
An automated manufacturing process uses machines and technology to do production work. Control systems help finish tasks with little help from people. This method tries to make work faster, more correct, and more productive. It also helps cut down on hard work and mistakes. In the past ten years, factories have used more robots and AI. This has made production reach new highs. The table below shows how automation helps make work better and more correct in factories:
Benefit Area | Statistic / Improvement |
|---|---|
Conveyor systems | Productivity increase by 60% |
RFID technology | Inventory accuracy improved to 99% |
Human-robot teams | 85% more productive than only humans or only robots |
Key Takeaways
Automation makes things faster, lowers mistakes, and saves money by letting machines and technology handle boring jobs.
There are many kinds of automation like fixed, programmable, flexible, and integrated. Each type fits different factory needs.
Good automation uses clear steps. First, check how things work now. Next, set goals. Then, pick the right technology. After that, make a plan. Test it, start using it, and keep checking how it works.
Important tools like robots, CNC machines, sensors, and AI help factories get better quality, work faster, and stay safe.
Problems like data troubles and worker training can happen. But smart planning and new technology help companies fix these problems and get bigger.
Automated Manufacturing Process
Definition
An automated manufacturing process uses machines and robots to do jobs people used to do by hand. Technology helps control and watch each step of making things. Sensors and software help the machines work together. This keeps everything running well. In many factories, automation moves materials, puts products together, and checks if they are made right.
Automation in manufacturing covers many jobs. Robots weld car frames. CNC machines cut metal parts. Automated inspection systems look for mistakes. These systems follow set instructions. This helps them do the same job over and over with high accuracy. Companies can make more products in less time and with fewer errors.
Note: Automation does not take away all human jobs. People still design systems, fix problems, and watch over the work. Automation helps workers by doing boring or risky jobs.
Core Purpose
The main goal of automation is to make production faster, more reliable, and cheaper. Companies want to make more products, improve quality, and waste less. Automation helps by doing tasks with care and the same way each time.
Many industries have improved a lot with automation. Xiaomi’s “Dark Factory” in China uses robots with AI to build smartphones very fast. No people work on the shop floor. BMW worked with Figure Robotics to use humanoid robots. These robots made work go 400% faster. They place 1,000 auto parts every day with perfect accuracy. In biotech, Cellares made the Cell Shuttle. This robot system makes cell therapy faster and cheaper.
Sustainability is another reason for automation. Samsung’s automated PCB line used 40% less energy and made 60% less scrap. Airbus used automation to cut energy use by 30% and carbon fiber waste by 50%. BASF and Dow Chemical used less energy and made less waste too. These examples show that automation helps the planet and saves money.
Automation in manufacturing brings clear results:
Automation makes products better by being more exact and making fewer mistakes.
Machining automation helps make more products, lowers labor costs, and stops delays.
Automated inspection systems find mistakes early so they can be fixed fast.
Automation lowers human error by doing the same job again and again.
