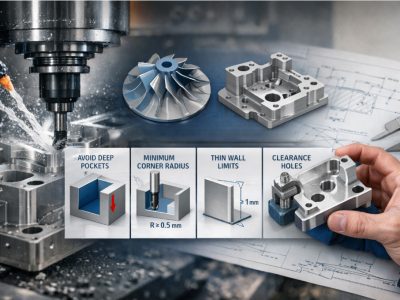
CNC machinists operate computer-controlled machines to produce precision parts and components. This crucial role involves programming and maintaining equipment to meet detailed design specifications. As technology advances, the demand for skilled CNC machinists is rising, making this a promising career path. This article will outline the duties of the CNC machinist, required skills, and career opportunities.
Key Takeaways
CNC machinists are essential in modern manufacturing, requiring a mix of technical skills, attention to detail, and strong problem-solving abilities to ensure precision in high-quality component production.
The career path for CNC machinists is promising, offering opportunities for advancement into specialized roles, management positions, and competitive salaries, driven by increasing demand for skilled professionals.
Aspiring CNC machinists should focus on gaining practical experience through vocational training, internships, and networking to stay updated on industry advancements and enhance their career prospects.
Understanding the CNC Machinist Role
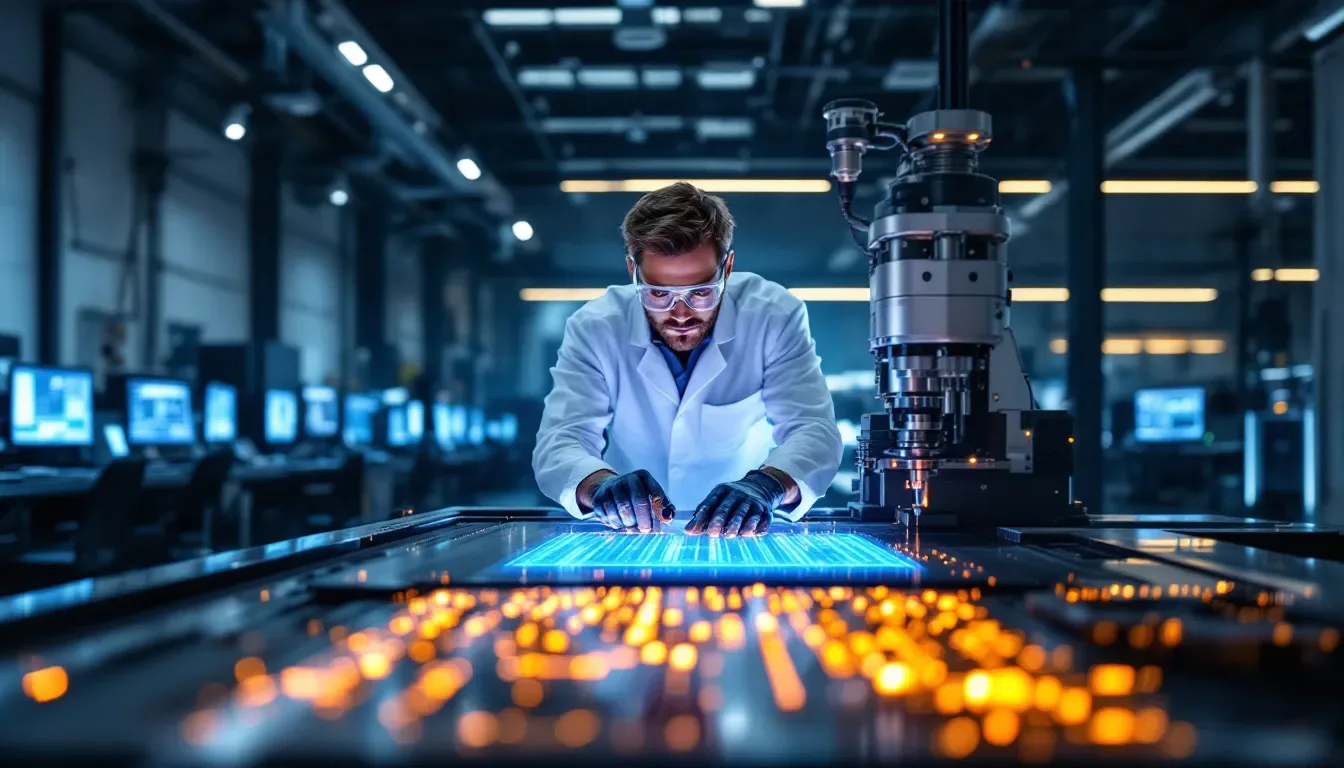

what is a cnc machinist? CNC machinists form the cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing, responsible for fabricating components with exceptional accuracy that are essential to a variety of sectors. These specialists adeptly handle and program CNC machines, performing exact cutting and shaping aligned with design blueprints. Mastery in areas such as design interpretation, mathematical calculations, mechanical knowledge, and production methodologies is pivotal to fulfill their role effectively—maintaining high standards of quality for each manufactured part.
