If you’re looking to learn how to make an injection mold, understanding the steps is crucial. The process includes designing the mold, prototyping, machining, and assembling. This guide will walk you through each stage, helping you create a functional injection mold.
Key Takeaways
Injection molding is a crucial manufacturing technique that involves injecting molten plastic into metal molds to produce high-quality parts efficiently.
Key factors in mold design include the choice of materials, cooling channel optimization, and detailed design features such as draft angles and parting lines, all of which ensure product quality and production efficiency.
Proper maintenance and care of injection molds are essential for their longevity and performance, including regular inspections, cleaning, and following preventive maintenance schedules.
Understanding Injection Molds
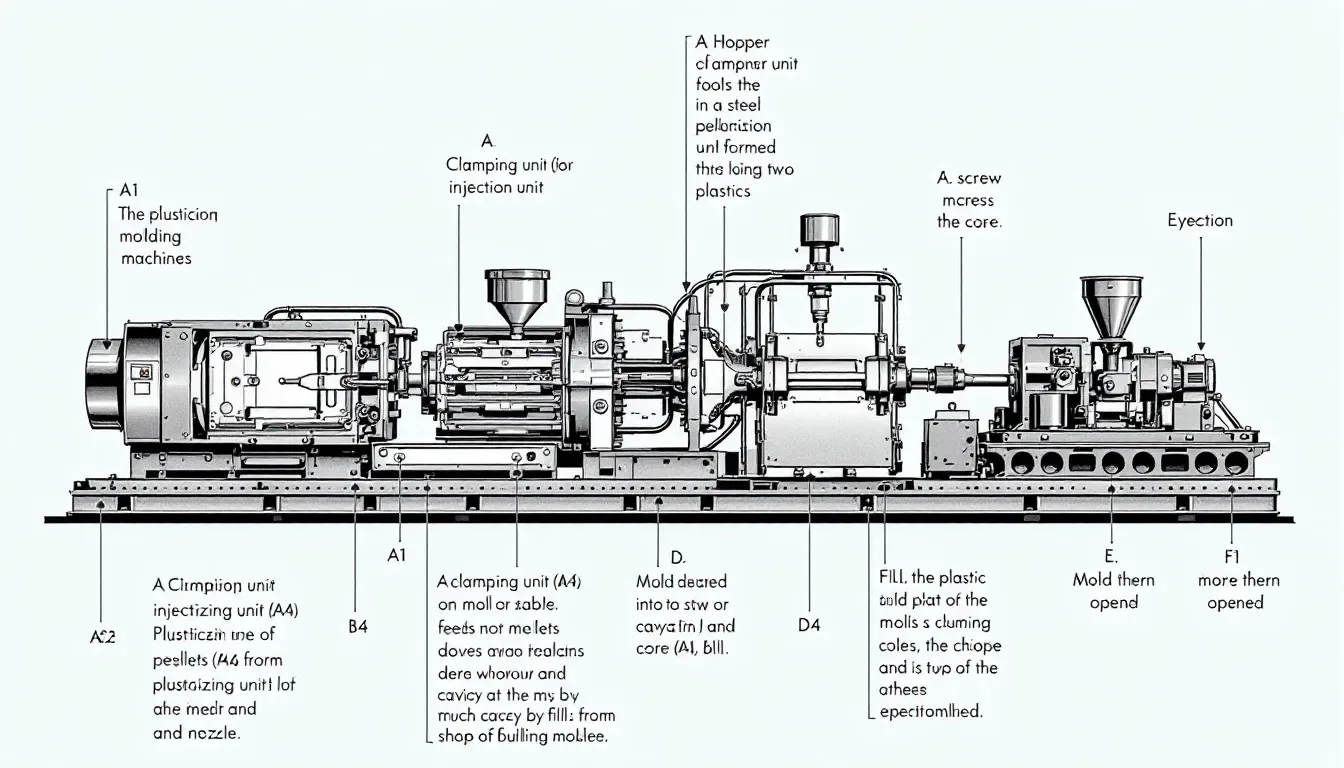
The technique of plastic injection molding involves propelling molten plastic into a metal mold to create parts through the process of injection molding. This method plays an essential role in mass production, ensuring that products are both high-quality and robust. Its capacity for quickly generating large quantities of components makes injection molding a favored approach across multiple sectors.