Companies save money and time, which helps them compete.
Metric / Improvement Area | Numerical Data / Percentage Improvement | Description / Impact Summary |
|---|---|---|
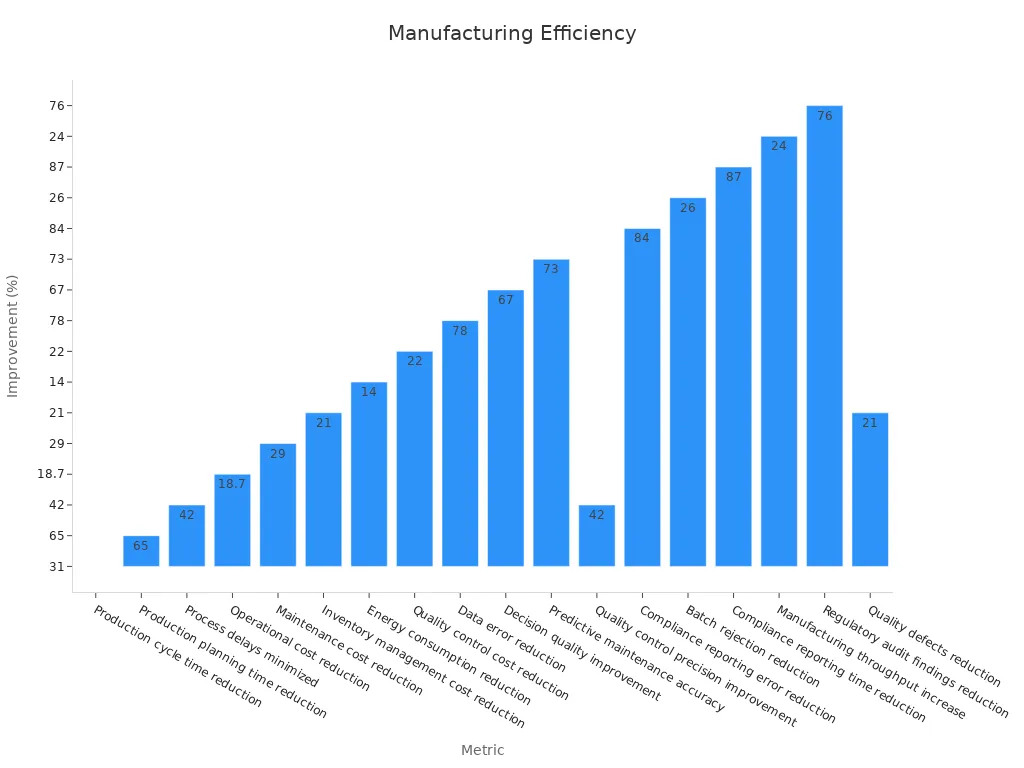
Production cycle time reduction | Up to 31% | A car maker cut cycle time from 24 to 16.5 days in 9 months after using data fabric. |
Production planning time reduction | 65% | Real-time data helped plan faster. |
Process delays minimized | 42% | Automated data flows cut delays. |
Bottleneck identification speed | 3.5x faster | Data analysis found problems faster. |
Operational cost reduction | Average 18.7% | Savings came from maintenance, inventory, energy, and quality control. |
Maintenance cost reduction | 29% | Predictive maintenance saved money and made machines last longer. |
Inventory management cost reduction | 21% | Better stock levels lowered inventory costs. |
Energy consumption reduction | 14% | Data-driven changes used less energy. |
Quality control cost reduction | 22% | Finding defects early saved money. |
Data error reduction | 78% | Data fabric made data much more accurate. |
Decision quality improvement | 67% | Better data helped make better choices. |
Predictive maintenance accuracy | 73% | Maintenance predictions got more accurate. |
Quality control precision improvement | 42% | Quality control became more exact. |
Compliance reporting error reduction | 84% | Reporting mistakes dropped a lot. |
Unplanned downtime reduction | Average 32%, up to 45% | Predictive maintenance and automation cut downtime; a chemical plant saved $4.2 million in capacity. |
ROI over 3 years | 273% average | Data fabric projects did better than old solutions (157% ROI). |
Batch rejection reduction | 26% | A drug maker found new quality checks and had fewer rejected batches. |
Compliance reporting time reduction | 87% | A drug company saved a lot of time on compliance. |
Batch release time reduction | From 14 to 3 days | Faster batch release helped make more products. |
Manufacturing throughput increase | 24% | More products were made without new machines. |
Regulatory audit findings reduction | 76% | Compliance got much better. |
Quality defects reduction | 21% | An auto supplier had fewer defects by linking quality and production data. |
Inventory cost savings | $12.4 million annually | An auto supplier saved money by managing inventory better. |
Unplanned downtime decrease | 32% | An auto supplier had much less downtime. |
ROI over 3 years (automotive) | 312% | Data fabric gave a high return on investment. |
Automation in manufacturing makes work faster, cuts mistakes, and saves money. Companies that use automation have a big advantage in today’s market.
Types of Industrial Automation
Fixed Automation
Fixed automation uses machines that do the same job again and again. Companies use this for making lots of the same thing. Conveyor belts and bottle filling machines are examples. These machines work fast and are very exact. Factories use fixed automation for jobs like packaging, welding, and painting. This type helps work go faster and makes fewer mistakes in simple jobs.
Fixed automation helps save money and time for jobs that stay the same.
Programmable Automation
Programmable automation lets machines change jobs by updating their instructions. This type is good for making different things in groups. Car factories use programmable automation to switch between car models. Workers can give machines new tasks, so it is flexible. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) help run these systems.
Programmable automation helps industries that need to change what they make.
It is good for batch jobs, like mixing chemicals or putting together electronics.