Their significance within the industry is undeniable. CNC machinists are key players in generating parts for fields as diverse as aerospace and automotive by ensuring all products adhere strictly to predefined measurements. As technological advancements proliferate, there’s an escalating need for proficient CNC machinists—a trend which signals robust career opportunities for individuals drawn toward precision engineering and innovative technology.
Defining CNC Machinists
CNC machinists hold the critical role of programming, setting up, and managing CNC machines to craft precise parts. They are responsible for loading raw materials into equipment, monitoring production runs, and checking completed pieces against design requirements to confirm they conform to specifications. To embark on a career as a CNC machinist requires one’s proficiency in reading blueprints and computer-aided design (CAD) documents that dictate the exact parameters for creating each component through the machining process.
These professionals utilize an extensive range of machine tools including lathes, milling machinery, laser cutting devices, and comprehensive machining centers to manufacture diverse components with utmost accuracy. Given their reliance on varied implements such as drill bits or end mills tailored for distinct manufacturing operations, understanding tool specifics is vital for any CNC operator aiming to understand their functional scope thoroughly.
Beyond just mechanical knowledge in manipulating heavy-duty equipment safely and effectively. Dexterous metalworking abilities along with meticulous attention-to-detail come into play in this field substantially too. Aspiring practitioners should be conversant not only technically but also practically via hands-on involvement—dedicating themselves fully toward delivering superior-quality products consistently amidst operating multifaceted machinery setups.
Key Responsibilities of CNC Machinists
CNC machinists are primarily responsible for the operation, setup, and upkeep of diverse CNC machine tools. They oversee aspects such as adjusting machine feed and speed, ensuring machinery functions at its best by carrying out routine maintenance checks, all while maintaining process efficiency and precision.
These machinists meticulously measure and inspect the completed items to identify any flaws or defects. It’s crucial that they guarantee each product meets established specifications to uphold production quality standards and avoid expensive mistakes.
To ensure that machines remain in excellent working order with minimal interruptions in operation, CNC machinists regularly clean their equipment and perform necessary maintenance tasks on their CNC machinery.
Essential Skills for CNC Machinists

Being a proficient CNC machinist requires an amalgamation of distinct skills, encompassing technical acumen, analytical thinking, and communication prowess. A keen attention to detail is essential in this role, along with strong capabilities in mathematics and the aptitude for solving complex problems. Since CNC machinists often operate within team settings, exemplary communication and teamwork abilities are critical to ensure seamless workflow.
Candidates who have completed vocational training at a trade school are typically favored by employers due to the comprehensive technical knowledge and practical experience gained through such programs.
Discussion will delve into the specific competencies needed by CNC machinists. These include not only their technological know-how, but also their capacity for analysis, problem-solving techniques, as well as their facility for both interpersonal communication and group collaboration.
