Urethane casting is an effective and economical way for the production of prototypes and small scale production. This is particularly used in the design, development of prototypes and manufacturing of small-volume products due to the flexibility that it provides. In this guide, you will explore the urethane casting process, materials, benefits, applications and its comparison to other casting methods. Urethane casting involves injecting polyurethane and additive resins into soft silicone elastomer molds, highlighting its cost-effectiveness and suitability for short production runs.
What is Urethane Casting?
Urethane casting is a kind of process where liquid urethane is filled into the mold to manufacture a part or a prototype. This process is most suitable for small scale production, allows control over the material properties and thickness, has good dimensional accuracy and cost effectiveness. Unlike injection molding, urethane casting allows for quick fabrication of parts without the need for expensive molds, making it preferable for many manufacturers and product designers.

Urethane Casting Workshop
Definition and Overview
Urethane casting is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process that utilizes a two-part urethane resin to produce production-quality replicas of a master model. This method is ideal for creating low to medium volumes (less than 30) of parts, particularly those with intricate geometries. The urethane casting process involves pouring liquid urethane into a silicone mold, which then cures to form a solid part. Despite the growing popularity of additive manufacturing, urethane casting remains a viable and cost-effective choice for low-volume production. It allows you to quickly fabricate a part that is close to the real molded part without the need for an expensive injection mold.
The Urethane Casting Process
Developing the Master Pattern
The master pattern is the cornerstone of the entire urethane casting process, and its precision and quality directly impact the final cast parts. The master model is typically fabricated using advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or traditional sculpting methods. When designing the master pattern, it is crucial to consider how the pattern will be molded and how the urethane cast will be removed. The master pattern should be designed with a draft angle to ensure easy removal from the mold. This attention to detail ensures that the final cast urethane parts will have the desired accuracy and finish.
Model Creation
The master model is created using a 3D printing technique such as SLA, PolyJet, or FDM. CNC machining is another option for creating the master model. The model creation process begins with creating a CAD model of the part to be cast. The CAD model is then used to create the master model using the chosen manufacturing technique. This step is critical as it sets the foundation for the entire urethane casting process. The precision and quality of the master model will directly influence the final cast urethane parts, making it essential to use high-quality materials and techniques.
Creating the Silicone Mold
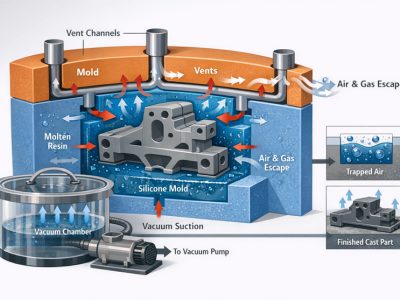
The silicone mold is created by placing the master model inside a containment box. The master part is securely fixed to the bottom of the mold using glue, styrene blocks, and modeling clay to ensure the silicone does not flow inside the part. Dowel pins are added to any through holes to maintain their integrity during mold-making. Before pouring silicone, it is essential to place it in a vacuum chamber to eliminate any bubbles that may have formed during mixing. This step ensures that the silicone mold will accurately capture all the details of the master model, resulting in high-quality cast urethane parts.
Mold Creation
The mold creation process involves creating a silicone rubber mold around the master model. The silicone mold is created by pouring liquid silicone around the master model and allowing it to cure. The cured silicone mold is then removed from the master model, and the urethane resin is poured into the mold to create the final cast part. The mold creation process is a critical step in the urethane casting process, as it directly affects the quality of the final cast part. Using high-quality silicone rubber and ensuring proper curing times will result in durable and precise silicone molds, which are essential for producing high-quality cast urethane parts.
·Model Creation:
The first process that occurs in urethane casting is the making of master patterns, which are usually a master model of the casting. This model can be made using a 3D-printed model, using machine parts or they can even be carved out by hand. Good detail and accuracy are vital because the model will be used to create a mold.
·Mold Creation:
Once the model is prepared, a mold must be made in order to produce the design. Silicone is used to create flexible molds capable of replicating all of the features of the master model. It can be of single mold or multi mold depending on the complexity of the product to be manufactured. Unlike the substantial investment required for an injection molding tool, creating silicone molds for urethane casting is more cost-effective and quicker for producing small quantities of high-quality parts.
·Mixing Urethane:
After designing the mold, the process that follows is to prepare the urethane material. Urethane casting involves injecting polyurethane and additive resins into soft silicone elastomer molds. Urethane resins are mainly two-component systems comprised of a base resin and a curing agent or a hardener. There may be some other additives that may be included in this formulation to modify the flexibility, hardness or color.