Flexible Automation
Flexible automation uses computers to help machines switch jobs fast. This type is best for companies that make many things in small amounts. CNC machines are a good example. They can cut, drill, or shape parts using computer commands. Flexible automation helps factories change quickly for customers.
Flexible automation helps make special products and saves time between jobs.
It is used for things like robotic assembly, grinding, and polishing.
Integrated Automation
Integrated automation links all machines and systems in a factory. Sensors, software, and data work together to control everything. Smart factories use integrated automation to watch materials, save energy, and keep quality high. This type of automation means people do less work and companies make better choices.
Integrated automation checks water supply and quality.
It controls things like temperature and energy use.
It connects production and inventory data for better planning.
Companies like Amazon and Rolls-Royce use integrated automation to save money and work better. Smart factories show how automation can change how things are made.
Manufacturing Process Automation Steps

Manufacturing process automation has a set order of steps. Each step builds on the one before it. This helps the system work better. Companies use these steps to move from manual work to automated processes. This change helps them work faster, make better products, and save money.
Assessment
Assessment is the first step in automation. Teams look at how things are made now. They find slow steps, bottlenecks, and jobs that repeat a lot. This step helps leaders see where automation can help most.
Assessment helps companies focus on the right problems. It keeps them from wasting time and money.
A good assessment can show hidden problems. For example, a machine might slow things down. Workers might spend too much time entering data. Knowing these facts helps leaders make better plans.
Key outcomes of assessment:
Finds slow spots and bottlenecks in production.
Points out jobs that are good for automation technology.
Builds a strong base for the next steps.
Goal Setting
Goal setting gives the project a clear path. Teams set goals that are easy to measure. They use the SMART method: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Setting goals helps everyone know what to aim for. For example, a company might want to cut lead times by 20%. They might want to make better products or spend less money. These goals guide every step of the process.
Clear goals make it easy to see progress and show the value of manufacturing automation.
Companies with SMART goals often do better. They can see if they are working faster, making fewer mistakes, or saving money. This focus keeps the project moving forward.
Technology Selection
Technology selection shapes what the project will look like. Teams pick the best automation technology for their needs. They look for tools that can grow with the company and work with other systems.
Robots, AI, IoT devices, and production monitoring software are common choices. The right tools help companies reach their goals faster. Good choices also make it easier to add new features later.
Picking automation technology that can grow and connect with other tools helps the project last.
A strong selection process helps avoid costly mistakes. It helps companies pick tools that fit their needs and support automated production monitoring.
Planning
Planning puts all the pieces together. Teams make a plan for the project. They set dates, give out jobs, and get ready for problems.
A good plan covers every part of the process. It includes training for workers and steps for adding new machines. It also shows how to measure if things are working.
Planning Checklist | Purpose |
|---|---|
Timeline for each phase | Keeps the project on schedule |
Role assignments | Makes sure everyone knows their job |
Risk management plan | Gets ready for possible problems |
Training schedule | Prepares workers for new systems |
Success metrics | Tracks progress and results |
Careful planning helps things go smoothly and stops surprises.
Real projects show that good planning helps teams avoid delays and confusion. It also makes it easier to change plans if needed.
Testing
Testing checks if the new automated processes work. Teams run small tests first. They watch numbers like cycle time, error rates, and system reliability.
Testing helps teams find and fix problems early. It also shows if the automation will help the company reach its goals.
Testing uses methods like A/B testing or controlled experiments.
Teams check how the new system changes production and quality.
Feedback from workers and managers helps make the system better.
Pilot testing and checking results give proof that automation works.
Many companies test in stages to lower risk. They start small and grow as the system proves itself.
Rollout
Rollout means using the new automation system everywhere. Teams may use slow rollout methods, like canary or blue-green deployments. These ways lower risk by starting with a small part of the factory.
During rollout, teams watch for problems and listen to feedback. They use feature flags or version control to manage changes. If something goes wrong, they can go back to the old system.
Slow rollout helps stop big problems.
Teams use real-time monitoring to catch issues early.
Rollback plans keep production safe.
Careful rollout helps people accept the new system and keeps things running well.
Case studies show that careful rollout leads to happier workers and fewer problems.
Monitoring
Monitoring keeps the automation system working well. Teams use automated production monitoring and production monitoring software to watch key numbers. They look for errors, slowdowns, or changes in quality.
Continuous monitoring helps teams spot problems early. They can fix things before they get worse. Monitoring also shows if the automation is working as planned.
