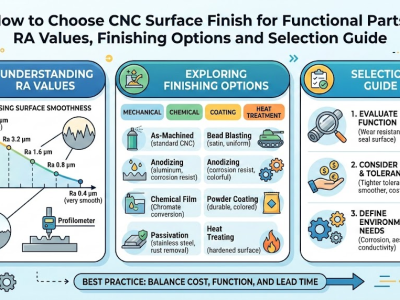
When utilizing CNC machining, you should consider the importance of CNC machining heat treatment for your metal parts. CNC machining heat treatment alters the behavior of metal during the machining process and after the part is completed. Research indicates that CNC machining heat treatment can enhance machining speed and facilitate the removal of more material. Additionally, it strengthens parts and increases their reliability. If you neglect or improperly apply CNC machining heat treatment, your parts may not achieve the correct dimensions, may exhibit more defects, or could even fail. Therefore, it is crucial to select the most effective CNC machining heat treatment process and duration to ensure optimal results in your CNC machining projects.
Key Takeaways
CNC machining heat treatment makes metal parts stronger and harder. This helps them last longer and work better.
Good heat treatment helps parts stay the right size. It also makes fewer mistakes happen in CNC machined parts. This keeps the parts high quality.
Picking the best heat treatment, like annealing or quenching, is very important. It helps your metal parts have the right strength and hardness.
Using stress relief before or after machining can stop warping and cracking. This keeps your parts steady and trustworthy.
Always think about what your metal and project need when you pick heat treatment. This helps your parts work well and saves money.
Why Heat Treatment Matters for CNC Machined Parts (cnc machining heat treatment, post machining heat treatment)
Impact on Mechanical Properties (metal heat treatment for cnc parts, hardness vs machinability)
It is important to know how cnc machining heat treatment changes metal. Heat treatment can make steel parts harder or softer. You can pick what you need for your part. This helps you control how strong or easy to cut your CNC prototype part is. For example, you can make a part harder so it lasts longer. Or you can make it easier to cut. You need to find the right mix of hardness and machinability. This is important for how well the part works and how easy it is to make.
Here is a table that shows how different heat treatment methods affect mechanical properties in metals like steel:
Heat Treatment Method | Effect on Hardness | Effect on Toughness | Effect on Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|
Annealing | Decreases hardness | Increases toughness | Increases ductility |
Normalizing | Improves toughness | Improves strength | N/A |
Hardening | Increases hardness | Decreases toughness | Decreases ductility |
Tempering | Decreases hardness | Increases toughness | Increases ductility |
Each method changes steel in its own way. This helps you pick the best one for your cnc machining project.
Precision, Tolerance, and Error Reduction (dimensional stability after heat treatment)
Precision is very important in cnc machining heat treatment. You want your steel parts to be the right size and shape. Heat treatment helps you control this. Without heat treatment, temperature changes can cause many errors. Up to 75% of mistakes in machined parts come from temperature changes. This is a big problem for aluminum alloys.
A table below shows why heat treatment is important for precision:
Evidence Description | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Heat treatment improves dimensional stability in CNC machined parts | Thermal expansion and temperature variations can lead to significant geometrical errors, especially in aluminum alloys. |
Up to 75% of geometrical errors in machined workpieces are due to temperature effects | Managing heat treatment is critical for enhancing precision and compensating for dimensional errors. |
Predictive compensation strategies can reduce thermally induced dimensional errors | A proposed strategy aims to bring errors within an acceptable tolerance range (± 0.1 mm). |
Using cnc machining heat treatment helps stop warping. It keeps your steel parts the right size. Your CNC prototype machining results will be more reliable. They will meet industry standards. You also save money by making fewer mistakes. You can use cheaper metals instead of expensive ones like titanium.
Key reasons to use heat treatment for cnc machined parts:
You get better precision and quality.
You save money and still meet tough rules.
Tip: Always plan your cnc machining heat treatment process to fit your part’s job and what it needs to do.
Key Benefits of CNC Machining Heat Treatment (cnc machining heat treatment, hardness vs machinability)
Increased Hardness and Strength (post machining heat treatment)
CNC machined parts need to be strong and last long. Heat treatment helps make this happen. When you heat metal and cool it fast, the inside changes. This makes the part harder and stronger. Hardening forms a tough structure inside the metal. This can make parts up to five times harder. The amount depends on the metal and method. Car gears can last much longer after heat treatment. Some last 30% longer. Airplane parts can handle more stress. They can get up to 45% more strength before breaking. These changes turn simple parts into high-performance ones.