·Pouring and Curing:
Once mixed, the urethane resin is then poured into the mold. The mold is then left to cure at room temperature or in an oven. Three hours to 24 hours suffices as the curing period for the resin. In this last step, the urethane solidifies forming the shape of the mold and becomes a strong finished component.
·Demolding and Finishing:
After the curing process, the part is carefully removed from the mold. This process is called demolding and should be done with the lowest impact possible over the part and the mold. Then the part may need secondary operations including cutting off excess material, polishing or painting.
Types of Urethane Materials for Casting
·Flexible Urethane:
Flexible cast urethanes are used if a part is required to have rubber-like characteristics such as flexibility, elasticity, and impact strength. These materials are widely employed to fabricate seals, gaskets, soft-contact elements, and cushion parts. The flexible urethane can be processed in a wide range of hardness simultaneously ranging from very soft to slightly rigid.
·Rigid Urethane:
Rigid urethane is a strong and durable material. Thus, it is the most suitable for producing parts that have to bear high loads and work in conditions of wear or other hostile environment. It can be drawn to resemble the characteristics of ordinary plastics, such as ABS, PVC or even polycarbonate, and provide high mechanical strength and resistance.
·Urethane Foam:
Urethane foam is used where parts should be as light as possible but also have heat or shock-resistant characteristics. It is an elastomeric foam and may assume either flexible or rigid characteristics, dependent on the composition used.
·Specialty Urethanes:
Apart from these two types of urethanes, there are those that are specially developed for certain uses. These may involve high-temperature urethanes, flame retardant urethanes, or those urethanes with special customer desired colors or special additives. In particular, specialty urethanes enable manufacturers to produce parts with new characteristics and adjust them according to requirements.
Benefits of Urethane Casting
·Cost-effectiveness:
The urethane casting is relatively low cost for manufacturing of low volume parts. The molds and materials costs are considerably lower than most other techniques such as injection molding. This is due to the fact that the molds can be used repeatedly and therefore is even more cost-effective.
·Speed:
Urethane casting is much faster than other manufacturing processes. Depending on the curing time once the mold is created, parts can be generated within a few hours. One of the most important benefits of urethane casting is that the whole process is very fast, making it ideal for prototyping.
·Customization:
Urethane casting is a highly developed technology which enables changes in such properties as color, surface finish or rigidity. When a specific manufacturer needs soft and flexible parts or hard and extremely strong, rigid units, the urethane casting is extremely suitably for it and could be used in numerous commercial applications.
·Accuracy:
Urethane casting creates relatively complex and precise components that have close tolerances. This makes it ideal for functional prototypes and parts that require high precision since layers can easily be joined to give a strong bond. The flexible molds can capture the small features from the original model thus making the final part to resemble the designed part properly.
