Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them into molds to create parts and products, making it a versatile method for manufacturing plastic parts. But what is plastic injection molding? It is widely used because it allows for high-volume production with consistent quality and minimal waste. This method is essential in various industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in the process, the benefits of using plastic injection molding, and its common applications.
Key Takeaways
Plastic injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that efficiently produces high-quality plastic components through melting and injection of various plastic materials into molds.
The process consists of six essential stages, including clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, mold opening, and ejection, ensuring precise and consistent results.
Recent technological advancements, such as CNC machining and smart machinery, enhance mold accuracy and allow for the production of intricate parts with diverse material properties.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?

Plastic injection molding is an advanced production method that shapes plastic into intricate forms by melting it and forcing it into metal cavities. The process begins with plastic resin, which is heated until it becomes molten plastic. This complex technique takes simple raw plastic pellets and crafts them into high-quality, detailed parts utilized throughout many sectors. The procedure includes a series of steps: the heating up of the plastic until molten, its subsequent injection under pressure into a pre-shaped mold, followed by cooling to set the material firmly in place. Finished products are noted for their precise replication of intended designs alongside their robustness.
For mass manufacturing needs across various industries, plastic injection molding stands out as a premier choice due to its cost efficiency and proficiency in outputting substantial numbers of uniform quality parts with scant waste generation. It is this level of productivity that renders it exceptionally suitable for large-scale mass production efforts, thereby significantly diminishing total expenses associated with manufacture.
Demonstrating remarkable adaptability through its use in numerous applications highlights the importance of injection molding within modern manufacturing landscapes—ranging from automotive fixtures and domestic gadgets right through to medical apparatuses—the process proves vital for crafting myriad items needing convoluted design parameters while also delivering heightened precision coupled with staunch dependability essential for certain market segments.
Definition and Overview
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic components by injecting molten plastic into a metal mold. This process begins with raw plastic pellets, which are heated until they become molten plastic. The molten plastic is then injected into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This method is highly valued in various industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods, due to its ability to produce high-quality parts with complex geometries and precise tolerances. The efficiency and versatility of plastic injection molding make it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing, enabling the mass production of intricate and durable plastic components.
Key Components of the Injection Molding Machine
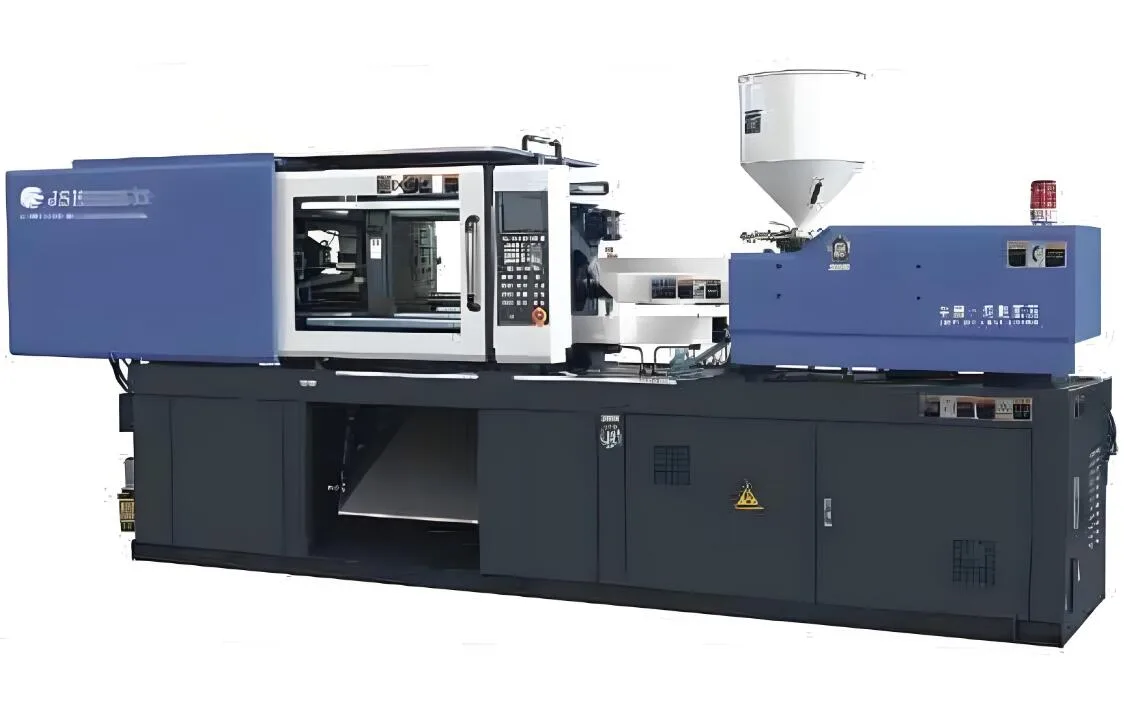

The plastic injection molding machine is an intricate piece of engineering, comprised of several essential components that collaborate seamlessly to create exact plastic parts.