Improved Machinability and Tool Life (stress relief cnc machining)
Heat treatment does more than make parts strong. It also makes them easier to work with. Annealing and normalizing make the metal softer. The inside of the metal becomes even. This helps you cut and shape parts with less effort. Your tools last longer too. After heat treatment, tools wear out slower. Tool wear can drop by over 24%. The surface of the part gets smoother. It can improve by more than half. This means you can work faster and save money. You also get better and more exact parts.
Tip: Use heat treatment before or after CNC machining to relieve internal stresses. This step helps you avoid cracks and keeps your parts in top shape.
Enhanced Dimensional Stability and Wear Resistance (dimensional stability after heat treatment)
It is important for CNC parts to keep their shape. Heat treatment removes stress left from making or welding parts. This keeps parts from bending or changing size. Parts also last longer in tough places. Heat treatment makes metals stronger and harder to wear out. You can trust your parts to meet strict rules. Heat treatment gives you stronger, better, and more reliable parts.
Key benefits of heat treatment for CNC machined parts:
Relieves internal stresses
Improves wear resistance
Enhances fatigue strength by up to 45%
Provides dimensional stability
If you want your CNC parts to work their best, use heat treatment. You will see stronger, easier-to-make, and better parts.
Main Heat Treatment Processes for CNC Machined Metals (annealing cnc machined parts, tempering and quenching cnc)
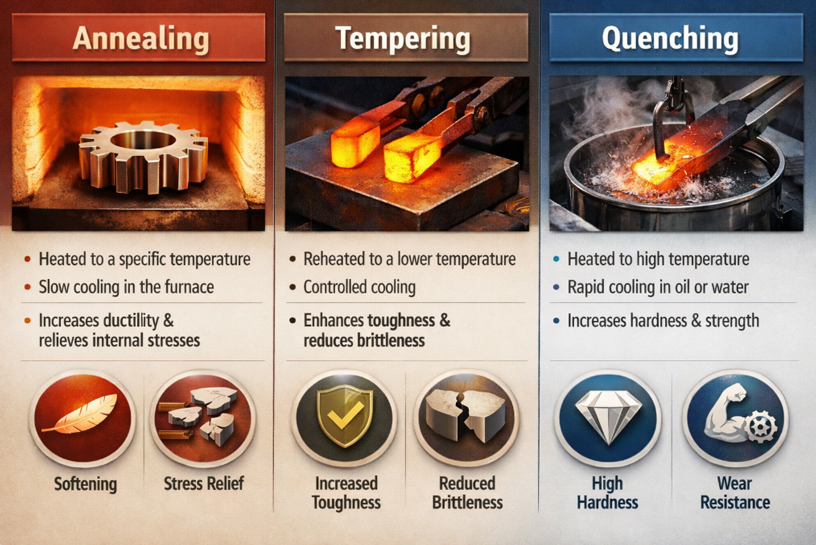
It is important to know the main heat treatment steps for CNC machined metals. These methods change how steel and other metals act. You can make metals easier to cut, harder, or less stressed. Each process helps you get the right mix for your CNC part.
Description | Typical Applications | |
|---|---|---|
Annealing | Heating metals to high temperatures and cooling slowly to improve machinability. | Steel and aluminum alloys before machining. |
Quenching | Rapid cooling of heated metal to increase hardness but may increase brittleness. | Gears and cutting tools requiring wear resistance. |
Tempering | Reheating quenched metal to reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness. | Tool steels and high-carbon steels in machining. |
Case Hardening (Carburizing) | Infusing the surface with carbon for a hard exterior while keeping the core ductile. | CNC turning services and camshafts. |
Precipitation Hardening | Heating and aging to form precipitates that enhance strength. | Aluminum alloys and titanium in aerospace. |
Stress Relieving | Heating to reduce internal stresses without changing microstructure. | Large components like machine frames. |
Annealing: Stress Relief and Softening (stress relief cnc machining, annealing cnc machined parts)
Annealing is a common heat treatment. You heat metal until it is very hot. Then you let it cool down slowly. This makes the metal softer and easier to cut. Annealing also helps remove stress from the metal. It stops cracks from forming.
