Vacuum Casting Services are extensively applied to short-time producing processes and designing trial production. Polyurethane vacuum casting is a specific technique used in these services, known for producing high-quality prototypes and small to medium production runs. This process results in parts with good detail and surface finish and with considerably less tool wear. It is effective in prototyping new designs, making fully functional prototypes and for developing relatively small numbers of components.
What is Vacuum Casting?
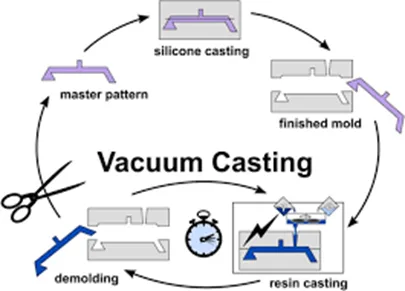
Vacuum casting is one in which the silicone rubber molds are made under a vacuum. These molds are then used to pour parts of various materials. For instance, polyurethane resin. Vacuum casting can produce both rigid or flexible parts, highlighting its versatility. The work is very streamlined which results in giving the materials smooth and detailed surface finishes. It is commonly applied for the production of prototypes or when in small batches of products are to be made.

Vacuum Casting production

Vacuum Casting – Step by Step Process
Vacuum casting is a multi-step process that involves creating a master pattern, making a silicone mold, and casting the final parts. Here’s a detailed overview of the step-by-step process:
Master Pattern Creation: The first step in the vacuum casting process is to create a master pattern, which is a precise replica of the desired part. This can be achieved using various methods such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or even hand modeling. The master pattern must have the exact dimensions and surface finish required for the final product.
Silicone Mold Creation: Once the master pattern is ready, a silicone mold is made around it. The master pattern is placed inside a casting box, and liquid silicone is poured over it. The silicone is then cured, typically in an oven, to form a flexible and durable mold that captures every detail of the master pattern.
Mold Preparation: After the silicone mold has cured, it is prepared for casting. A release agent is applied to the mold to ensure that the final part can be easily removed without damaging the mold or the part.
Casting: The casting material, usually a polyurethane resin, is mixed and poured into the silicone mold. The mold is then placed in a vacuum chamber to remove any air bubbles that may have formed during the pouring process. This step is crucial for achieving a high-quality surface finish and structural integrity.
Curing: The casting material is allowed to cure inside the mold. The curing time can vary depending on the material used and the size of the part, ranging from a few minutes to several hours.
Demolding: Once the casting material has fully cured, the part is carefully removed from the silicone mold. The mold can be reused multiple times, making vacuum casting a cost-effective method for producing small batches of parts.
Finishing: The final part may require additional finishing processes such as sanding, painting, or texturing to achieve the desired appearance and functionality. These finishing touches enhance the aesthetics and usability of the vacuum cast parts.
Vacuum Casting –Step by Step Process
During the casting step, it is crucial to maintain a consistent wall thickness to prevent warping and ensure uniform curing of the resin. A typical wall thickness range of 1.5 to 5 mm is recommended for optimal results.
l Master Model Creation:
There is a large maintenance process, the first step of which is to make master patterns. These master patterns serve as the original models from which silicone molds are created in the vacuum casting process. This model is commonly produced from a material that is sturdy such as wax, plastic or metal. This kind of model must have the precise measurements and texture as the final product that needs to be manufactured.
l Mold Making:
Thus, when the master model is made then of silicone rubber mold is prepared. The master model is then located inside a container with the liquid silicone rubber poured and around it. This mold is then under UV light that hardens the silicone to give the desired shape.
l Resin Pouring:
Once the mold is prepared, the cyclist pours resin into the silicone mold. Urethane casting plays a crucial role in the vacuum casting process, as it uses polyurethane resin to produce high-quality prototypes and small to medium production runs. Depending on the application, different materials may be used. The molten polymer is poured into the mold which acquires the shape of the master model.
l Curing and Demolding:
After the resin has been filled in it is left to solidify. Normally the curing time is determined by the type of material that is being used. After complete solidification of the silicone rubber, the mold is carefully peeled off.
l Post-Processing:
Following demolding, further treatments can be performed, for instance, trimming, sanding, or painting of the part. This is in order to trim, refine or polish them in one way or another to accomplish the intended final appearance. This process enhances the cosmetics and utility of the particular for testing or low quantity production process.
