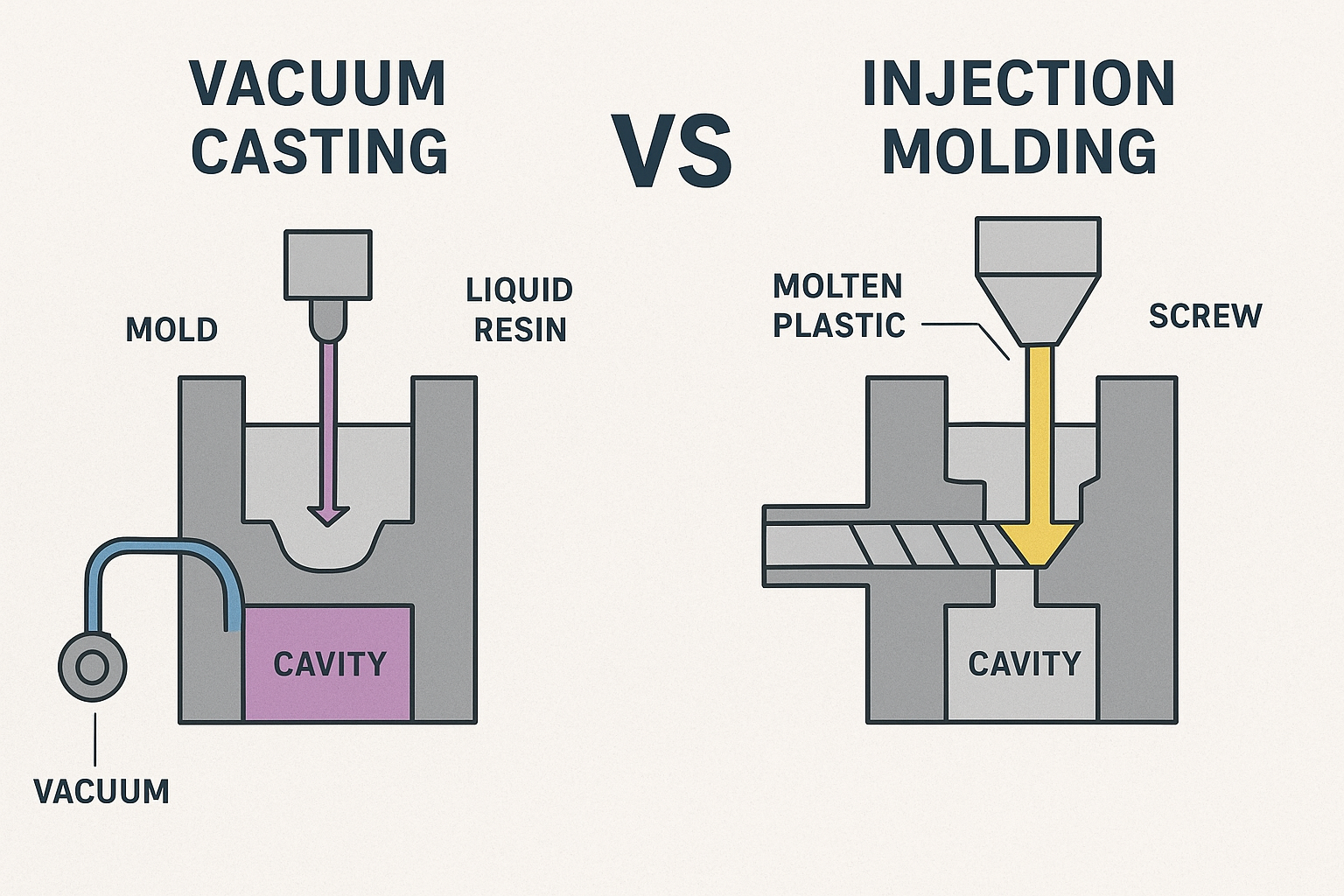
If you want to make a few parts or test ideas, vacuum casting is fast and costs less at the start. However, if you need to make many parts, injection molding is cheaper for each part and can produce millions. When considering your options, think about factors like price, the quality of the parts, how quickly you need them, the materials you want, and the complexity of the parts. Below is a comparison of Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding:
Factor | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Tooling Cost | $200–$1,000 | $10,000+ |
Per-Part Cost | $10–$100 | <$1 (at scale) |
Lead Time | 10–20 days | 4–12 weeks |
Production Volume | 50 prototypes | 2 million units |
Material Options | Limited resins | Wide range of plastics |
This chart helps you choose the best method for your project by comparing Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding.