Technical Skills
Mastery of technical abilities is fundamental to the proficiency of CNC machinists. These experts oversee the functioning, programming, and generation of G-code for the efficient management of CNC machines. The skill to interpret blueprints and technical drawings is crucial as it empowers machinists to fabricate components with precision that adhere strictly to design guidelines. It’s advisable for those seeking a career in this domain to pursue courses in blueprint interpretation, technical drafting, and machining tool operations.
For CNC Machinists, software applications such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) are vital tools of their trade. CAD programs facilitate detailed creation designs by machinists while CAM systems convert these designs into executable machine code used during production processes—augmenting accuracy and productivity which are key elements in CNC machining.
As manufacturing becomes more dependent on automation and sophisticated technologies continue to advance rapidly, there is an escalating need for skilled CNC machinists within the industry. A combination of hands-on experience along with expertise in various tech skills can propel these professionals towards thriving careers amidst ongoing industrial transformations.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills
CNC machinists are heavily reliant on their analytical thinking and problem-solving capabilities. These competencies are key to effectively diagnosing and resolving the intricate issues that can occur within the machining process. Their ability to meticulously scrutinize details and apply strong problem-solving techniques is instrumental in enhancing operational productivity and streamlining the production process.
To excel in their field, CNC machinists require a combination of sharp analytical skills alongside adeptness at solving problems. This skill set is vital for pinpointing faults or refining production workflows, ensuring adherence to high-quality standards, and facilitating uninterrupted machinery performance during operations.
Communication and Collaboration Skills
For CNC machinists to excel in a collaborative, team-based professional environment, having excellent communication skills is vital. These skilled workers must frequently engage with various departments and demonstrate adaptability as well as a capacity for teamwork to boost their performance. When CNC machinists possess a strong work ethic centered on collaboration, both productivity and the quality of their output are significantly enhanced.
Beyond mastering the technical aspects of CNC operation, it’s crucial that these specialists can convey information clearly with colleagues. Effective dialogue regarding machine setups, diagnosing problems promptly, and orchestrating joint efforts are key elements to maintain streamlined production processes.
Possessing robust communication and cooperative skills lays the foundation for fostering a professional atmosphere where collective effort flourishes amongst CNC machinists.
Educational Pathways to Become a CNC Machinist
To embark on a career as a CNC machinist, one can opt for either an academic or vocational track. It is essential to have a solid grasp of mathematics, especially in areas such as algebra and geometry.
Moving forward, we will delve into the various educational avenues that one may pursue. These include obtaining a high school diploma, engaging in vocational training programs, acquiring certifications, participating in apprenticeships, and gaining valuable on-the-job experience.
High School Diploma or GED
The minimum educational requirement to become a CNC machinist is a high school diploma or GED. Completing science and mathematics courses in high school significantly benefits aspiring CNC machinists, as these subjects provide a strong foundation for the technical skills required in the field.
Apart from a diploma, an affinity for computers, problem-solving skills, attention to detail, basic skills, and math skills are essential for success in this career.
Vocational Training and Certifications
Enrolling in technical colleges is critical for gaining the necessary skills and expertise needed to pursue a career in CNC machining. Pursuing Education and obtaining certifications can significantly improve career progression prospects for those working as CNC machinists. Trade schools often collaborate with local businesses to offer practical training opportunities, which are invaluable for students aiming to gain experience in CNC machining.
Earning a certification demonstrates proficiency in operating CNC machines, requiring one to successfully pass both a written examination and an assessment of hands-on competencies as a machinist. Becoming involved with professional organizations offers important benefits such as network building and access to current information within the industry for those specializing in CNC.
Engagement in workshops and events specific to the industry not only bolsters networking opportunities, but also ensures that CNC machinists remain informed about technological advancements. It’s imperative for individuals involved with cnc machinery operations who wish maintain their competitive edge within this dynamic sector of technology-driven manufacturing, embracing continuous educational growth plays an essential role.