Initiating with the heating phase, this procedure requires the material to be heated within the barrel of an injection molding machine until it reaches a liquid state. Subsequently, injecting molten plastic into a cavity within the mold occurs where it cools and sets firmly. Following solidification, opening the mold allows for removal or ejection of each part. This sequence is then continuously repeated to enable swift creation of numerous identical pieces.
A comprehensive plastic injection moulding system encompasses elements such as hopper, barrel with its screw mechanism, and clamping unit all designed to cooperate in effectively melting, introducing (injecting) and shaping (molding) plastical materials precisely within desired parameters. By choosing suitable molds coupled with appropriate materials can dramatically decrease defect rates potentially down below one percent, testimony to not only precision but also consistency inherent within these manufacturing processes.
Key Factors in Injection Mold Design
Designing an injection mold involves several factors to ensure high-quality parts. A critical aspect is choosing the right mold material. Steel molds are highly durable, capable of producing millions of parts, making them ideal for high-volume production. Aluminum molds, on the other hand, cool faster than steel molds, reducing the overall production cycle time but are less suitable for high-melting-point resins.
Cooling channel design is another critical factor. Optimized channels ensure efficient heat distribution, significantly impacting the injection molding cycle. Conformal cooling channels, which adapt to the shape of complex parts, ensure even cooling and prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage. Using multiple smaller cooling channels can be more effective than a single large channel for heat distribution.
The design must include features like draft angles, parting lines, runners, and gates. Draft angles of two to five degrees facilitate easier removal of the molded parts. Proper placement of parting lines, runners, and gates ensures the mold fills correctly and the finished product is defect-free.
Combined, these elements ensure the mold functions efficiently and produces high-quality parts.
Materials Used for Injection Molds
The selection of materials for injection molds greatly affects the caliber and longevity of the end product. Steel, valued for its strength, can endure substantial pressure and elevated temperatures making it a preferred material. The resilience of steel allows these molds to generate millions of parts with consistent precision throughout their extensive service life.
Aluminum is also frequently used in mold production due to its cost-effectiveness and faster manufacturing time compared to steel. Although aluminum has limitations concerning high-melting-point resins, which it cannot accommodate, it does yield superior quality finishes when initially utilized. Over extended periods, this surface quality may decline. An advantage is that aluminum helps expedite cooling times thereby shortening overall production cycles.
When facing exceedingly high temperatures during the process, molds are often fashioned from specialized high-temperature resins capable of sustaining such conditions without damage or deformation. Crafting traditional injection molding tools comes at a steep price point—a pivotal factor in deciding on what materials should be used as well as how these molds are designed—necessitating careful balancing between affordability against performance requirements and durability expectations for successful mold fabrication endeavors.
Steps to Create an Injection Mold

The process of manufacturing an injection mold encompasses a sequence of intricate and essential steps that are pivotal for the final product’s excellence. The procedure is initiated by crafting a three-dimensional model of the component, which acts as a foundation for subsequent prototyping, testing, and tooling phases with the objective of fabricating a mold adept at dispensing molten plastic into its cavity to form the intended part.
Spanning several months, this development journey incorporates multiple iterations and enhancements aimed at ensuring that both specifications and quality benchmarks are satisfactorily met for the end product crafted from these molds.
In cases where molds are engineered to yield more than one piece per cycle, it may be imperative first to conceive, construct, and evaluate a solitary cavity instrument. This test ensures that all aspects of design function optimally before progressing towards mass production scale-up within injection mold making processes.
Designing the Mold
The process of designing an injection mold commences by employing CAD software, which facilitates the exact depiction and alteration of the design. The software is instrumental in experimenting with various configurations and permits streamlined tweaks. This repetitive procedure refines the mold design to align with production demands and specific dimensions of the part.
Trustworthy producers of molds utilize CAD software to formulate meticulous and precise designs. This tool assists designers in anticipating and rectifying possible complications prior to the commencement of mold construction. The ability to visualize and iteratively adjust designs is essential for fabricating efficient molds that exhibit superior performance during production.
Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping is a critical phase in creating injection molds. Methods like 3D printing, polymer casting, and CNC machining create prototypes. Prototypes test and validate the mold design, ensuring it meets the final product’s functional and aesthetic requirements.
Testing prototypes verifies the fit and function of the mold. It allows designers to address issues before full-scale production. This phase ensures the mold performs as expected and produces high-quality parts.
Prototyping and testing prevent costly errors, saving time and resources.