Key Takeaways
Vacuum casting works well for small amounts and prototypes. It has lower starting costs and is faster for testing new designs.
Injection molding is good for making many parts at once. The cost for each part goes down when you make more, so it saves money for big orders.
Think about how hard your parts are to make. Vacuum casting is great for making detailed samples. Injection molding is better for tricky shapes and thin parts.
Look at what materials you need. Injection molding lets you pick from more materials. This helps make parts that are stronger and last longer.
Use the checklist in the blog to help you choose. Pick the best method for your project by looking at how many parts you need, how hard they are to make, and your budget.
Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding: Process Overview

Vacuum Casting Basics
Vacuum casting is good for making a few plastic parts fast. First, you make a master model, often with 3D printing. Next, you pour liquid silicone over the model to make a mold. The mold has two pieces. When the silicone sets, you take out the master model. Then, you put the empty mold in a vacuum chamber. You pour liquid resin into the mold. The vacuum pulls out air bubbles. This helps the parts look smooth and detailed. The mold sits in an oven or at room temperature to harden. When the part is hard, you open the mold and take it out. You can use the same silicone mold about 20 to 25 times. After that, it wears out. Vacuum casting is best for making prototypes or small batches. It gives nice details and a good surface, but you cannot use as many materials as other ways.
Injection Molding Basics
Injection molding is used to make lots of parts, even millions. You start with a metal mold, made from steel or aluminum. The mold costs more, but it lasts a long time. Plastic pellets go into a machine and melt. The machine pushes the melted plastic into the mold with high pressure. The plastic cools and gets hard inside the mold. Then, the machine opens the mold and pushes out the part. This process is very fast and can be repeated many times. Injection molding makes strong and exact parts. You can use many kinds of materials. It is best for making a lot of parts because the cost per part goes down as you make more.
Here is a quick comparison of the main process steps:
Process Step | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Mold Preparation | Two-piece silicone mold placed in a vacuum chamber | Machined mold made from steel or aluminum |
Material Preparation | Raw material mixed and degassed | Raw plastic material melted in the injection unit |
Filling | Liquid plastic poured into the mold | Melted plastic injected into the mold |
Curing | Cured in an oven or at room temperature | Cools and solidifies in the mold |
Mold Removal | Mold opened to release the casting | Ejection of the final part from the mold |
Reusability | Silicone mold can be reused | Machined molds are typically not reused |
When you look at vacuum casting and injection molding, you see some big differences. Vacuum casting is better for small batches and quick jobs. Injection molding is better for making lots of parts over a long time. Injection molding also lets you use more materials and gives stronger parts. If you want to save money on a small batch, vacuum casting is a good pick.
Cost Comparison: Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding

Tooling and Setup Costs
When you look at vacuum casting and injection molding, you see a big difference in setup costs. Vacuum casting uses a silicone mold. This mold costs much less than the metal molds for injection molding. You can start vacuum casting for a few hundred dollars. Injection molding needs at least $10,000 just for the mold.
Vacuum casting has lower starting costs. It is good for small batches or prototypes.
Injection molding needs expensive metal molds. These molds last a long time, but you must make many parts to make the cost worth it.
The total cost for vacuum casting includes the master pattern, resin for each part, and labor to make the mold.
For injection molding, the setup cost is high. But you save money as you make more parts.
If you want to test a design or make a small number of parts, vacuum casting keeps your costs low. For making lots of parts, injection molding saves money over time.
Per-Part Cost Analysis
The price for each part changes based on how many you make. In vacuum casting, each part costs more. The process is slower and the silicone mold wears out after 20 to 25 uses. Material costs for vacuum casting can be 40-60% of the total cost. Labor is also important because making each mold and part takes time and skill.
Picking materials matters. Cheaper plastics like HMWPE lower your cost. High-performance plastics like polycarbonate cost more.
Labor costs depend on worker skill. Skilled workers make better parts faster, but they cost more.
In injection molding, the cost per part drops when you make more parts. The machine works fast. The metal mold can make thousands or millions of parts before wearing out.
If you only need a small number of parts, vacuum casting gives you flexibility and keeps costs down. If you need lots of parts, injection molding gives you a much lower cost per part.
Cost Efficiency by Volume
How many parts you need affects which process is best. Vacuum casting is better for small batches, like 20 to 30 pieces. You can change your design easily and avoid high starting costs. Injection molding is best for making lots of parts. The high mold cost is worth it when you make thousands or millions.