Description | |
|---|---|
Improved Ductility | Enhances the ability of metal to deform without fracturing, essential for forming and welding. |
Reduced Hardness | Lowers hardness to facilitate machining and reduce cracking risks, improving tool life. |
Relief of Internal Stresses | Neutralizes internal stresses to prevent warping and increase reliability during use. |
Annealing gives you metal that bends more before breaking. It makes the metal less hard, so it is easier to work with. It also takes away stress inside the metal. This helps your CNC parts last longer and work better.
Tempering and Quenching: Hardening Metals (tempering and quenching cnc)
Tempering and quenching are ways to make metal harder. First, you heat the metal and cool it very fast. This is called quenching. It makes the metal very hard but also brittle. Next, you heat the metal again at a lower temperature. This is tempering. Tempering makes the metal less brittle and more tough. These steps help you get strong and stable metal parts.
Nitriding and Carburizing: Surface Hardening Techniques (metal heat treatment for cnc parts)
Surface hardening is important for CNC metal parts. Nitriding and carburizing are two ways to make the outside of metal harder. Nitriding gives the metal a very hard surface. It also helps the part last longer and fight rust. You do not need to cool the metal fast, so it does not crack or bend. This is good for parts that must keep their shape.
Advantages of nitriding:
Very hard surface
Better fatigue strength
Fights rust
No fast cooling needed
Keeps its shape
Lasts longer
Limitations of nitriding:
Takes a long time
Only works well on some steels
Needs costly machines
Hard to use on sharp corners
Not good for soft, low-carbon steels
Can hurt the environment
Carburizing is another way to harden the outside of steel. You add carbon to the surface. The outside gets hard, but the inside stays soft and bendy. This is good for parts like camshafts. You get strong and tough CNC parts.
Tip: Pick the best heat treatment for your CNC project. This will help your parts work better and last longer.
Selecting the Right Heat Treatment for CNC Machined Parts (post machining heat treatment, metal heat treatment for cnc parts)
Material and Application Considerations (dimensional stability after heat treatment)
Think about what metal you have and how you will use your CNC part. Steel and aluminum need different heat treatments. Some alloys need special steps to get strong and hard. The right heat treatment helps you keep the part the right size and shape. This is important if your part needs to fit very closely.
Good heat treatment helps your part stay the right size.
It also helps your part meet the rules it needs to follow.
Heat treatment takes away stress from making the part.
This means your part is less likely to bend or twist later.
Some steels can bend more than others when heated.
You can use even shapes and walls to help your part stay flat.
Try not to use sharp corners or big changes in thickness.
These can make your part bend or twist.
Using oil instead of water to cool can help stop bending.
You should also pick heat treatment based on how the part will be used. Gears need to be hard so they do not wear out fast. Airplane parts need to stay strong when used a lot. If you want to learn more, check our CNC part machining service page.
Pre-Machining vs Post-Machining Heat Treatment (post machining heat treatment)
You need to choose if you heat treat your metal before or after you cut it. Each way has good and bad points. When you do it can change how well your CNC part works.
When to Heat Treat Before Machining
If you heat treat before cutting, the metal gets softer. This makes it easier to cut and shape. Your tools will last longer. But, if you make a mistake, it is harder to fix after hardening. Sometimes, heating before cutting can make the part bend.
When to Heat Treat After Machining
You can also heat treat after you finish cutting. This lets you fix problems based on how the part works. Heating after cutting can fix bending or twisting from hardening. But, it takes more time and work because the metal is harder. There is also a chance the metal gets too hot when grinding.
Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
Easier to cut, tools last longer, better control of part strength | Mistakes are harder to fix, can bend or twist | |
Post-Machining Heat Treatment | Can fix bending, lets you make small changes | Takes more time, metal can get too hot |
Always pick the heat treatment that matches your metal and how you will use the part. This helps you get the best CNC parts.
CNC Machining and Heat Treatment Coordination (cnc machining heat treatment)

Process Integration Strategies (post machining heat treatment)
You need to think ahead about how you mix heat treatment with CNC machining. This helps you get the best parts. First, pick the right metal for your part. Some metals, like steel, work better with certain heat treatments. Check how easy it is to machine the metal before you start. This can help you avoid problems later.
When you design your CNC prototype part, remember that heat treatment can change the size of the metal. For example, steel can get bigger or smaller by 0.1% to 0.3% when you harden it. You should cut your part close to its final shape, but leave a little extra metal. This extra is called a stock allowance. Most of the time, you leave about 0.010" to 0.015" for most metals. After you harden the part, you can finish cutting it to the right size.