Apprenticeships and On-the-Job Experience
Internships and apprenticeships are vital avenues for aspiring CNC machinists to acquire practical, hands-on experience. Participating in internships, apprenticeships, or entry-level positions is essential for gaining hands-on experience in CNC machining. Many CNC machinists begin their careers in lower-level positions before advancing to machinist roles.
Participating in internships or co-op programs can significantly enhance practical skills for aspiring CNC machinists. Hands-on experience is required to become a CNC machinist, and on-the-job training in an entry-level position is one way to gain this experience.
The purpose of a formal apprenticeship for aspiring CNC machinists is to gain hands-on experience and apply theoretical knowledge.
Daily Life and Work Environment of CNC Machinists

Operating within a hygienic and professional setting, CNC machinists combine mechanical design with advanced technology. For these specialists, possessing robust skills in teamwork is imperative when working together in collaborative manufacturing settings. To excel in the field of CNC machining, machinists must not only be adept at collaboration, but also proficient in effective communication.
CNC machinists are responsible for performing meticulous quality inspections on completed items to ensure they meet established manufacturing criteria. It’s part of their routine to carry out consistent maintenance on machines to maintain peak functionality and avoid operational interruptions. A keen focus and an eye for detail are vital attributes that aid CNC machinists in avoiding mistakes during the machining process.
Typical Daily Tasks
Previously, CNC machinists were involved in a variety of day-to-day responsibilities that ranged from initializing machines and operating parts to supervising G code. Standard duties for a CNC machinist included the loading and unloading of machinery, undertaking programming tasks, and managing different types of machines. In this context, the Setup Man was pivotal in confirming that CNC machines were appropriately prepared prior to commencing production.
Subsequently: The daily routine for CNC machinists includes:
Machine setup
Operation of components
Oversight of G code
Machinery loading and offloading activities
Execution of programming
Handling various machinery
A vital figure within this system is the Setup Man whose primary function involves certifying accurate configuration settings on all CNC equipment before initiating any manufacturing process.
The proficiency in swiftly pinpointing problems followed by immediate rectification actions is indispensable among CNC technicians as they are tasked with troubleshooting without delay so as to maintain seamless operations. These professionals regularly encounter unforeseen predicaments which require robust critical-thinking abilities along with adept problem-solving capabilities aimed at preserving operational effectiveness.
Through an amalgamation comprised both regularity in standard chores coupled with dynamic resolution when facing issues allows those specializing as CNM Machiners expertly fine-tune ongoing productive endeavors.
Work Procedures and Safety Measures
CNC machinists must comply with rigorous safety protocols to guarantee the secure utilization of machinery. It is essential for prospective CNC machinists to possess a thorough understanding of these safety procedures in order to avoid incidents at work. They are obligated to follow OSHA safety regulations, which ensure the machinery operates safely.
It’s critical for those involved in operating heavy machinery in the realm of CNC machining to comprehend and put into practice these safety measures. Adhering to such protocols is indispensable for fostering both a safe and productive atmosphere within manufacturing facilities.
Career Progression and Job Outlook for CNC Machinists
CNC machinists have the potential for a dynamic career trajectory, with various avenues available for professional development and specialization. Individuals beginning at the CNC operator entry level may progress to roles such as CNC programmer, setup machinist, or quality control inspector. The future prospects for those in the field of CNC machining appear positive due to consistent demand fueled by technological advancements in automation and manufacturing.
Career progression is influenced by factors including an individual’s job performance, skill set proficiency, and academic qualifications. With accruing experience and honed expertise, machinists are able to ascend to positions of leadership or management where they supervise production operations and guide teams comprising fellow machinists.
Subsequent sections will provide a more thorough examination into ascending the ranks within this profession along with insights into labor market tendencies regarding employment opportunities for those skilled in CNC machining.
Climbing the Professional Ladder
CNC machinists are presented with a variety of pathways for career growth, including the possibility to advance to positions like supervisor, journeyman machinist, and CNC technician. Those who have garnered significant experience in the field may also progress into more niche roles such as setup machinist, CNC programmer, quality control inspector or take on managerial duties. With these higher-level roles typically come greater responsibilities and an increase in pay.