Vacuum casting can save you 30–60% compared to injection molding for small batches.
For lots of parts, injection molding is the cheapest choice. The more you make, the lower the cost per part.
Vacuum casting is great for testing and small orders, where you might change the design.
Injection molding is best for making lots of parts, where you want the lowest cost per part.
Tip: If you plan to make less than 100 parts, vacuum casting is usually the best deal. If you need thousands or more, injection molding saves you money over time.
Cost Table Overview
Here is a table to help you compare costs for both ways:
Feature | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Initial Setup Cost | Low to moderate | High |
Tooling | Silicone mold | Steel or aluminum mold |
Tooling Cost | $200–$1,000 | $10,000+ |
Per-Unit Cost | Higher for large volumes | Lower for large volumes |
Cost per Part | $10–$100 | <$1 (at scale) |
Cost Effectiveness | Best for small batches | Best for high volumes |
Small Production Runs | Very cost-effective | Not cost-effective |
High Volume Production | Not cost-effective | Very cost-effective |
Vacuum casting is best for small batches and testing ideas. Injection molding is better for making lots of parts. It gives the lowest cost per part and is most cost-effective for big jobs.
Scenario | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Production Volume | Good for smaller runs | Good for high-volume runs |
Cost per Part | Higher for lots of parts | Lower per unit in big batches |
Flexibility in Prototyping | Easy to change designs | Hard to change after setup |
When you pick between vacuum casting and injection molding, think about how many parts you need, your budget for molds, and if you want to change your design. This helps you choose the best way to save money for your project.
Quality Factors: Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding
Precision and Detail
Vacuum casting and injection molding are different in how exact they are. Vacuum casting uses silicone molds. These molds copy every tiny part of the master model. The parts made have tight tolerances, usually within ±0.2mm. This is good for prototypes or parts with tricky shapes. You can expect high accuracy for small details. It works well for low-volume runs. It is great for making parts with lots of detail.
Injection molding also makes good plastic parts. It is faster and makes more parts at once. It can make detailed parts, but the tolerances are not as tight. You might see small changes in big batches.
Surface Finish
Vacuum casting gives smooth surfaces. The silicone mold copies the finish of the master model. The part looks and feels like the final product. This makes vacuum casting a good pick for fancy items or display models.
Injection molding also makes nice surfaces. Polished metal molds help make them smooth. Sometimes, you see small marks from the mold or when the part comes out. Both ways make quality parts, but vacuum casting is often better for surface finish in small batches.
Tip: If you want a prototype that looks finished, vacuum casting is a strong choice.
Material Choices
Both processes let you pick from many materials. Injection molding has more options. Vacuum casting uses resins and rubbers like ABS, PC, PMMA, and PP. These work well for most prototypes. Some resins, like X522HT, let light pass through. These are good for clear parts, such as lenses.
Injection molding uses many plastics. These include PMMA, PC, ABS, HDPE, PP, PA, and PBT. This lets you choose what you need, like strength, flexibility, or clarity.
Vacuum Casting Materials | Injection Molding Materials |
|---|---|
PX5210, PX520, PX223, Hei-Cast 8150, ABS, PC, PMMA, PP | PMMA, PC, ABS, HDPE, PP, PA, PBT, and more |
Durability
Durability is important when picking a process. Vacuum casting uses silicone molds. These molds last for 10 to 25 parts. The parts have good detail and are flexible. They do not last as long or are as strong as injection molding parts.
Injection molding uses metal molds. These molds can make millions of parts. The parts are strong and resist impacts. This makes injection molding best for tough jobs, like cars or airplanes.
Method | Durability (Lifespan) | Mechanical Properties |
|---|---|---|
Vacuum Casting | Limited (10-25 parts) | Lower durability and strength |
Injection Molding | High (millions of cycles) | Higher durability and strength |
Pick vacuum casting for prototypes or short runs. Choose injection molding for strong plastic parts that last a long time.
Production Volume and Speed
Low-Volume Suitability
Sometimes you only need a few parts to test or sell early. Vacuum casting is good for this. You can make high-quality prototypes and small batches. Usually, you make between 20 and 100 pieces. This method lets you change designs easily. It also keeps your costs low. You do not need to buy expensive metal molds. Many industries use vacuum casting for car parts and other products. It works well when you do not need many pieces.