Automated processes need regular checks to stay reliable.
Teams use alerts and dashboards to watch system health.
Feedback from users helps make the system better.
Continuous monitoring and care help keep things running smoothly and make the system better over time.
Companies that monitor their systems have fewer mistakes and more steady production. They can also find new ways to improve manufacturing automation.
Tools for Industrial Automation
Robots
Robots are very important in automation. They do jobs like welding and painting. Robots also move heavy parts in factories. Many factories use robots to work faster and better. One company used FANUC robots and made 30% more products. Robots made products stronger and needed fewer repairs. These machines work with automated assembly machines. This keeps the production line moving all the time.
Technology Component | Performance Metric / Benchmark | Efficiency and Accuracy Gains |
|---|---|---|
Robotics | Throughput increase ~30% | Higher production rates, consistent quality |
Robots help companies make more things with fewer mistakes.
PLCs
PLCs control machines and processes right away. They help factories run smoothly by making fast choices. PLCs make machines work better and change jobs quickly. Real-time programming and control help watch machines and stop errors.
CNC Machines
CNC machines cut, drill, and shape materials very exactly. They use computer commands to follow instructions. These machines can be accurate to ±0.01 mm. This helps lower mistakes and makes better products. AI in CNC machines can make jobs 25% faster and waste 30% less material. Factories use CNC machines to make parts fast and with little waste.
Aspect | Metric / Improvement | Impact on Efficiency and Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
Cycle Time Reduction | 15-25% | Faster machining cycles |
Material Waste Reduction | 30% | Cost savings, sustainability |
Downtime Reduction | 85% | Increased machine availability |
AGVs
Automated guided vehicles, or AGVs, move things around factories. They follow paths and use sensors to avoid bumping into things. In car factories, many AGVs keep lines full of parts. AGVs help cut down on hard work and make factories safer. They work with other automation tools to keep things on time.
MES Software
Manufacturing execution systems, or MES, track and manage production as it happens. MES software links machines, workers, and data together. Big companies use MES to work better and make higher quality products. MES also connects with production monitoring software. This helps leaders see how the factory is doing.
MES software helps keep all data in one place.
It helps make production better and checks quality.
Sensors & IoT
Sensors and the Internet of Things, or IoT, collect data from machines and the factory. These tools check things like temperature and pressure. IoT sensors send data to AI for fixing machines before they break. This helps stop surprise breakdowns and saves money on repairs. Sensors also help automated assembly machines work more exactly.
AI & Machine Learning
AI and machine learning look at data from sensors and machines. These tools help factories find problems early and plan repairs. AI helps with scheduling, finding odd things, and making choices. Predictive maintenance with AI and IoT can be over 90% right. This can cut downtime by 85%. Automation becomes more reliable and saves money.
Automation tools like robots, PLCs, CNC machines, AGVs, MES software, sensors, and AI work together to make smart factories. These tools help companies make better products, faster, and with fewer mistakes.
Increase Speed and Efficiency
Productivity Gains
Automation helps companies work faster and make more things. Machines and robots do the same jobs over and over. This lets workers do more important tasks. When people and machines work together, they can get 30% more done. Many companies use automation tools to run many jobs at once. This makes them more flexible and helps them make more products.
Automation means workers do less manual work and more planning.
Teams use real-time monitoring and AI to find problems early and keep things moving.
Almost 60% of companies use automation because it helps them do more work.
A metal company used automated machine tools. Workers watched many machines at the same time. This cut down on waiting and made the company more flexible. The company became more productive and efficient.
Quality Improvement
Automated systems help factories make better products with fewer mistakes. Machines follow the same instructions every time. This means each product meets the same standards. Automation also helps catch mistakes early. For example, a heat treatment company used digital records and tablets to enter data right away. This step lowered defects and recording errors. It made quality more steady.
Automation lowers mistakes and defects, so workplaces are safer and products are better.
Digital control and real-time data help keep quality steady and stop problems before they get big.
Workers trust automation, with 88% saying they believe it works well.
AI in packaging can cut material waste by up to 40%. This saves resources and helps products meet strict quality rules.
Cost Reduction
Companies save money when they use automation in manufacturing. Automation lowers labor costs and cuts down on accidents. Robotic process automation software costs less than hiring more workers. AI-driven predictive maintenance can lower costs by 25%. These savings come from fewer breakdowns and less wasted material.
