What is Urethane Casting Process: Benefits, Materials, Applications
Cast urethane, also known as polyurethane casting, has emerged as a versatile and cost-effective method for producing high-quality prototype parts and low-volume production components. Unlike traditional manufacturing techniques such as injection molding or CNC machining, urethane casting provides unparalleled flexibility in material selection and design replication. This guide dives deep into the core aspects of urethane casting, offering fresh insights into its processes, applications, and innovations that go beyond common industry narratives.

Urethane casting
What Is Urethane Casting?
Urethane casting is a manufacturing process that uses silicone molds to produce parts made from polyurethane resin. It’s widely adopted for prototyping and small-batch production due to its:
- Rapid turnaround time: Ideal for time-sensitive projects.
- Material flexibility: Wide range of resin options for varied mechanical properties.
- Design accuracy: Replicates complex geometries with high fidelity.
Cast urethane parts can be customized for wall thickness, reinforced with ribs, and finished using various techniques to achieve exceptional strength and detail.
Innovative Perspective: While most guides highlight the basics, few discuss how urethane casting is evolving. New hybrid resins now allow for enhanced heat resistance and biocompatibility, opening doors to applications in high-performance industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Definition and Overview
Urethane casting is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process that utilizes a two-part urethane resin to produce production-quality replicas of a master model. This method is ideal for creating low to medium volumes (less than 30) of parts, particularly those with intricate geometries. Urethane casting remains a viable and cost-effective choice for low-volume production despite the growing popularity of additive manufacturing. It allows you to quickly fabricate a part that is close to the real molded part without building an expensive mold.
Materials and Urethane Casting Process
Materials
- Standard Polyurethane Resins: For general-purpose parts.
- Elastomeric Resins: Offering rubber-like flexibility, used in gaskets and seals.
- High-Temperature Resins: For components exposed to heat or UV radiation.
- Transparent Resins: Ideal for aesthetic or optical applications.
- Urethane Materials: Versatile solutions offering UV stability, temperature resistance, and a range of colors. Suitable for applications requiring clarity, compliance with food or medical standards, and high-quality finishes in both rigid and flexible forms.
Process Steps
- Master Model Creation: Typically produced using CNC machining or high-resolution 3D printing. The quality of the 3D printed master models directly influences the final cast products, making it essential to achieve precise details and smooth finishes.
- Silicone Mold Making: The master model is used to create a mold.
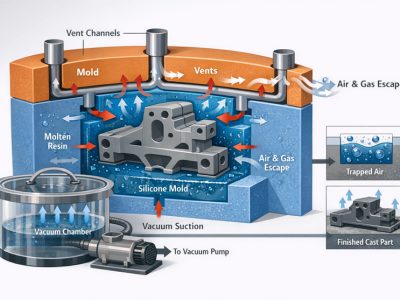
- Casting: Polyurethane resin is mixed, degassed, and poured into the silicone mold.
- Curing: Molds are placed in an oven to solidify and enhance material properties.
- Finishing: Parts undergo additional treatments such as polishing or painting.
Innovative Perspective: Advanced degassing techniques now allow for bubble-free, optically clear parts, a significant improvement over traditional methods that often struggle with micro-defects.

Developing the Master Pattern
The most common methods for creating a master pattern include 3D printing techniques such as SLA, PolyJet, and FDM. CNC machining is another option. All methods begin with creating a CAD model of the part to be cast. When designing the 3D model, it is crucial to consider how the pattern will be molded and how the urethane cast will be removed. The master pattern is the cornerstone of the entire process, and its precision and quality directly impact the final cast parts.
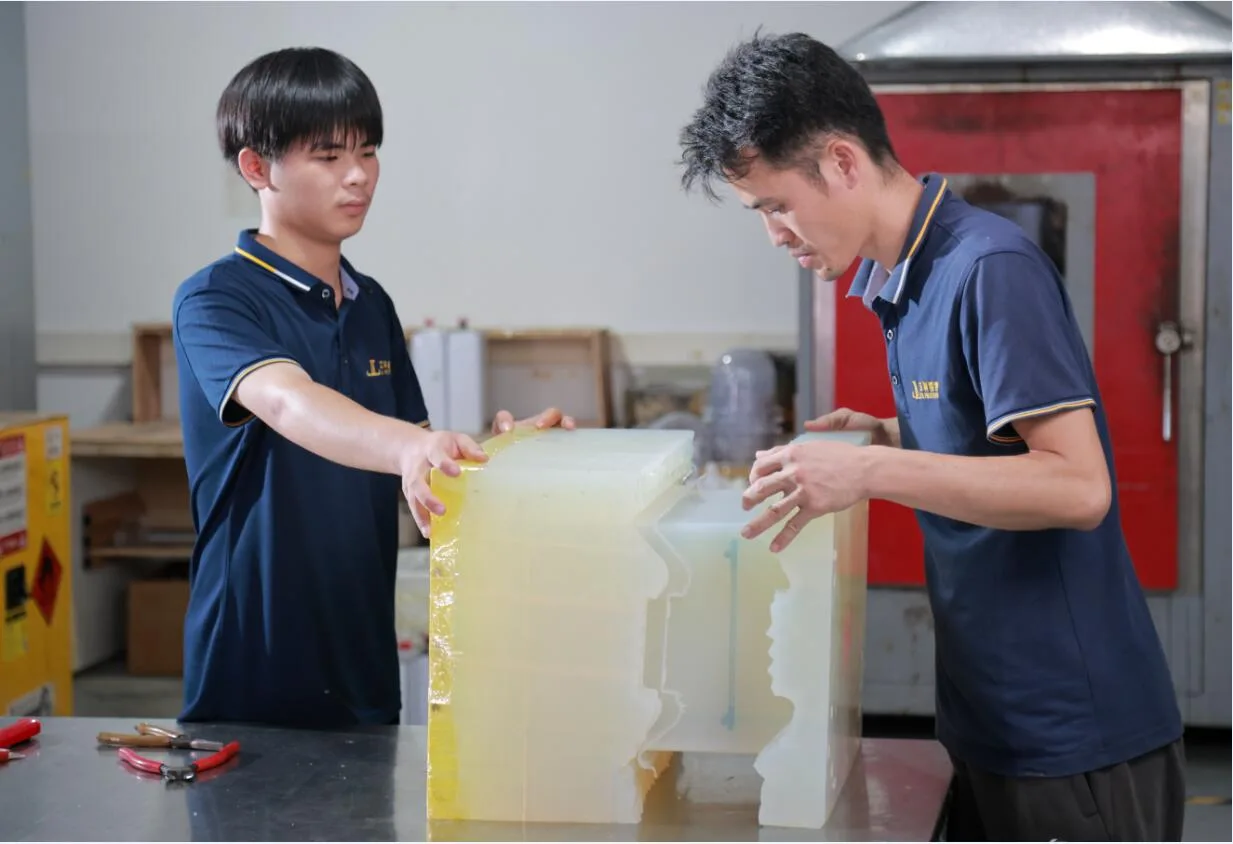
Creating the Silicone Mold
The next step is to prepare the silicone mold. A mold box or frame is set up to contain the silicone during the pouring process. The master pattern is placed inside the mold box, and the silicone and catalyst mixture is poured over it. The silicone mold is then allowed to cure, creating a negative impression of the master pattern. This mold will be used to cast the urethane resin.