Equipment and Technology Used:
Vacuum casting coupled with resin batch mixtures, require vacuum chambers, and curing ovens. The vacuum chamber here plays important role when pouring the resin by eliminating the bubbles in the unit.
Materials Used in Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting utilizes a variety of materials to create high-quality prototypes and functional parts. Here are some of the key materials used in the process:
Polyurethane Resins: Polyurethane resins are the most commonly used materials in vacuum casting. They offer a wide range of properties, including flexibility, rigidity, and impact resistance, making them suitable for various applications.
Silicone: Silicone is used to create the molds in vacuum casting. It is flexible, durable, and capable of capturing fine details from the master pattern. Silicone molds can be reused multiple times, adding to the cost-effectiveness of the process.
Master Pattern Materials: The master pattern can be made from a variety of materials, depending on the desired properties and the method of creation. Common materials include 3D printed plastics, CNC machined metals, and hand-modeled waxes. Each material offers different advantages in terms of precision, durability, and ease of use.
Benefits of Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is an advanced technique that has high advantages which make it favorable for use in the process of rapid prototyping and small-scale production. The following advantages show how many industries consider vacuum casting their most favorable solution for cost-effective and high-quality products.
Compared to injection molded parts, vacuum casted parts offer similar durability and quality, making them an excellent alternative for various applications.
l Cost-Effective for Small Batches:
Vacuum casting is one of the most economical methods of production for small quantities. It does not need large investments in manufacturing tools or other manufacturing or production system designs as most conventional manufacturing processes do.
l Rapid Turnaround:
Probably, the biggest benefit of vacuum casting is that it is a very fast method. The process from creating a mold to delivering the part takes no more than a few days. This is an advantage in situations where a company needs to get results quickly for instance for prototyping or testing.
l High Accuracy and Detail:
Vacuum casting because of its efficiency gives reproduction easy and as accurate as the master model in terms of surface patterns. For this kind of casting, the molds used are silicons, and are quite fitting because they are flexible and very precise to give out parts that have an exact structure of the model used as the template.
l Material Versatility:
One strength of vacuum casting is the versatility it offers with regard to the material; it can utilize both hard polymers and rubber-like materials. To suit the context in which they are to be applied, the materials can be chosen on the grounds of strength, elasticity, or heat resistance.
l Prototyping and Low-Volume Production:
Prototyping and low volume production is a combination of phases that are considered to produce prototypes and create prototypes of small number of products for its clients. It is mostly used to produce rapid tooling and low volume production.
l Complex Geometries:
The vacuum casting process prefers when producing intricate components with a complicated shape. The silicone molds are capable of expanding and getting back to their normal state, thus suitable for products with undercuts or deep cavity.
Comparison to Injection Molding
Vacuum casting and injection molding are both popular methods for producing plastic parts, but they have distinct differences that make them suitable for different applications:
Tooling Costs: Vacuum casting has significantly lower tooling costs compared to injection molding. This makes it an ideal choice for small to medium-sized production runs where the high initial investment in injection molding tools is not justified.
Lead Time: Vacuum casting offers a faster lead time compared to injection molding. Parts can typically be produced within a few days, making it a preferred method for rapid prototyping and short production cycles.
Material Options: Vacuum casting provides a wider range of material options, including both flexible and rigid polyurethane resins. This versatility allows for the production of parts with varying properties to meet specific application requirements.
Part Complexity: Vacuum casting is better suited for producing complex parts with intricate details, undercuts, and fine surface textures. Injection molding, on the other hand, is more efficient for high-volume production of simpler parts with consistent quality.
Tolerances and Accuracy
Vacuum casting is known for its ability to achieve high tolerances and accuracy, making it suitable for producing precise and detailed parts. The typical tolerances in vacuum casting range from +/- 0.01 mm to +/- 0.1 mm, depending on the material and the size of the part. Some materials and processes can achieve even tighter tolerances, ensuring that the final parts meet stringent quality standards.
Finishing Options for Vacuum Cast Parts
Vacuum cast parts can undergo various finishing processes to enhance their appearance and functionality. Here are some common finishing options:
Sanding: Sanding is used to smooth out the surface of the part and remove any imperfections. It is an essential step for achieving a high-quality finish.
Painting: Painting adds color and texture to the part, allowing for customization and improved aesthetics. Different types of paints can be used depending on the desired finish and application.
Texturing: Texturing involves adding specific patterns or textures to the part’s surface. This can be done to improve grip, enhance appearance, or meet specific design requirements.
