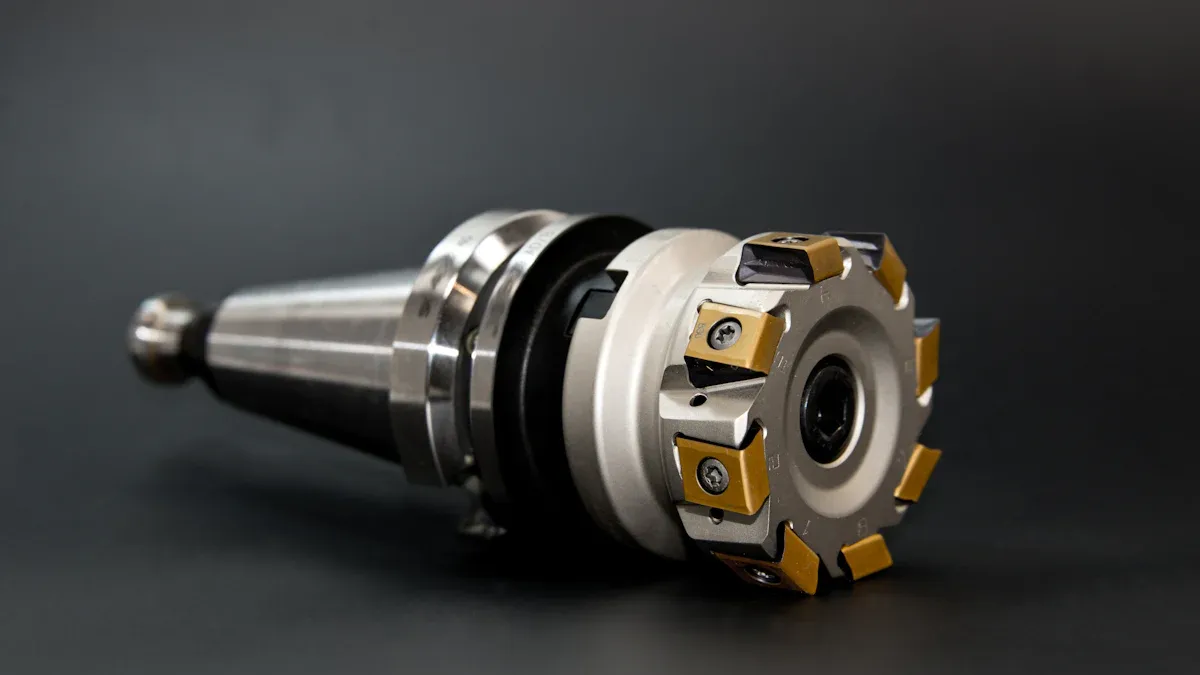
Precision is very important in CNC machining bronze. Bronze is strong, resists rust, and handles heat well, making it great for producing parts like bushings and gears. However, its unique traits can make CNC machining tricky. To achieve good results, it's essential to use the right tools and methods. With practice, you can address issues like worn tools or rough surfaces, which helps create high-quality parts.
Key Takeaways
Pick the correct bronze type for your work. Each type has special traits that affect strength and use.
Use strong carbide tools to cut bronze. They last longer and make smooth surfaces.
Change cutting speed and feed for each job. Right settings save tools and reduce mistakes.
Use coolants well to stop overheating. Coolants keep tools safe and improve cutting results.
Check and adjust machines often. This keeps work accurate and quality high.
Key Considerations for CNC Machining Bronze
Picking the Right Bronze Alloy for Your Needs
Choosing the correct bronze alloy is very important. Each type has special features for different uses. For example, C932 Bearing Bronze is easy to machine and lasts long, making it great for gears and bearings. C954 Aluminum Bronze is strong and resists rust, so it works well for marine parts. If you need something easy to machine, C260 Cartridge Brass is perfect for fasteners and fittings. C510 Phosphor Bronze is both strong and flexible, making it ideal for springs and bushings.
Bronze Alloy / Metal | Strength | Wear Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Machinability | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C932 Bearing Bronze | Medium | High | Moderate | Good | Bearings, gears |
C954 Aluminum Bronze | High | Very high | Excellent | Moderate | Marine components |
C260 Cartridge Brass | Low | Low | Good | Excellent | Fasteners, fittings |
C510 Phosphor Bronze | Medium | Medium | High | Moderate | Springs, bushings |
Knowing these differences helps you pick the best alloy for your project.
How Bronze Traits Impact Machining
The traits of bronze affect how you machine it. Strong alloys like C954 Aluminum Bronze can wear out tools faster. Softer alloys, such as C260 Cartridge Brass, are easier to machine but need careful handling to avoid damage. Bronze spreads heat well, but bad coolant use can still cause overheating. Understanding these traits lets you adjust your process for better results.
Choosing the Right Tools for Bronze Machining
The tools you use are very important for machining bronze. Carbide tools are tough and handle bronze’s rough surface well. Sharp edges and positive rake angles on tools make cutting easier and improve the finish. Mount tools properly to reduce vibrations and keep precision. Check tools often and replace worn ones to keep your work high-quality.