The key elements of this machine are:
The base
The hopper
The barrel
The clamping unit
Each component plays a crucial role in the transformation process from raw plastic pellets to final products within the realm of injection molding.
Initiating at the hopper, where raw plastic pellets are deposited. This segment typically houses a dryer which eradicates moisture from the plastics—this step aids in preserving quality and uniformity throughout the molding process. Following their deposit, these pellets transition into the barrel and become gradually liquefied by heat.
Within this chamber are reciprocating screws pivotal for modulating both temperature and flow consistency for molten plastics. These mechanisms certify even melting prior to commencement of injection. Various heating systems maintain precise temperatures tailored for specific parts within apparatus operations.
The assembly encompassing hopper, barrel, and screw—the injection unit—is tasked with channeling molten materials into molds through nozzles situated on barrels’ extremities. Serving as filtration points or mixers when needed.
Responsible for mold opening-closing dynamics during injections stands clamping units outfitted with either hydraulic or toggle devices—a necessary function due to split mold designs synonymous with this field: two halves conjoining along parting lines producing secure cavitation space filling conditions once closed upon melted substrates infusion eligibility initiated via provided jets plungers exertion mechanism orchestrated by accompanying requisite hydraulic systematic controls installed duty ensuring smooth operational transitions thereof.
The Plastic Injection Molding Process Explained

The plastic injection molding process begins by introducing raw plastic materials into a hopper. These plastic materials, often in the form of pellets, are progressively heated until they become molten plastic, setting the stage for the rest of the injection molding cycle.
Upon closure of the mold, melted plastic is propelled into it under stable temperature conditions to ensure uniform flow across all cavities. Concurrently, as pressure mounts behind these flows of molten material due to screw retraction, preparation for its entry into the mold ensues.
Following this is the dwelling phase where sustained pressure guarantees full occupancy of all cavities within the mold by molten plastic. This step also accounts for potential shrinkage during cooling and is pivotal in achieving parts with exacting standards and consistent quality.
Subsequent to complete cavity filling comes cooling time when molds remain sealed, allowing solidification of injected plastics. The mold then carefully opens after adequate cooling has taken place so that each manufactured item maintains both structure and integrity upon removal.
Comprising clamping, injecting, dwelling, etc.
Cooling phases along with opening and ejecting actions - these six critical stages come together in precision fashion making sure every output produced via this method demonstrates top-notch quality while upholding efficiency traits inherent within this method.
The manufacturing protocols governing successful outcomes attributed to processes involved in crafting items through means associated with the manufacturing process.
Plastic injections machinery operations.
Step-by-Step Process
The plastic injection molding process involves several steps that work together to produce high-quality plastic parts. Each step is crucial in ensuring the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
Step 1: Selecting the Right Thermoplastic and Mold
The first step in the plastic injection molding process is to select the right thermoplastic material and mold for the part being produced. The choice of thermoplastic material is critical and is based on the specific properties required for the final product, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Common materials include Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polyethylene, and Polypropylene, each offering unique benefits. Simultaneously, the mold must be meticulously designed and manufactured to produce the desired shape and size of the part. This involves considering factors like the part’s geometry, the material’s flow characteristics, and the cooling rate to ensure optimal performance and quality.
Step 2: Feeding and Melting the Thermoplastic
The next step is to feed the selected thermoplastic material into the injection molding machine and melt it into a molten plastic. This process begins with the plastic pellets being loaded into the hopper, which then feeds them into a heated barrel. Inside the barrel, the plastic is gradually melted by a combination of heat and the mechanical action of a reciprocating screw. The temperature and pressure within the barrel are carefully controlled to ensure the plastic reaches the correct consistency for injection. This precise control is essential to prevent defects and ensure the molten plastic flows smoothly into the mold cavity.
Step 3: Injecting the Plastic into the Mold
Once the plastic is melted, it is injected into the mold through an injection unit. The injection unit is responsible for forcing the molten plastic into the mold cavity under high pressure. This step is critical as it determines the final shape and quality of the part. The injection pressure and speed are meticulously controlled to ensure the plastic fills the mold cavity completely and uniformly. After the mold is filled, the plastic is allowed to cool and solidify, taking on the shape of the mold. The mold is then opened, and ejector pins push the finished part out of the mold cavity, ready for any necessary post-processing.