·Low-volume Production:
Urethane casting suits low volume production since the high tooling and set up costs that are found in injection molding are not incurred. Small business, product designer and manufacturers who adhere into this direction can make complex parts in low volumes and still achieve high precision without a lot of investment. While urethane casting is ideal for low-volume production, injection molding is more suitable for mass production due to its efficiency in producing large quantities of identical items.
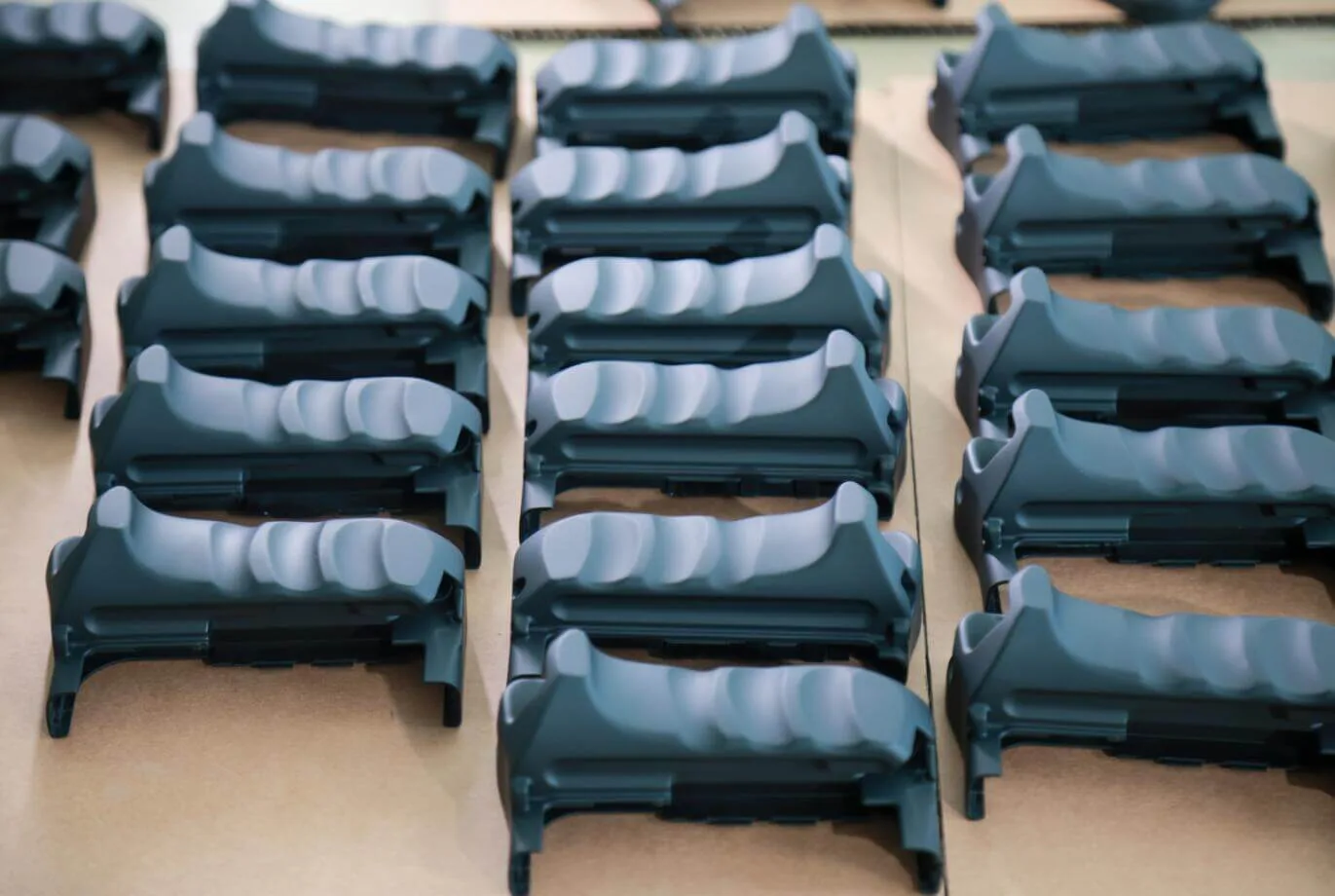

Applications of Urethane Casting
·Prototyping:
Urethane casting is commonly applied in the prototyping process due to the ability of making fast and precise functional prototypes. During the development, manufacturers can experiment with form, fit and function without having to use costly production processes. This permits quick prototyping and improvement before the shoot or widespread replica. Urethane casting can achieve similar or superior qualities in terms of detail and strength compared to injection molded parts, making it a cost-effective option for prototyping.
·Replacement Parts:
Urethane casting is a preferred method of making replacement parts, particularly when new parts are impossible to find or very costly. Due to its versatility, it is easy to make parts from urethane material that has the same performance and durability as the original part.
·End-use Parts:
At times, urethane casting is utilized as a form of direct production of the final parts, particularly in automotive and medical applications where high quality, low volume parts are often required. These parts can be applied in real world for functionality and can last long even without using complex tool for manufacturing.
·Industries:
Urethane casting is used across a broad range of industries, including:
Automotive industry: It is used for making of seals, gaskets, and prototype automotive parts.
Aerospace: Manufactured for low production and high accuracy parts for specialty applications.
Medical Devices: For making functional models on products or distinct components.
Consumer Products: In product development for creating functional prototypes or produce few number of products.
Consumer Electronics: For enclosure and for other subassemblies.
Urethane Casting vs. Other Casting Methods
·Urethane Casting vs. Silicone Molding:
Although both processes involve making molds for the parts, urethane casting yields somewhat stiffer and more wear-resistant output. Silicone molding is ideal for flexible components while urethane casting can come both flexible and rigid which gives it an added advantage with many applications.
·Urethane Casting vs. Injection Molding:
Injection molding is effective for large quantity production, it has high initial costs and setup costs. On the other hand, while urethane casting is cheaper and much quicker in a large number of prototypes or small production. Urethane casting machines are essential tools that help produce custom polyurethane parts efficiently, supporting diverse applications such as medical devices and automotive components.