Tip: Talk to your engineering team early. They can help you find design features that might cause problems during heat treatment, like sharp corners or thin walls.
Here are some best ways to mix these steps:
Pick metals that are easy to cut and stay strong after heat treatment.
Cut your part almost to the final size, but leave a little extra.
Finish cutting after hardening to fix any changes in shape.
Only cut fully hardened metals if you need very exact sizes.
Plan for more setup time and tool costs when working with hard metals.
If you use two steps, you first cut your part roughly, then heat treat it, and finally finish the important areas. This way helps you save money, make tools last longer, and get more accurate parts.
Preventing Warping, Distortion, and Cracking (dimensional stability after heat treatment)
You want your CNC parts to stay flat and strong after heat treatment. Warping, distortion, and cracking can ruin your part. You can stop these problems by following some simple rules.
Do not use sharp inside corners. Use a rounded corner to lower stress.
Make changes in thickness smooth and slow. Sudden changes can bend your part.
Try to keep your part even on both sides. Balanced shapes help the metal cool evenly.
Do heat treatment after rough cutting but before the last cuts. This lets you fix small bends before you finish the part.
You should also pick metals that may be harder to cut but work better after heat treatment. Some steel alloys do not warp as much as others. Always think about how heat treatment will change your metal.
If you follow these steps, your CNC prototype machining will meet high standards. Your parts will stay strong, the right size, and work well. For more details, see our CNC part machining service page.
Quality Assurance and Inspection in Heat Treatment (metal heat treatment for cnc parts)
Certifications and Industry Standards (hardness vs machinability)
You must follow rules when you heat treat metals. These rules help keep your CNC parts safe and good quality. Many jobs need special certificates to check steel and other metals.
Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Mill Certificates tell what is in the metal and how strong it is. You need these for big projects.
Certificates of Conformance (CoC) or Certificates of Conformity show your part meets all rules. These certificates help you prove your parts are safe and strong.
Some industries use standards like AS9100 for airplanes and ISO 13485 for medical tools. These standards help you track each step in making your part.
Always keep these certificates for your records. They help you show your heat treatment works and your metals are ready to use.
Inspection and Testing Methods (stress relief cnc machining)
You must check metals after heat treatment to make sure they are strong and safe. Testing helps you find problems before using the parts. There are different ways to test steel and other metals.
Hardness testing checks if your metals are hard enough. You do this after heat treatment to see if it worked.
Stress relief cnc machining lowers stress in metals. This step helps stop cracks and bending.
Visual checks let you see cracks or changes in shape.
Special machines measure the size and shape of your CNC part. This helps you make sure your part fits right.
Always test metals before using them in big jobs. Good inspection keeps your CNC machining safe and reliable. For more details, visit our CNC part machining service.
Common Challenges and Solutions in CNC Machining Heat Treatment (cnc machining heat treatment)
When you use metals in CNC machining, you can face many problems with heat treatment. You want your CNC prototype part to be high quality. You need to watch out for things like bending, cracks, and hardness problems. These issues can change how your parts work and how easy they are to make.
Managing Material Deformation and Warping (dimensional stability after heat treatment)
Your metal can bend or twist after heat treatment. This happens if the metal heats or cools unevenly. Warping can mess up your CNC prototype machining project. Here are some ways to help stop bending and warping:
Make your design with extra space for final cuts after heat treatment.
Use stress relief steps to help stop bending.
Cool your metal slowly and in a careful way.
Use advanced CNC technology to fix changes as they happen.
Pick metals that do not bend easily during heat treatment.
Tip: Always plan to use stress relief and slow cooling. This helps your steel parts stay flat and strong.
Controlling Tolerances and Accuracy (precision cnc machining, hardness vs machinability)
You want your parts to fit together just right. Keeping tight tolerances and good accuracy is important. You can cut your metal before or after heat treatment. If you cut before, you get better accuracy. If you cut after, you can remove stress and keep your part stable. This step also helps you get the right hardness and machinability for your metals.
Cut before heat treatment for best accuracy.
Use heat treatment after cutting to make your metal more stable and even.