By following these steps, the plastic injection molding process ensures the efficient production of high-quality plastic components, making it an indispensable method in modern manufacturing.
Types of Thermoplastic Materials Used
The selection of the appropriate thermoplastic material is a pivotal aspect of the plastic injection molding process. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) stands out as a common choice owing to its robustness and high-quality finish, which renders it perfect for manufacturing consumer goods and automotive parts. Meanwhile, Polyethylene claims the title of being the most extensively utilized plastic on a global scale with variations like high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE), finding uses in items ranging from food containers to automobile components.
Widely recognized for its superior melting point and ability to be recycled, Polypropylene earns favoritism in crafting toys as well as packaging materials. Likewise, Polystyrene’s claim to fame includes its featherlight nature coupled with resistance against moisture, leading it towards applications within medical devices alongside plastic toys.
Merging characteristics typical of both rubber and plastics is thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), whose utility extends into making medical apparatuses along with car components due to this fusion. Praised for stretchability combined with resilience against chemicals is thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), frequently found in sports gear and shoes.
Turning our attention toward other distinguished thermoplastics such as Polycarbonate—known not only for its enduring strength but also superb transparency—it often appears in safety shields plus housings designed for electronics. Nylon distinguishes itself by offering exceptional resistance against wear and tear, including fatigue. Hence one may find it useful in fabricating mechanical elements or interlocking closures.
Known alternatively as acetal, Polyoxymethylene delights users thanks to steadfast rigidity accompanied by minimal friction traits that lead directly towards their application within machinery involving gears or bearings specifically designed around those properties. Similarly favorable when discussing impact-resistant qualities together with visual lucidity would be Acrylic—a preferred option pertaining essentially anytime windows or solar panels are required.
Given their inherent property, allowing them repeatedly endure melting followed by recasting without degradation forms an integral component enabling flexibility alongside broad applicational scope granted through utilization across varying types regarding resins employed throughout processes comprising mold injections made up predominantly of these thermoplastic materials. These materials are often referred to as plastic resin, which is essential for creating high-quality plastic parts.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is renowned for its high efficiency and cost-effectiveness, especially when it comes to producing items in bulk. Although the upfront costs associated with mold creation can be significant, these expenses become much more manageable on a per-unit basis as production volumes increase. As such, this method is favored by manufacturers who need to produce large quantities of components quickly and cost-efficiently.
Injection molding boasts incredibly short production cycles that usually last anywhere from 10 seconds to a couple of minutes (120 seconds). This expedited cycle time drastically cuts down on overall manufacturing duration compared to alternative techniques, leading to quicker product delivery times and shortened lead periods.
A key benefit of plastic injection molding lies in its ability to craft complex geometries while maintaining strict tolerances. Thanks to advanced control systems outfitted in contemporary injection molding machines, each phase of the plastic material’s injection process is highly precise ensuring uniformity across produced parts.
The integration of automation and robotics has revolutionized plastic injection operations by reducing manual intervention thus diminishing human errors while boosting operational efficiency. These cutting-edge technologies not only facilitate continuous data collection but also enable ongoing enhancements throughout the production process thereby increasing output quality consistently.
Lastly, one cannot overlook the versatility inherent within the realm of plastic material options suitable for use within an injector – both thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics are eligible candidates here. Through recycling any excess polymer substance generated during manufacture — namely via reprocessing sprues or runners —the technology underscores commitment towards eco-friendly practices contributing towards sustainability efforts.
Common Applications of Plastic Injection Molding
The automotive sector extensively utilizes plastic injection molding to manufacture components like bumpers, dashboards, and additional interior and exterior elements. The resilience and preciseness of parts created through injection molding make them exceptionally suitable for enduring the demanding conditions associated with vehicle usage.
Within the realm of construction, various components are fabricated using injection molding due to the material’s robustness and cost efficiency. This manufacturing process is vital as it allows for consistent production of components that adhere strictly to required specifications, an essential factor in construction endeavors.
For point-of-purchase goods that require a harmonious blend of aesthetic appeal and practicality, injection molding is frequently employed. Its adaptable nature enables designers to craft products that not only look good but also perform excellently. Plastic injection molding is indeed a fundamental aspect of many industries’ operations because it supports the creation of a wide array of items with diverse functions.
Troubleshooting Common Injection Molding Issues
Ensuring the consistent quality of products in plastic injection molding necessitates resolving prevalent problems encountered throughout the process. Issues such as defective components and variations in procedural attributes can be pinpointed using techniques like industrial CT scanning, which uncovers flaws and irregularities not readily apparent to human vision.