Automation saves over 500 hours each year in finance departments, showing clear time and money savings.
Cheaper robotic automation helps companies get more value for their money.
Real-time monitoring helps companies make production better and avoid expensive mistakes.
A payment company finished its budget 66% faster after using automation. The time went from six weeks to just ten days. This shows how automation can make work faster and cheaper.
Real-World Examples

Automotive
Car makers use automation a lot. One big car company put robots in for welding and painting. These robots made cars faster and made the workplace safer. Workers said their bodies hurt less and they got hurt less often. A survey showed 53% of workers liked having robots around. Most people liked that robots did boring jobs. The company also used automated production monitoring to watch every step. This helped bosses find problems early and keep things on time. Workers got new jobs instead of losing them.
Electronics
Electronics factories use automation for tiny, fragile parts. A big electronics company added CNC machines and other automated systems. About 47% of workers liked the automated systems. About 45% liked the CNC machines. Workers saw fewer mistakes and better products. The company made things 15% faster during test runs. Watching the process all the time made production 20% faster. Digital tools made it easier to collect data and report right away.
Food & Beverage
Food and drink companies use automation for packing and checking quality. One food plant changed how workstations were set up. This made work go faster and cut down on extra walking. Automated systems made the plant safer and lowered injury risks. The plant had fewer injury reports after using automation. Workers liked the safer place and not having to do boring jobs.
SMEs
Small and medium businesses also use automation. One small factory used digital tools to watch production. This helped them see how much they made and find slow spots. The company had problems like workers not wanting change and trouble collecting data. Leaders and training helped fix these problems. Talking clearly and having meetings helped keep things better.
Case studies show automation helps companies work faster, safer, and with better quality. Companies do face problems, but good leaders and digital tools help them win.
Challenges of Automation
Implementation Barriers
Many factories have problems when they start using automation. These problems can slow things down and make it hard to get good results. Some main problems are:
Data comes from many places and does not always match. This makes it hard to use the information the right way.
Machines and systems often do not work well together. It takes time and skill to connect them.
Factories need to use data fast. It is hard to make quick choices without the right tools.
Workers need new skills to use and fix automated systems. Learning these skills takes time and training.
Cybersecurity risks get bigger as more machines go online.
Changing how people work and think is not easy. Some workers worry about losing jobs or learning new things.
Good data is needed for the best results. Collecting and cleaning data is a big job.
Studies show companies spend over $1 trillion each year to update factories. They must spend money on new things but also keep work going. Technology changes fast, so factories must keep learning and trying new ideas.
Solutions
Factories can solve these problems by using smart plans and new technology. Some good ways to help are:
Using a step-by-step plan for making choices with data. This helps leaders make better decisions.
Adding IoT devices to get real-time data from machines. This shows what is happening in the factory right now.
Connecting machines with digital systems using cyber-physical systems. This makes it easier to control and watch everything.
Using big data analytics to find patterns and make things work better.
Training workers so they can use and manage automation tools. This helps everyone feel ready for change.
Focusing on getting good data and using cloud computing to store and use it.
Building a culture that likes new ideas and teamwork between people and machines.
A case study with CNC milling machines showed these ideas can help factories work better and more exactly. Factories that close the “automation gap” can save up to 25% in costs. They also make better products and use their workers’ time well.
Automation is changing how factories do their work. It lets companies use machines and smart tools to make things faster. These tools also help make things more accurate. Teams plan each step and test how things work. They watch every part of the process. Robots, sensors, and software help workers do better. Real examples show that automation makes jobs safer. It also helps make better products. Companies can make more things with fewer mistakes. Many leaders want to use automation in the future. Factories will keep finding new ways to get better and stay ahead.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of automated manufacturing?
Automated manufacturing lets companies make things faster. It also helps them make fewer mistakes. Machines do the same job each time. This means products are better and cost less to make.
Do workers lose jobs because of automation?
Many workers get new jobs. They learn how to run and fix machines. Automation can create jobs in programming, fixing, and watching over systems.
How do companies choose the right automation tools?
Companies think about what they need first. They look for jobs that happen again and again. They compare robots, sensors, and software. The best tools match the company’s goals and money plan.
Is automation only for large factories?
No, small and medium businesses use automation too. They start with easy tools like sensors or software. As they grow, they add more advanced machines.
 LKprototype
LKprototype