Techniques to Improve CNC Machining Bronze
Setting the Best Cutting Speeds and Feeds
Picking the right speeds and feeds is important. These settings affect tool life, surface finish, and efficiency. Adjust them based on the task, tool type, and bronze alloy. For rough turning, use slower speeds and higher feeds. For finish turning, faster speeds and finer feeds work better. Below is a table with recommended settings:
Operation | Spindle Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (in/rev for turning, in/tooth for milling) | Depth of Cut (in) | Tool Type | Coolant Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Rough Turning | 180–300 | 0.006–0.018 (turning) | 0.050–0.150 | Coated Carbide | Flood or High-Flow |
Finish Turning | 250–350 | 0.003–0.012 (turning) | 0.010–0.050 | Coated Carbide | Flood or Mist |
Rough Milling | 150–250 | 0.002–0.006 (per tooth) | 0.030–0.100 | Indexable Carbide | Flood or Air Blast |
Finish Milling | 200–300 | 0.001–0.004 (per tooth) | 0.010–0.040 | TiAlN Endmill | Flood or MQL |
Drilling | 80–150 | 0.003–0.010 (per rev) | N/A | Carbide Drill | High-Pressure Coolant |
Tapping | 80–120 | 50–70% of typical steel feed | N/A | Spiral Flute (HSS or Carbide) | Mist or Oil |
Reaming | 50–100 | 0.001–0.003 (per rev) | Light pass | Carbide Reamer | Flood or Oil |
Follow these tips to reduce tool wear and get better results.
Using Coolants and Lubricants Effectively
Coolants and lubricants are very helpful when machining bronze. They stop overheating, which can harm tools and parts. Oil-based coolants work well because they cool and lubricate better. Use coolants with additives to reduce rust, foam, and friction. These additives improve cutting and protect tools and parts.
Good cutting fluids make machining easier. Apply coolant evenly using flood or mist cooling. This spreads heat and avoids damage. Match the coolant to the task and tool for the best results.
Programming CNC Machines for High Precision
Programming your CNC machine correctly improves accuracy and efficiency. Set cutting parameters to avoid tool wear and work hardening. Use heat control methods like special coolants and intermittent cutting. Calibrate your machine often to keep it accurate.
Quality checks are also important. Check dimensions, surface finish, and material properties. Below is a table with tips for better precision:
Strategy/Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Heat Management | Use special coolants, adjust cutting settings, and cut intermittently. |
Quality Control Measures | Check dimensions, surface finish, and material properties. |
Machine Calibration | Regularly maintain and calibrate machines for accuracy. |
Cutting Speeds and Feed Rates | Proper settings prevent tool wear and work hardening. |
By following these steps, you can make precise, high-quality bronze parts.
Overcoming Challenges in CNC Machining Bronze
Managing Tool Wear and Prolonging Tool Life
Tool wear is a big problem when machining bronze. Harder alloys, like C954 Aluminum Bronze, can quickly dull tools. To fix this, use strong tools like carbide or coated carbide. These tools last longer and stay sharp.
Cutting speeds and feeds are also important. High speeds create heat, which wears tools faster. Slower speeds and proper feed rates reduce friction and help tools last. Check tools often for dull edges or chips. Replace worn tools quickly to avoid bad cuts or rough surfaces.
Coolants and lubricants help reduce tool wear. They keep tools cool and lower friction. Apply them evenly to protect the cutting edge. Following these tips makes tools last longer and improves machining efficiency.
Controlling Chip Formation and Removal
Machining bronze creates long chips that can clog tools. Controlling chips is key to keeping precision and avoiding tool damage. Use tools designed to break chips into smaller pieces. Sharp edges and positive rake angles make cleaner cuts and better chip removal.
Adjusting cutting settings also helps with chip control. Higher feed rates and shallow cuts stop long chips from forming. For milling, use carbide tools with chip breakers for smoother work.
A good coolant system clears chips away. High-pressure coolant removes chips from the cutting area. Air blasts work for lighter tasks. Keeping chips away protects tools and the workpiece while improving accuracy.
Preventing Surface Defects and Overheating
Surface defects and overheating are common issues in bronze machining. Problems like cracks or rough finishes happen from poor methods or bad materials. Overheating can weaken the material and cause discoloration.
To avoid defects, check that the bronze alloy meets standards. Too much iron or sulfur can make it brittle. Pouring bronze at the right temperature prevents cracks. Dry ladles stop porosity in the final product.
Overheating happens when heat isn’t managed well. Oil-based coolants with additives help spread heat and protect the workpiece. Intermittent cutting lets heat escape and avoids damage. Watching speeds and feeds also reduces heat buildup.
By fixing these issues, you get smooth finishes and strong bronze parts. These steps ensure your machining projects are high-quality.
Benefits of Proper CNC Machining Practices for Bronze
Getting a Smooth Surface Finish
A smooth surface makes bronze parts last longer. It reduces friction and wear, helping parts like bushings and bearings work better. Smooth surfaces also make contact more even, improving performance.