Crucial factors that must be managed during the injection molding cycle are temperatures, overall pressure levels, specifically injection pressure, and achieving equilibrium between the pressures of both injection and clamping. Regulating these variables is essential for uniform product quality and decreasing defect occurrence.
The cooling period is pivotal for the part’s solidification within its mold, a key step to ensure it takes on its intended shape correctly. Subsequent stages involve extracting the finished piece from its mold followed by possible refinement processes such as polishing when aiming for a specific end texture or appearance. It is vital that parts have adequately cooled before being ejected to avoid any warping or distortion.
Implementing trial runs prior to commencing mass production aids in anticipating potential defects while establishing accurate specifications geared towards reducing chances of quality concerns. These preliminary tests enable producers to adjust their methods appropriately so that all produced items adhere strictly to expected industry benchmarks.
Innovations in Injection Molding Technology

Recent advances in the field of injection molding technology have markedly advanced the precision and intricacy with which molds can be crafted. The introduction of CNC machining and Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) stands out as critical enhancements, facilitating mold designs that accommodate complex shapes while maintaining tight dimensional tolerances.
The integration of smart technologies into injection molding machines has been a game-changer. These machines are now outfitted with sensors capable of capturing data in real-time, thereby streamlining production workflows and increasing productivity levels. This analytical approach significantly refines control during the rubber injection moulding process, lowering defect rates, and bolstering overall operational effectiveness.
To these advancements is the advent of multi-shot molding technology—this innovation allows for injecting multiple materials into one singular mold cycle. As a result, manufacturers can produce components exhibiting varied characteristics by combining disparate materials within one product for enhanced performance outcomes.
These technological strides signal an exciting future for those engaged in plastic injection practices. They lay foundations on which more sophisticated and superior-quality parts may be manufactured going forward. With ongoing developments within this domain, it seems clear that capabilities surrounding plastic injection will continue expanding far beyond their current horizons.
Summary
Plastic injection molding stands as a pivotal manufacturing method, renowned for its exceptional efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability. This technique meticulously manages each phase from the precise feeding of plastic pellets into the hopper to the ejection of cooled components, ensuring superior quality products. The availability of diverse thermoplastic materials like ABS, Polyethylene, and Polypropylene expands this process’s applicability across countless sectors.
The multitude of benefits offered by injection molding include cost savings in large-scale production runs, rapid cycle times for part creation, and the capacity to fabricate complex shapes with close tolerances. Technological advancements such as sophisticated control systems and automation have significantly elevated industry standards by guaranteeing uniform product quality while minimizing manual errors. Reusing surplus plastic highlights the environmental conscience inherent in this production technique.
Looking ahead at what is on the horizon for this field reveals that forthcoming innovations within injection molding technology are set to redefine manufacturing capabilities further. Developments such as CNC machining processes (Computer Numerical Control), EDM technologies (Electrical Discharge Machining), intelligent machinery implementation, and multi-shot mold applications promise heightened precision and complexity in molds alongside refined operational efficiencies. Solidifying plastic injection molding’s dominance within modern-day production landscapes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic steps in the plastic injection molding process?
The basic steps in the plastic injection molding process are feeding plastic pellets into the hopper, melting them, injecting the molten plastic into the mold, applying pressure, cooling, and ejecting the finished part.
Following these steps ensures the efficient production of molded plastic components.
Which industries commonly use plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding is commonly utilized in the automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries for producing various components efficiently.
What materials are used in plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding commonly utilizes materials such as ABS, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polystyrene, TPE, TPU, Polycarbonate, Nylon, POM, and Acrylic.
These materials are selected based on the desired properties of the final product. These materials are often referred to as plastic resin, which is essential for creating high-quality plastic parts.
What are the advantages of plastic injection molding?
Injection molding is an excellent option for mass production due to its high efficiency and cost-effectiveness, coupled with the capability to rapidly create complex geometries. This method suits perfectly when dealing with detailed designs or large-scale manufacturing requirements.
How can common injection molding issues be troubleshooted?
Industrial CT scanning can be employed to troubleshoot prevalent issues in injection molding, while paying close attention to essential parameters and engaging in pre-production testing is also beneficial. Optimizing cooling and ejection mechanisms contributes significantly.
Focusing on these crucial elements can result in enhanced outcomes for the production process.
Still, need help? Contact Us: [email protected]
Need a PROTOTYPE or PARTS machining quote? Quote now
 LKprototype
LKprototype