Finalizing the Mold Design
Once the prototype has been tested and validated, adjustments to the mold design constitute the concluding step. These modifications might include reshaping through metal cutting or welding techniques, in response to any problems that arose during testing. Such resolutions are critical for confirming that the mold operates effectively and generates parts as intended.
With all necessary alterations finalized and confirmation that the design aligns with specifications, production using the mold can commence. At this juncture, it is pivotal to ensure that mass production will benefit from an optimized mold capable of reliably yielding superior quality components. Consequently, a finished product emerges that fulfills all anticipated standards of design and functionality.
Manufacturing the Injection Mold

The process of manufacturing brings the mold design to life, converting it into a physical object. During tooling—which marks the conclusion of building a mold—meticulous machining is employed to shape both the cavity and core components accurately. This critical phase guarantees that the finished mold possesses the capability to replicate parts in large quantities while maintaining high precision and uniformity.
It’s imperative for a trusted mold maker to possess an on-site tool room furnished with diverse materials and machines suited for tooling. Such an arrangement enables swift production as well as prompt modifications when necessary. The culmination of all prior work happens during this tooling stage, producing a completed mold that stands ready for active use in production lines.
Machining the Mold
Machining creates the mold cavity and core, defining the shape and details of the final product. Common methods include milling (rotating cutters remove material) and drilling (creating holes). These techniques ensure precision and meet specifications.
If needed, the mold cavity can be adjusted by cutting away parts or welding metal into the cavity. Sometimes, creating a new cavity or an entirely new mold may be necessary if modifications are not feasible.
Machining prepares the mold for the next phase of assembly and the manufacturing process of production.
Assembling the Mold
Careful fitting of the mold halves is necessary to achieve precise alignment, which is vital for both the optimal operation of the mold and the quality of the part produced. It’s also important to meticulously install ejector pins that assist in removing parts from the mold.
Once assembling and pin installation are complete, conducting a detailed check for proper alignment becomes crucial. This step ensures that any misalignment—which could potentially lead to problems with the final product—is addressed. Hence, this process is pivotal in ensuring both performance and reliability of the mold.
Polishing and Finishing
Enhancing the surfaces of molds through polishing and finishing improves the quality of appearance for parts produced, ensuring they have a smooth finish that reduces imperfections.