Assembly: Assembly involves combining multiple parts into a single unit. This is often necessary for creating complex products that consist of several components.
Machining: Machining is used to add features such as holes, slots, or other details to the part. This process can be performed after casting to achieve precise dimensions and functional features.
By understanding and utilizing these finishing options, manufacturers can produce vacuum cast parts that meet the desired specifications and quality standards.
Applications of Vacuum Casting
l Automotive Industry:
Vacuum casting, in automotive industry is among the most commonly employed methods of rapid tooling to make functional parts for items such as the dashboard of a car, knobs, and switches. This it makes it possible to quickly prototype design ideas before they are released into the market.
Aerospace and Defense:
Thanks to the vacuum casting, the aerospace and defense industries have thin-walled, high-strength components for their applications. This makes it possible to produce prototypes of subsequent versions of crucial sections including those of structural frames and enclosures.
Medical and Healthcare:
In medical and health care industries, vacuum casting comes with use in the development of prototypes of surgical tools and medical devices and patients' models. The high degree of accuracy, which in turn translates into the ability of using biocompatible materials makes it ideal for making functional prototypes.
l Consumer Electronics:
Consumer electronics use vacuum casting for prototyping casings, housings, and working parts of the equipment. It affords the opportunity for companies to evaluate such aspects as ergonomics, fitting and usability of their products to the end users.
Design and Concept Models:
Currently, designers and engineers rely on vacuum casting to generate concept models and actual visual prototypes. These models are particularly useful in the assessment of design ideas without necessarily committing large amounts of capital.
l Jewelry and Fashion:
When it comes to the Jewelry and fashion industry vacuum casting is widely used in developing great designs that have finer details. It can also be used to make exact copies of the initial designs that include the making of rings, pendants and other accessories.
Choosing the Right Vacuum Casting Service Provider
The services of a vacuum casting company are well determined by the kind of company that an individual hires to do the work. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a provider that suits your project needs.
l Experience and Expertise
Thus, one should search for the provider who specializes in the case of vacuum casting and has a record of work done previously. An experienced staff of literates armed with evident technical proficiency guarantees optimal execution of your project.
l Quality Control:
Check out whether the services provider has very high standards of quality control in place. Tight tolerances, smooth surfaces and, more importantly, material homogeneity in the parts are crucial.
l Material and Process Flexibility:
Select a provider to whom you can turn over your printing needs with a variety of materials and processes available. This flexibility permits the different resins or silicones to be selected for the optimal application.
l Lead Time and Cost Considerations:
Talk with the provider about the expected lead time and the cost issue. It is also fast since most of the costing processes take a shorter time; nevertheless, guarantee that the provider completes the work within the agreed time and cost. Find out how you will be charged so that you don't end up paying more than expected.
l Customer Support and Communication:
People's communication with each other must be effective in order to create harmonious and efficient relations. Pick a provider whom you feel comfortable, who is more likely to communicate with you often and should have quality customer relations.
Challenges of Vacuum Casting
But like with any other method, vacuum casting has its benefits as well as its drawbacks.
Limited to Small and Medium Runs:
Compared to traditional casting, vacuum casting is most appropriate for mid to small runs production. From its perspective, it is uneconomic in mass production industries. The process becomes inefficient when large quantity of parts are needed in the production chain.
Material Limitations:
The versatility of the vacuum casting is much lower than the traditional injection molding in terms of the selection of materials to be used. While polyurethane resins are likewise used, they are usually not as strong or as rigid as metals or some other polymers.
Potential for Imperfections:
Nonetheless, vacuum casting can be imperfect even though the imperfections seen on the solid Castings are minimal. Blemishes on the surface or a slight in accurate dimensions could be realized, particularly if the process is not followed to the latter detail. That is why even these small imperfections might influence the property of the final part.
Size Limitations:
One of the major constraints in vacuum casting is that is mainly used for manufacturing small parts. Both the size of the mold and the resin used to fill the cavity in most applications and can limit the size of the final part. When it comes to the larger parts, it is possible to consider the use of other production techniques such as CNC machining or injection molding.
Conclusion
Therefore, vacuum casting services are reliable methods for rapid tooling and small volume production. It is very accurate, can be used on a vast range of materials and has a short cycle time for manufacturing so the industry it can be most advantageous for is automotive, aerospace and medical. Nevertheless, some limitation such as size or kind of the material may be restricted.
 LKprototype
LKprototype