Benefits and Applications
Benefits
- Cost-Efficiency: Eliminates the need for expensive metal molds.
- Scalability: Suitable for both prototypes and low-volume production.
- Customization: Tailored material properties and finishes for specific applications.
- Efficient Production: Urethane casting machines, such as the Moldman™ 8000, are essential for the efficient production of custom polyurethane parts. These machines offer automated solutions and advanced software controls, improving process efficiency and control. They are particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and medical devices, where high-quality prototypes and testing products are crucial before mass production.
Applications in Low Volume Production
- Medical Devices: Biocompatible and sterilizable parts.
- Automotive Industry: Functional prototypes for design validation.
- Consumer Electronics: Housings and transparent components for aesthetic validation.
- Mold Construction: Silicone rubber is crucial for creating flexible molds that accurately replicate master models, ensuring high-fidelity castings and prototypes for various applications.
Innovative Perspective: Emerging bio-based polyurethane resins are reducing environmental impact, making urethane casting an eco-friendlier option for industries moving towards sustainability.
Comparison with Injection Molding and Other Methods
| Aspect | Urethane Casting | Injection Molding | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooling Cost | Low | High (injection molding tool) | Moderate |
| Production Volume | Low to medium | High | Low to medium |
| Material Options | High | Limited | High |
| Lead Time | 1-2 weeks | 4-8 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Precision | High | Very high | Very high |
| Simulation of Injection Molded Parts | Yes | N/A | N/A |
Innovative Perspective: Traditional comparisons often stop at cost and speed. A newer dimension to consider is the carbon footprint. Urethane casting, with its lower tooling and energy requirements, offers a greener alternative for sustainable manufacturing.
Urethane Casting vs. Injection Molding
Urethane casting and injection molding are both manufacturing processes used to produce plastic parts, but they have distinct differences. Injection molding is a high-volume production process that uses a metal mold to produce parts. Urethane casting, on the other hand, is a low-volume production process that uses a silicone mold to produce parts. Urethane casting excels in producing low-to-medium volumes and intricate, customized parts, whereas injection molding is designed for high-volume production with limited design variability. Unlike injection molding, urethane casting does not require expensive equipment such as injection pumps, heaters, or kneading machines, further reducing overall investment costs.
Quality Assurance
Ensuring consistent quality in urethane casting involves:
- Material Testing: Verifying resin properties before casting.
- Process Control: Maintaining precise temperatures and curing times.
- Defect Mitigation: Using vacuum degassing to prevent bubbles.
- Inspection: Conducting dimensional analysis and functional testing.
Urethane casting is scalable and serves as a flexible alternative for low-to-medium volume production and prototyping, allowing designers to refine their products before committing to full-scale mass production.
Innovative Perspective: AI-based inspection systems are being integrated into the quality assurance process, providing real-time defect detection and reducing manual intervention.
How to Choose a Service Provider
When selecting a urethane casting partner, consider:
- Experience: Proven track record in your industry.
- Material Expertise: Access to a wide range of polyurethane resins.
- Technological Capabilities: Advanced equipment for precision casting.
- Lead Times: Ability to meet project deadlines.
- Post-Processing Options: Availability of finishing services like painting or assembly.
- Master Patterns: Importance of master patterns in creating accurate silicone molds for rapid prototyping and pre-production runs.
Innovative Perspective: Many top-tier providers now offer digital twin simulations, allowing clients to preview how their designs will perform before production begins.
Conclusion
Urethane casting is more than just a prototyping solution; it’s a gateway to innovation, bridging the gap between concept and production. With advancements in materials, eco-friendly options, and AI-driven quality assurance, urethane casting continues to redefine its role in modern manufacturing. Urethane resins, with their flexibility, rigidity, heat resistance, and UV resistance, play a crucial role in the casting process, allowing for tailored formulations to meet specific application needs.
As industries prioritize speed, customization, and sustainability, choosing the right urethane casting approach and partner becomes crucial. Whether you’re designing the next breakthrough in medical devices or crafting consumer electronics, urethane casting offers a scalable, reliable, and cutting-edge solution.
 LKprototype
LKprototype