·Urethane Casting vs. Resin Casting:
In Urethane and Resin casting, the basic idea is to cast through pouring the liquid material to mold but urethane is relatively stronger and more useful. Urethane materials can be molded into almost any type of plastic, rubber or foam and resin casting is generally used in small ornamental type products.
Common Challenges in Urethane Casting and How to Overcome
·Air Bubbles:
Insignificant trapped air gets into the mold during some mixing and pouring process, and this leads to formation of defects on the exterior of the part. To reduce this problem, it is advisable to stir the urethane resin gently, use vacuum chambers to remove air from the material and to pour the resin slowly in order not to introduce much air with it.
·Incomplete Curing:
If the urethane does not cure fully then the final part can be weak or unusable. This can be prevented by observing the correct proportion of the ingredients, the manufacturer's instructions on curing time and temperature. Curing of the resin is also sensitive to contamination and therefore requires proper storage of the resin before use.
·Mold Problems:
If the molds are not well maintained, there are high chances you are going to experience problems like tears or even improper releases. Problems such as this can be avoided by using high quality silicone and applying a mold release agent.
·Surface Finish:
The urethane casting sometimes include the fact that the finish of the product may be rough or of irregular texture. This can be solved by polishing the parts right after demolding process or by selecting the appropriate urethane materials that are ideal for polished surfaces.
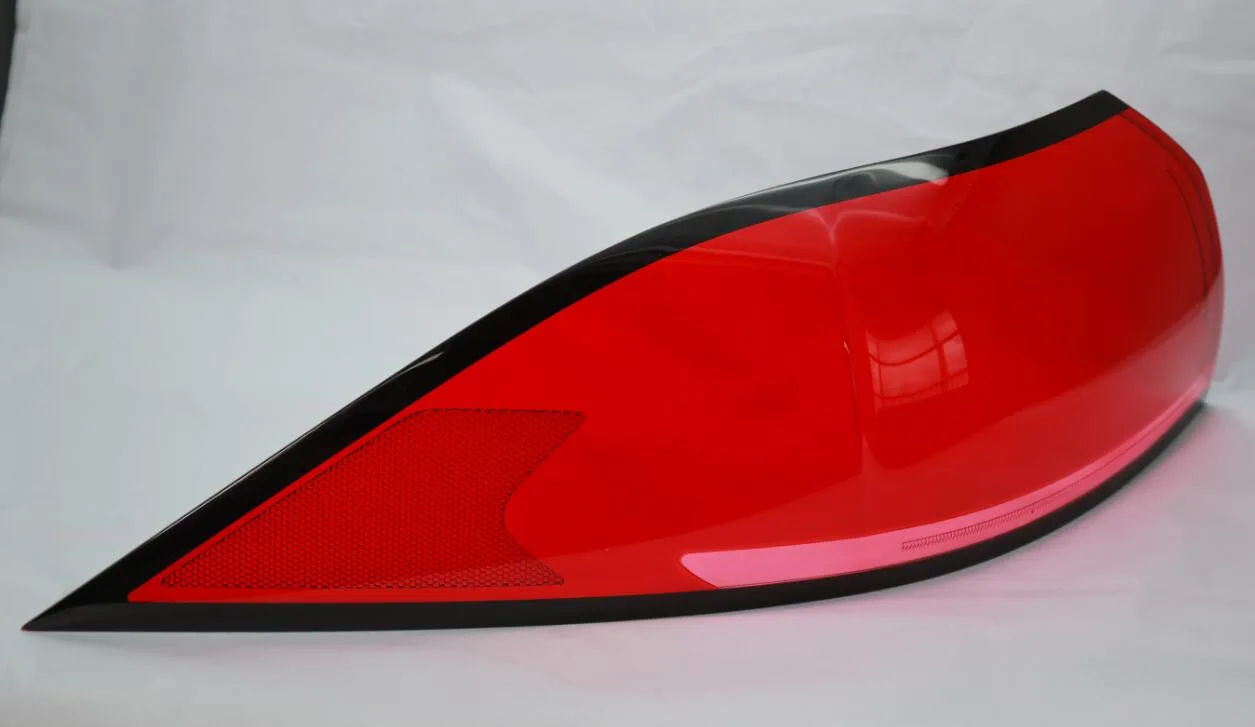

Polyurethane Casting Surface Finish
Conclusion
Urethane casting as an efficient way that is versatile, cheap and fast for making prototypes and short run parts. Due to the rate at which it operates, urethane casting appears to be a feasible solution for the companies who want to create sturdy parts at a reasonably short time. For more information about urethane casting services, explore our Rapid prototype company LK Prototype.
 LKprototype
LKprototype