It is essential for CNC machinists aiming to climb their career ladder to gain direct hands-on experience with both machine operation and related software applications. As they ascend through their professional trajectory, CNC machinists frequently transition from hands-on interaction with machines towards leading teams and directing production processes. Achieving this level of advancement necessitates a blend of technical proficiency specific to machining equipment (CNC skills), leadership capabilities as well as comprehensive knowledge about the intricacies involved in machining operations.
Job Market Trends and Demand
CNC machinists can look forward to a favorable job outlook, as employment in this field is anticipated to grow by 3% each year through 2029. The number of jobs available for CNC machinists may be influenced by the economic climate and the geographical region, with some areas offering more opportunities than others. Presently, California, Ohio, and Michigan are the leading states when it comes to hiring rates for those specialized in CNC machining.
An average yearly wage of approximately $64,981 can be expected for professionals working as CNC machinists. Salaries often vary depending on where they work within different regions. Skilled CNC machinists remain highly sought after due to ongoing advancements in manufacturing technology and automation processes — factors which contribute significantly toward making this profession an appealing option characterized by consistent growth prospects in terms of employment.
Salary Expectations and Earning Potential
CNC machinists receive a strong wage as they undergo training in a Manufacturing Apprenticeship program. Their earnings potential rises notably with the accumulation of experience and specialization within their field.
Subsequent sections will offer comprehensive details about the typical salary range for CNC machinists and outline the various elements that influence their income.
Average Salary Range
CNC machinists typically earn an average annual income of approximately $47,000. Labor statistics indicate that the mean yearly compensation for CNC machinists stands at around $48,510. This can fluctuate depending on factors such as experience and geographic location.
In 2019, it was documented that CNC machinists had an average yearly salary of $44,420.
Factors Affecting Earnings
The earnings of CNC machinists are impacted by several key factors, which include:
The state in which they work
The size of their employer
The particular industry in which they operate
Their level of experience
In states like Washington, New York, and Massachusetts, CNC machinists tend to receive higher pay. Those with extensive experience can command hourly rates exceeding $50.00, thereby considerably boosting their yearly income.
Geographical location is a major determinant in the variation of salaries for CNC machinists. On average, their median annual salary stands at $42,260. Both the dimensions of an employing organization and its specific sectoral focus play roles in shaping potential earnings – larger enterprises and industries with niche specializations typically present more substantial wage offerings.
Tools and Technologies Used by CNC Machinists

CNC machinists harness the capabilities of advanced equipment and technology, such as computer numerical control (CNC), to achieve precision and efficiency when machining parts. The integration of specialized machine tools with complex software is essential for fabricating components that meet exacting standards. In their operation of CNC machines, these skilled professionals meticulously utilize machine tool technology to produce high-quality results.
Subsequent segments will explore the various machine tools and equipment utilized by CNC machinists. To discussing the supportive role played by software and programs in enhancing their work.
Machine Tools and Equipment
CNC machines serve as sophisticated equipment that facilitates the automation of machining operations, ensuring accuracy and consistency when crafting components. The array of CNC machinery encompasses lathes, mills, routers, and plasma cutters designed for distinct roles within the machining realm. Additional vital instruments and apparatus encompass cutting implements, holders for these tools, gauges for measurement purposes, as well as clamping devices to assist throughout the production process.
Choosing appropriate machine tools and related equipment is paramount to achieving efficiency, maintaining safety standards, and securing effective outcomes in CNC machining endeavors. These resources empower CNC machinists in handling a diverse range of raw materials like metal alloys or plastics while they manufacture meticulously crafted final products with high precision.
Software and Programs
Software for CNC machining integrates systems of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), facilitating the efficient production of parts. Autodesk Fusion, a well-regarded CNC software, assists in creating toolpaths and translating designs into G-code that operates machines. An effective piece of CNC software can significantly improve workflow by merging the processes of designing and manufacturing into one seamless system.