Production Volume Range | Description |
|---|---|
20-100 pieces | Good for small runs, especially for prototypes and limited production because it saves money and lets you change designs. |
Vacuum casting works well for small batches, often up to 100 pieces.
You can test new ideas quickly and change them without spending a lot.
High-Volume Suitability
If you need thousands or millions of parts, injection molding is better. This process uses strong metal molds that last a long time. You can make parts quickly and pay less for each one. Injection molding is best for making lots of parts. It can handle big jobs. You get strong and tough parts. You can use many kinds of plastics.
Injection molding saves money and works well for big jobs.
Vacuum casting does not work well for large batches. The silicone molds wear out fast and need to be replaced often.
Injection molding gives you more choices for materials and stronger parts.
Lead Times
Speed is important when you need parts fast. Vacuum casting is quick for prototypes and small batches. You can make and cure parts in just a few hours. This helps you go from design to finished part quickly. Injection molding takes longer at first. You must make a complex mold. After the mold is ready, you can make parts very fast. It only takes seconds or minutes.
Tip: Pick vacuum casting for fast prototypes and small batches. Choose injection molding for quick production after the mold is made.
Vacuum casting is faster for small batches. Injection molding is faster for making lots of parts.
Part Complexity and Design Flexibility
Design Freedom
When picking how to make parts, you want to know how much you can change your design. Vacuum casting lets you change designs easily. You can test new ideas fast and not spend a lot. Silicone molds let you add cool features, but they do not work well with deep undercuts or very thin walls. Injection molding is good for making shapes with thin walls and undercuts. You can make detailed and tricky inside parts. But changing your design costs more and takes longer because metal molds are pricey.
If you want to try many versions, vacuum casting helps you do it quickly. If you need a final part with hard shapes, injection molding is the best way.
Feature | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Design Complexity | Handles some tricky designs | Great for hard shapes, thin walls, and undercuts |
Flexibility in Design Changes | Easy to change designs fast | Hard to change because molds cost a lot |
Iteration Speed | You can test ideas quickly | Testing takes longer and costs more |
Internal Structures | Not good for tough inside shapes | Can make tricky inside shapes |
Tolerance and Repeatability
You want your parts to be the same every time. Vacuum casting uses soft silicone molds that copy small details. At first, you get very accurate parts. But after many uses, the mold wears out. This can make later parts a little different. Injection molding uses strong metal molds. These molds keep their shape for thousands of parts. You get parts that are always the same.
Vacuum casting is great for detailed prototypes.
Injection molding makes sure every part is just like the last one.
Complex Geometries
Sometimes you need parts with hard shapes. Vacuum casting works well for thin walls and big hollow parts. It is best for simple shapes like panels or blister packs. Injection molding lets you make solid parts with tiny details and tight fits. You can make shapes that are hard to do with other ways.
Vacuum casting is good for quick prototypes and simple hollow parts.
Injection molding is best for making solid, detailed parts in big numbers.
If you want to balance design freedom, accuracy, and tricky shapes, think about what your project needs. Vacuum casting helps you test and change designs fast. Injection molding gives you strong and exact parts for lots of products.
Best Use Cases: Vacuum Casting vs Injection Molding

When to Choose Vacuum Casting
Pick vacuum casting if you need prototypes or a few parts. This method is good for testing new ideas. It helps you make working models fast. You can change your design easily and save money on tools. Vacuum casting gives parts with lots of detail and smooth surfaces. Use it for test runs before making lots of parts.
Here are the best times to use vacuum casting:
You want to make prototypes for user testing or design checks.
You need working models for mechanical or looks testing.
You plan to make a small batch for customer trials or certifications.
You want to try different versions before picking a final design.
You need parts with fine detail, like dashboard pieces or light covers.
You work in fields like cars, consumer goods, electronics, or medical devices.
Tip: Vacuum casting lets you go from idea to finished prototype quickly. You can change things without spending a lot.
Industry | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|
Automotive | Intake manifolds, dashboard pieces, light covers, aerodynamic parts |
Consumer Products | Toys, sports gear, wearables, smart home gadgets |
Electronics | Housings, battery cases, cell holders, handheld devices |
Medical Devices | Prototyping for comfort, assembly fit |
Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|
Pre-series Production | Mechanical and looks testing |
Certifications | Customer trials |
When to Choose Injection Molding
Pick injection molding if you need lots of the same part. This method is best for making many parts. You get strong, tough pieces that look the same. Injection molding works with many plastics and tricky shapes.
Choose injection molding in these cases:
You need thousands or millions of parts for your product.