It is critical to carry out polishing meticulously in order to maintain the dimensions, thereby guaranteeing that the final product adheres to its specified requirements.
Maintenance and Care of Injection Molds
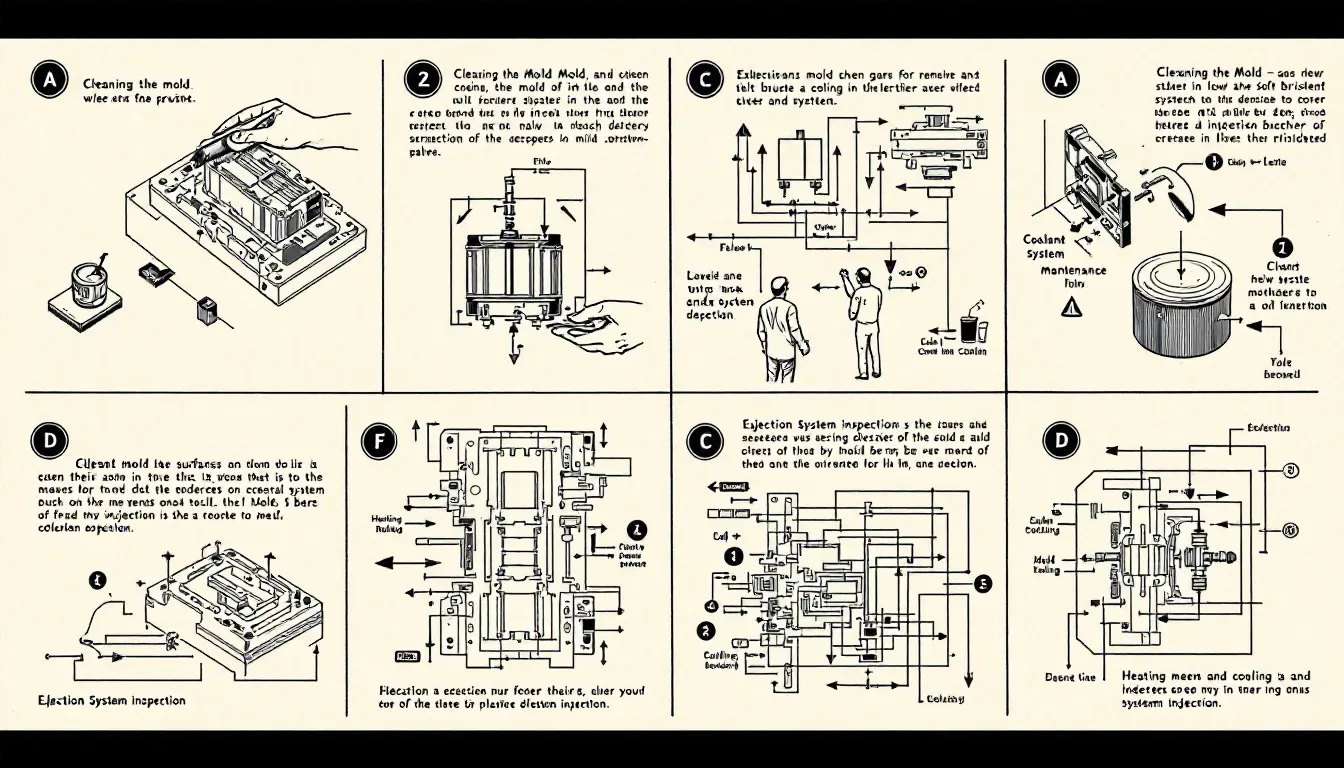
It’s critical to maintain diligent maintenance and care for the durability and efficiency of injection molds. Adhering to a preventative maintenance timetable, as suggested by the manufacturer, can prolong the life span of a mold. Routine cleansing is necessary to eliminate contaminants that may impair functionality and output quality.
Subsequent to cleansing, it is essential to conduct inspections on molds for any signs of wear, damage or misalignment in order to preserve their operational integrity. Keeping meticulous records regarding upkeep procedures assists in monitoring mold performance and organizing forthcoming maintenance tasks. Ensuring proper storage conditions in an environment that controls humidity will aid in preventing corrosion and deterioration during periods when molds are not actively being used.
Providing training for personnel on correct practices for handling and upkeeping these tools significantly contributes toward extending mold service life. Applying lubrication regularly helps reduce abrasion among components thereby facilitating smooth operations while managing thermal systems efficiently ensures prevention against undue stress which could lead to potential harm.
DIY Injection Molding Techniques
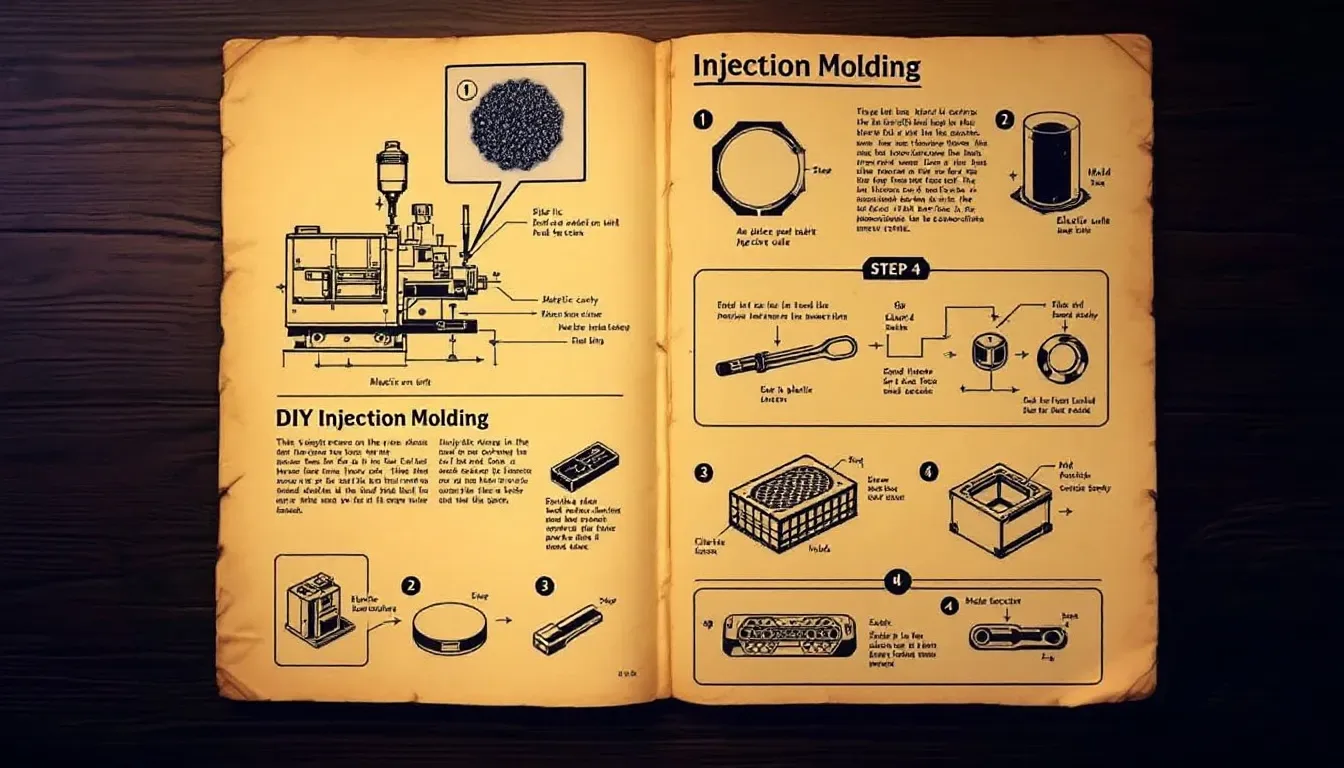
Engaging in DIY injection molding can be both fulfilling and economical for enthusiasts and modest production ventures. To carry out successful injection molding, one must gather essential items such as the appropriate tools, materials, and protective gear.
A prevalent method among DIY practitioners is to inject vibrant hot glue into molds while ensuring the edges are well sealed to block any air leakage. Vacuum casting stands as a reliable option that employs silicone molds when crafting prototype components, achieving exact detail fidelity.
These approaches enable individuals to delve into the world of injection molding with ease by circumventing the necessity for high-priced industrial machinery.
Case Study: Successful Injection Mold Project
The fabrication of a gutter cleaner serves as an exemplary case of effective injection mold deployment, facilitated by Rex Plastics, which efficiently escalated its production capabilities. Achieving completion of both the mold design and manufacturing stages within mere months evidences the expeditiousness and expandability afforded by plastic injection molding for crafting superior components.
Ongoing demand for the aforementioned gutter cleaner is on an upward trajectory, with order volumes consistently climbing—a testament to this endeavor’s triumph. This scenario underscores how proficiently plastic injection can accommodate urgent mass production needs while upholding exacting standards of quality and accuracy.
