to automation and less overall material and labor costs.
Production Speed
Cast urethane is especially beneficial for use in areas of prototyping as well as in limited production runs because of small amounts of mold creation time. This makes it suitable if you need to test designs or make prototypes. Injection molding tends to large-scale production of the parts although the initial time to prepare is relatively longer, the steps advanced are highly mechanical, making it easy to make a large number of products cheaply.
Surface Finish and Precision
The cast urethane offers good surface finishes which are appropriate for many uses but could not meet the tight tolerance of high accuracy parts. This process is often used on prototypes or low-volume runs where small variation is acceptable. However, injection molding is most effective in creating complex and accurate parts with intricately tight specifications for the formation of high standards of specialty parts. Due to its accuracy injection molding is excellent for mass production, and it is quite simple to reproduce the same item several times.
Tolerances
Cast urethane has moderate tolerances, it can be used to manufacture components with a low level of dimensional control, which is acceptable for some applications where the difference in size may not seriously interfere with operation. It can be applied in prototypes, low-volume production, and components that are not critical. Injection molding provides a tight tolerance so that it can offer maximum accuracy in parts that require high-level dimensions. Due to its reliability, injection molding is well suited for producing large numbers of intricate yet high-performing parts for which precision is paramount.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cast Urethane
Advantages
· Cost-effective for Low Volumes
Cast urethane offers a relatively low cost, which makes it ideal for the production of small batches, or prototyping models and versions without the outlay of a large-scale mold cost.
· Material Versatility
It provides for quite a large number of material selections when it comes to cast urethane and the variations include hardness levels as well as formulations that suit different applications.
· Faster Turnaround Time
In terms of the prototyping model, cast urethane has shorter cycle times than traditional sand cast urethane. It can facilitate the making of the parts in a short period.
· Ideal for Prototyping
Cast urethane is fast in production and can be easily modified to fit the design changes within the Product Development Process, making it good in Testing and Refining.
Disadvantages
· Limited Scalability
This material also has issues of scalability, and therefore cannot be used in large production runs. However, it is the most suitable method for low-production or small-scale productions.
· Lower Durability of Molds
Metal molds such as die-casting are more durable than silicone molds which are commonly used in cast urethane because if get worn out and can only be used for low-volume production.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding
High Production Efficiency for Mass Production
· High Production Efficiency
It has the benefits of a high production rate with short cycle time unlike other processes, thus making it ideal when it comes to bulk production of the part.
· Precision and Consistency
Injection molding offers precision and consistency. This makes injection molding ideal for manufacturing tight-tolerance parts of bulk production.
· Durability
The size of injection-molded parts is also suitable for very high-volume production. Combined with exceptional mold life, they can run for hundreds of thousands of cycles without fail.
· Material Variety
There is a large number of thermoplastic materials that can be used in injection molding like ABS, polypropylene, nylon, etc., thus the process offers opportunities to produce variable types of parts with different characteristics.
Disadvantages
High Initial Tooling Costs
Injection molding is characterized by high first costs. Consequently, the cost of setting up is higher and not in the best interest of producers of small production of parts.
Longer Lead Times
This has longer lead times because of the time taken to design and produce molds. It may affect production, especially when dealing with special or complex molds.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Cast Urethane and Injection Molding
· Production Volume
Cast urethane is suitable for small quantities of material, especially for sample parts, whereas injection molding is effective for large-scale production and its strength and adaptability to the production line.
· Budget and Cost Constraints
While cast urethane is cheaper in the short run and perfectly suitable for low-volume jobs, injection molding pays off after a certain number of parts are made.
· Design Complexity
Since injection molding is critical in the creation of parts with complex designs, it can copy an intricate design to achieve great detail as well as consistency in its repeat production of mass parts.
Thermoplastic Material Requirements
In deciding between cast urethane and injection molding, it is necessary to compare different material properties for each process. This should produce the specified properties and performance.
· Lead Time and Flexibility
Cast urethane is better for quick turn-around of prototypes and design changes. Moreover, it is better for small runs. On the other hand, injection molding provides a longer setup time but provides better turnaround for high runs needed.
Cast Urethane Design Guidelines
When designing a cast urethane part, it is essential to consider the material properties and the manufacturing process. Here are some design guidelines to consider:
· Design Considerations
Wall thickness: The wall thickness of the part should be uniform to ensure consistent material properties.
Draft angles: Draft angles should be included to facilitate mold release and prevent damage to the part.
Radii and fillets: Radii and fillets should be included to reduce stress concentrations and prevent cracking.
Material selection: The material should be selected based on the specific properties required for the application.
By following these design guidelines and selecting the right material, cast urethane parts can be designed and manufactured to meet the specific requirements of various applications.
Conclusion
Cast urethane and injection molding have distinct advantages depending on the prospective production line. The cast urethane is suitable for low quantity whereas injection molding is ideal for high quantity and accurate applications. At LK Prototype, we can help you analyze your requirements and provide you with the most appropriate method that will give you maximum value added.
 LKprototype
LKprototype