Handling High-Temperature or Hard Metals (metal heat treatment for cnc parts)
Some metals, like steel, need special steps during heat treatment. You must use the right way to get the best machinability and strength. Here are some common ways:
Description | |
|---|---|
Nitriding | Adds nitrogen to the surface for a hard, wear-resistant layer. |
Precipitation Hardening | Holds the material at high temperature to boost strength without fast cooling. |
Quenching | Cools the metal quickly to lock in a hard structure. |
Spheroidizing | Softens steel by making carbides round, which improves machinability. |
Cold Working | Changes the material at room temperature to increase strength and machinability. |
Note: Always match your heat treatment to your metal and part needs. This helps you avoid problems and get the best results.
Conclusion: Best Practices for CNC Machining Heat Treatment (cnc machining heat treatment, post machining heat treatment)
Summary of Key Benefits and Considerations
When you use heat treatment for metals in CNC machining, you get many good things. Heat treatment makes steel parts harder and stronger. Your parts can last longer and do not wear out fast. This process helps you keep your CNC prototype part the right size and shape. You make fewer mistakes and your parts stay steady. You can use cheaper metals and still follow strict rules. If you plan the steps well, you can stop warping and cracking. You get parts you can trust and you save money.
Benefit | How It Helps You |
|---|---|
Hardness and Strength | Parts last longer and resist damage |
Keeps parts the right size and shape | |
Wear Resistance | Reduces surface damage |
Cost Savings | Allows use of cheaper metals |
Meets industry standards |
Tip: Always pick the heat treatment that fits your metal and how you will use it. This helps your CNC prototype machining meet tough rules.
Tips to Optimize Process for Accuracy, Strength, and Longevity
You can do a few things to get the best results from heat treatment for metals:
Use stress relief heat treatment before the last cuts. This step lowers stress inside steel and other metals. You heat the part, keep it hot for a while, then cool it down slowly.
Do heat treatment between cutting steps. First, cut your CNC prototype part roughly. Then use stress relief. Last, finish cutting to the final size. This way works well for airplane and very exact parts.
Watch the temperature during heat treatment. Do not let metals get too hot. Too much heat can make steel weak or change how it acts.
Make your part with even shapes and smooth changes in thickness. These things help stop bending and twisting.
Check and test your parts after heat treatment. Look at hardness and shape to make sure they are good.
Note: You can find more about CNC prototype machining and heat treatment on our CNC part machining service page.
If you follow these tips, your parts will be more accurate, strong, and last longer. Your metals will stay tough and work well. You will meet industry rules and give people high-quality CNC parts.
FAQ
Do all CNC machined parts need heat treatment?
You do not need heat treatment for every CNC part. Some metals, like aluminum, work well without it. You may skip this step for parts that do not need extra strength or hardness. If you want your CNC prototype part to last longer or handle more stress, you should use heat treatment. Always check what your part needs before you decide.
Which metals require post-machining heat treatment?
You should use post-machining primary heat treatments for many metals. Steel often needs this step to get the right hardness and strength. Titanium and some stainless steels also need it. If you use tool steels or parts that face a lot of wear, you should heat treat them after machining. This helps your CNC prototype machining meet high standards.
How does heat treatment affect part hardness and machinability?
Heat treatment can make metals harder or softer. If you make steel very hard, it will last longer but may be harder to cut. Softer metals are easier to machine but may wear out faster. You need to find the right balance for your part. This step helps you get the best mix of strength and machinability.
Can heat treatment cause distortion or warping?
Yes, heat treatment can cause metals to bend or twist. This happens when the metal heats or cools unevenly. You can lower this risk by using slow and even heating and cooling. Try to design your CNC parts with even shapes and smooth changes in thickness. This helps keep your parts flat and strong.
What are best practices for stress relief in CNC machining?
You should use stress relief steps to keep your metals stable. Heat your part to a set temperature, hold it there, then cool it slowly. This lowers stress inside the metal. You can do this before or after you cut the part. Always check your part for cracks or changes in shape after stress relief.
Tip: Plan your heat treatment steps early. This helps you avoid problems and get better CNC parts.
You need to choose the right heat treatment and timing for your CNC machined metals. This step helps your steel parts stay strong, last longer, and keep the right shape. You can improve your CNC prototype part by following these best practices:
Use high-pressure coolant systems to remove heat from metals during machining.
Try through-spindle coolant for deep cavities to lower tool temperature.
Consider cryogenic cooling for extreme heat to stop distortion.
Work with your heat treatment supplier to keep steel uniform and avoid hard spots.
If you need to machine complex CNC prototype parts, please consult an expert for a CNC machining quote. Learn more about CNC prototype machining here.
 LKprototype
LKprototype