The table below shows how surface quality helps performance:
Aspect | Observation |
|---|---|
Surface Roughness | Smoother surfaces spread pressure evenly, lowering friction and wear. |
Tribological Properties | Smooth surfaces reduce friction and improve durability. |
Load and Pressure | Rough surfaces increase pressure, causing more friction and wear. |
By using good machining methods, you can create parts with better finishes. This improves how well they work and how long they last.
Making Parts Stronger and Work Better
Good CNC machining makes bronze parts stronger and more reliable. Bronze is tough and works well in hard conditions. For example:
C932 and C954 bronze resist wear, handling heavy loads and friction.
Bronze parts don’t rust easily, even in salty water.
Bushings, bearings, and marine parts use bronze because it’s strong and durable.
Using precise machining helps bronze parts keep these benefits. This ensures they perform well in tough situations.
Saving Material and Cutting Costs
Smart machining reduces waste and saves money. Picking the right tools and settings cuts bronze more accurately, leaving less scrap. This saves materials and lowers costs.
Using the right speeds and feeds avoids mistakes that waste time and materials. Keeping tools and machines in good shape prevents breakdowns. By improving your process, you save money and get better results.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Quality Control in CNC Machining Bronze
Regular Tool Checks and Replacement
Checking tools often is very important for good CNC machining. Look for signs like scratches or bent edges. Damaged tools can make rough surfaces and lower accuracy. Replace worn tools quickly to keep quality high and avoid problems.
Lubrication also matters, even for bronze parts that self-lubricate, like bushings. It reduces rubbing and wear, making tools and parts last longer. Clean tools and parts often to remove dirt that can cause damage. For phosphor bronze, cleaning is extra important to stop harm in wet or tough environments.
Tip: Make a schedule to check, clean, and lubricate tools. This keeps your work reliable and parts lasting longer.
Keeping Machines Calibrated and Working Well
Calibrating machines regularly keeps them accurate. Over time, machines can lose alignment, causing mistakes in parts. Calibration fixes this and keeps machines working their best.
Here’s a table showing common problems and fixes:
Problem | Fix |
|---|---|
Machine or tool issues | |
Fixing errors | Change machine settings or train workers to stop problems. |
Meeting industry rules | Follow strict standards for safety and quality. |
Watching how machines perform helps catch problems early. If something seems wrong, fix it fast. Adjust settings or teach workers better methods to avoid future issues.
Strong Quality Checks for Better Results
Quality checks make sure bronze machining meets high standards. Look at finished parts for cracks, size errors, or weak spots. Use measuring tools to confirm parts are correct.
A good quality system tracks steps and results. This shows where to improve and keeps work consistent. Train workers on quality rules to make sure all projects meet expectations.
Note: Good quality checks improve product strength and save money by reducing waste and fixing fewer mistakes.
To machine bronze well, focus on details and good methods. Pick the right alloys, set proper cutting speeds, and solve issues like tool wear and chip buildup. Managing these steps carefully gives better parts with fewer mistakes. Use these tips to make strong, top-quality parts while wasting less material. With regular practice and care, you can work more precisely and efficiently on every project.
Tip: Begin with simple tasks, improve your techniques, and grow your skills over time.
FAQ
What is the best bronze alloy for CNC machining?
The right bronze alloy depends on your project needs. C932 Bearing Bronze is great for gears and bearings because it resists wear. C954 Aluminum Bronze is strong and doesn’t rust, making it perfect for marine parts. Always choose the alloy that fits your application.
How can you reduce tool wear when machining bronze?
Use carbide or coated carbide tools for durability. Adjust speeds and feeds to lower friction. Apply coolant evenly to keep tools cool and prevent wear. Check tools often and replace them when worn to keep quality high.
Why is coolant important in bronze machining?
Coolant stops overheating, which can harm tools and parts. It also lowers friction and improves the finish. Oil-based coolants with additives work best for bronze, as they lubricate well and prevent rust.
How do you control chip formation during machining?
Use sharp tools with positive rake angles for cleaner cuts. Adjust feed rates and cutting depths to break chips into smaller pieces. High-pressure coolant or air blasts help remove chips from the cutting area.
What are the common challenges in bronze CNC machining?
Challenges include tool wear, chip buildup, and surface defects. Fix these by using strong tools, adjusting cutting settings, and applying coolant properly. Regular tool and machine maintenance also helps solve these problems.
Tip: Test your setup on a small piece of bronze first. This lets you adjust your process for better results.

Start your project with LKprototype
LKprototype company simplifies procurement for custom manufacturing, Suitable for making your products or prototypes with a variety of materials, such as metal or plastic, silicone rubber, from 3D Printing to CNC Machined Parts and Vacuum Casting , with a focus on speed and efficiency. Our platform provides instant quotes. With LKprototype, You can connect with the team to communicate your project to ensure quality and on-time delivery.
Start with an instant quote and experience how our technology and expertise can make custom part procurement faster and easier.
 LKprototype
LKprototype