Varied items ranging from commonplace playthings like LEGO bricks to sophisticated components such as space shuttle turbine blades are produced through plastic injection molding. These examples reflect the adaptability inherent in this mode of producing plastic parts critical to diverse sectors.
Summary
Injection molding stands as a critical manufacturing method that facilitates the efficient and economical production of top-tier plastic components. Mastery over essential elements such as mold design intricacies, appropriate material selection, and the nuanced steps necessary for constructing and upkeeping injection molds is fundamental for triumph in this field. This guide serves to arm both novices and seasoned experts with an exhaustive understanding vital to steering through the intricate landscape of injection molding.
As you venture into your endeavors within injection molding, maintaining meticulous attention to detail, ensuring diligent upkeep of your equipment, and committing to ongoing education are pivotal practices for securing optimal outcomes. Equipped with the insights from this comprehensive manual, you possess all that’s needed to undertake your projects in injection molding confidently and turn your creative concepts into tangible realities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How profitable is injection molding?
Injection molding is highly profitable primarily in large-volume production scenarios, as small quantity orders often lead to reduced profit margins due to substantial mold design and tooling costs.
Hence, profitability is contingent on production scale.
What is a cheaper alternative to injection molding?
3D printing is a cost-effective and efficient alternative to injection molding, particularly for early-stage prototypes and short production runs of smaller parts.
Consider it for your next project.
What material should I use for injection molding?
For injection molding, consider using High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) for its durability in tool cases and power tool bodies, or General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) if transparency is required.
Both materials are effective resins commonly utilized in the industry.
What is plastic injection molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique used to manufacture precise plastic components by injecting molten plastic into a metal mold.
The process is highly efficient and favored for its ability to generate complex geometries in produced parts.
What materials are used for injection molds?
Steel and aluminum are the primary materials used for injection molds, each providing specific benefits suited to different production needs.
Still, need help? Contact Us: [email protected]
Need a PROTOTYPE or PARTS machining quote? Quote now
 LKprototype
LKprototype