You want low cost per part for big batches.
You need parts that are strong and always the same.
You plan to use many materials for different needs.
You work in fields like aerospace, cars, electronics, or medical devices.
Note: Injection molding is best for making many strong, matching parts.
Industry | Common Applications |
|---|---|
Aerospace | Bezels, chassis pieces, covers, housings, panels |
Automotive | Housings, cupholders, dashboard pieces |
Electronics | Assemblies, battery covers, circuit board cases |
Medical | Plastic covers, parts for MRI machines |
Real-World Examples
You can see how vacuum casting and injection molding help in real projects. Here are some examples:
Car companies use vacuum casting to make detailed dashboard models for user tests. This helps them change designs faster and launch products up to 30% sooner.
Medical device makers use vacuum casting for working models of tools and implants. They get high accuracy and save 20-40% on costs for small batches.
Electronics companies use vacuum casting to make working models for phones and wearables. They test and improve designs quickly before making lots of parts.
Artists and jewelers use vacuum casting to copy detailed designs. They make custom products with fine detail and matching quality.
A startup used vacuum casting to make working models for a new electronic device. They tested and improved the design before switching to injection molding for big production.
Tip: Use vacuum casting for quick, flexible prototype runs. Switch to injection molding when you need lots of strong, matching parts.
Quick Decision Guide
Checklist
You want to pick the best way for your project. Use this checklist to help you choose between vacuum casting and injection molding. Think about each question and see which process fits you.
How many parts do you need?
If you need just a few or some prototypes, vacuum casting is good. If you need hundreds or thousands, injection molding is better.How complex is your part?
Vacuum casting works for detailed shapes and smooth surfaces. Injection molding is good for thin walls and hard inside shapes.What materials do you want to use?
Vacuum casting uses curable plastics and resins. Injection molding lets you pick from many thermoplastics and thermosets.How fast do you need your parts?
Vacuum casting gives quick results for small batches. Injection molding takes longer to set up but makes parts fast once ready.What is your budget for tooling?
Vacuum casting costs less for molds. Injection molding needs more money for metal molds.Do you care about environmental impact?
Some injection molding materials can be recycled. Vacuum casting molds wear out faster and may make more waste.
Tip: Write down your answers for each question. The process that matches most of your needs is probably the best choice.
Decision Table
You can use this table to compare vacuum casting and injection molding. Look at each row and see which way fits your project.
Criteria | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
Production Volume | Best for prototypes or small runs (1–10 parts/day) | Best for medium to large runs (hundreds to thousands) |
Tooling Cost | Low (uses silicone molds) | High (uses steel or aluminum molds) |
Part Cost | Higher per part | Lower per part at scale |
Material Options | Limited to curable plastics and resins | Wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets |
Lifespan | Silicone molds wear out quickly | Metal molds last for years |
Part Complexity | Good for detailed and smooth parts | Good for thin walls and complex shapes |
Environmental Sustainability | Less recyclable, more mold waste | More recyclable materials, longer mold life |
Production Speed | Fast for small batches | Fast for large batches after setup |
Lead Time | Short for prototypes and small runs | Longer for setup, then quick for mass production |
Use this table to match your project needs with the right process. If you want flexibility and quick results, vacuum casting is a strong choice. If you need lots of parts and lower costs, injection molding is the way to go.
You can pick vacuum casting if you need prototypes or a few parts. This way works well for tricky shapes and small details. You spend less money on starting and making molds. Injection molding is good for making lots of parts. You get tough pieces and pay less for each one. Look at the decision guide and tables to see what fits your project. If you want more help, check out guides on manufacturing or ask an expert.
Vacuum casting works best for small batches and detailed samples.
Injection molding is great for making many strong, matching parts.
FAQ
What is the main difference between vacuum casting and injection molding?
Vacuum casting uses silicone molds for small batches. Injection molding uses metal molds for large production. You get faster prototypes with vacuum casting. You get lower costs per part with injection molding.
Can you use the same mold for many parts in vacuum casting?
You can reuse a silicone mold about 20 to 25 times. After that, the mold wears out. For more parts, you need a new mold.
Which process gives you stronger parts?
Injection molding gives you stronger and tougher parts. Metal molds and high-pressure machines make parts that last longer and resist damage.
How fast can you get parts with vacuum casting?
You can get parts in about 10 to 20 days. This includes making the master model and curing the resin. Vacuum casting works well for quick prototypes.
 LKprototype
LKprototype