Selecting appropriate CNC software requires evaluating its compatibility with specific machines used in cnc operations as well as the tasks intended for production. The complexity of available cnc programs varies widely. Some provide simple functionality to transmit G-code to cnc machines while others are more elaborate packages offering CAD, CAM, and simulation features all together.
Tips for Aspiring CNC Machinists
Aspiring CNC machinists should have a desire to work in technology, a passion for precision, and the capability for complex tasks. Gaining relevant experience and networking with industry professionals are crucial strategies for success in this field.
The following sections will provide practical tips for aspiring CNC machinists, including gaining relevant experience and the importance of networking and continuous learning.
Gaining Relevant Experience
Acquiring pertinent experience is critical for prospective CNC machinists to improve their skills in the machining process and broaden their career prospects. Essential training and certifications from recognized trade institutions are vital in equipping individuals with the needed expertise in CNC machining. Gaining practical experience through apprenticeships and introductory roles at machine shops provides an opportunity to learn directly from experienced professionals while engaging hands-on with the work.
It is equally important for those aspiring to succeed as machinists to network with experts within the industry and commit to ongoing education, ensuring they remain abreast of technological advancements and enhance their machine operation competencies. Such experiences offer invaluable insight into actual production settings, laying a robust groundwork for forging a prosperous career path.
Networking and Continuous Learning
In the manufacturing sector, it’s imperative for CNC machinists to forge strong professional networks as this opens doors to new job prospects and essential industry contacts. This can be achieved by being present at trade shows, becoming a member of relevant organizations, and engaging in digital forums. Such interactions offer a glimpse into emerging trends within the industry and forthcoming employment opportunities, thus facilitating career progression.
For CNC machinists aiming to remain proficient and competitive in their field, it is critical to engage in ongoing education regarding the latest developments in both CNC technology and machine operation techniques. When these individuals blend networking with continuous learning efforts, they are able not only to gain valuable insights from colleagues, but also to exchange expertise while refining their abilities—thereby significantly bolstering their vocational trajectories.
Summary
To excel as a CNC machinist, one must integrate technical expertise, analytical thought processes, and proficient communication. Pursuing appropriate educational routes while acquiring practical experience and embracing ongoing learning will pave the way for hopeful CNC machinists to forge fulfilling careers. With the rising need for adept CNC machinists in the marketplace, plentiful prospects exist for professional development and progression. By confronting obstacles with enthusiasm and maintaining an inquisitive mind-set, you can position yourself at the cutting edge of the manufacturing sector—literally shaping what’s next with each meticulous incision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary responsibilities of a CNC machinist?
As a CNC machinist, you’ll set up and operate CNC machines, program them for precision work, and carry out quality checks while ensuring everything runs smoothly through regular maintenance.
Embrace these responsibilities for a successful and fulfilling career!
What educational background is required to become a CNC machinist?
To become a CNC machinist, you’ll need at least a high school diploma or GED, and pursuing vocational training or certifications can significantly enhance your skills and career opportunities.
Take that step towards a rewarding future today!
What is the average salary range for CNC machinists?
The average salary for CNC machinists is around $47,000, but it can vary based on factors like experience and location.
With skill development and industry experience, there’s potential to earn even more!
What tools and technologies do CNC machinists use?
CNC machinists operate sophisticated machine tools, including lathes and mills, in conjunction with CAD and CAM software to achieve accurate design and production.
By adopting these technologies, you can improve your machining skills and advance your career!
How can aspiring CNC machinists gain relevant experience?
To gain relevant experience as a CNC machinist, focus on vocational training and seek apprenticeships or entry-level positions to build your skills.
Networking with industry professionals can also provide valuable insights and opportunities to advance your career.
Still, need help? Contact Us: [email protected]
Need a PROTOTYPE or PARTS machining quote? Quote now
 LKprototype
LKprototype