Product design and prototyping mean making and improving a product. Prototyping is very important in this process. It helps test ideas, check if things work, and make sure the product is easy to use. This happens before making the product fully. It helps find problems early, saving time and money.
Prototyping makes products much better. Look at these facts:
Repeating design steps makes product launches 75% more successful.
Starting prototyping early cuts product failures by 75%.
Using user feedback during prototyping makes products 50% more successful.
By using prototyping, you can avoid risks, test ideas, and make products that users really want.
Key Takeaways
Prototyping is important to test ideas and fix problems early. It saves both time and money by spotting issues quickly.
Simple prototypes in the beginning allow fast changes and feedback. This encourages creativity and improves ideas without spending too much.
Detailed prototypes are needed for testing and user interaction. They show how a product works and help explain ideas to teams.
Getting user feedback during prototyping makes products better. It ensures designs match what users want, making them happier.
Picking the right prototyping tool depends on your project. Tools like Figma help teams work together, while Sketch and Adobe XD focus on detailed designs.
Why prototyping matters in product design
Cutting risks and saving money
Prototyping finds problems early in product design. Testing ideas before making the product avoids big mistakes. For example, a prototype shows if a feature works or needs fixing. This lowers the chance of making a product users won’t like.
A study comparing prototyping to old methods shows its value:
Metric | Prototyping Group | Conventional Group |
|---|---|---|
Final code size | 100% | |
Task effort needed | 45% less | 100% |
This proves prototyping saves time and effort, making it key in design.
Helping teams work better together
Prototyping helps teams by showing a clear product model. When everyone sees and uses the prototype, sharing ideas is easier. Designers, developers, and others can work together better and agree on goals.
Prototypes also help technical and non-technical people understand each other. This improves teamwork and avoids confusion, making the process smoother.
Making products better with user feedback
Testing prototypes with users early helps meet their needs. Feedback shows what works and what doesn’t. For example:
It makes products better by learning what users like.
It helps design for more people by broadening ideas.
Using feedback improves the product and makes users happy. Prototyping helps you make smart choices, creating something users will enjoy.
Types of prototypes
Low fidelity prototypes (e.g., sketches, wireframes)
Low fidelity prototypes are simple and quick to make. They include sketches, wireframes, or basic drawings. These focus on the product's structure, not detailed design. For example, a wireframe shows where buttons and text go on a webpage.
These are great for brainstorming and getting early feedback. They help find what works and what doesn’t before spending too much time. Since they are cheap and easy to change, you can quickly update them based on feedback.
High fidelity prototypes (e.g., mockups, interactive models)
High fidelity prototypes are detailed and look like the final product. Mockups and interactive models are examples of these. For instance, an app prototype might let users click buttons and switch screens.
These help test how easy and useful the product is. They show how users will interact with it. High fidelity prototypes also help explain ideas to teams and stakeholders. Though they take more time to make, they give helpful insights to improve the product.
Feasibility prototypes and live-data prototypes
Feasibility prototypes check if a product idea can work. They test specific features to see if they function well. Live-data prototypes use real user data to test ideas. For example, Kentico made a live-data prototype for a notification feature. Users tested it in a familiar setting, showing what worked and what needed fixing.
To test ideas, you can try:
User interviews and focus groups to learn user needs.
Surveys to check if ideas are good or not.
Usability testing to see how users use prototypes.
These prototypes help find problems early and ensure the product meets user needs.
When to use low fidelity vs. high fidelity prototypes
Picking between low fidelity and high fidelity prototypes depends on your project stage. Each type has its own purpose and benefits. Knowing when to use them helps save time and effort.
Low fidelity prototypes are best for early design stages. They are cheap and quick to make. Use sketches, wireframes, or simple drawings to try ideas. These let you test big concepts without much effort. You can easily change or throw away ideas that don’t work. This makes it easier to be creative and improve your plans before adding details.
High fidelity prototypes are better for later stages of design. They look and work like the final product. These are great for testing how users interact with the design. For example, an app prototype can show how users move between screens. High fidelity prototypes also help explain ideas clearly to your team and stakeholders. This ensures everyone understands the product the same way.
Tip: Use low fidelity prototypes to figure out "what" your product should do. Switch to high fidelity prototypes to test "how" it should work.
Think about your project’s needs to choose the right prototype. If you’re brainstorming, start with low fidelity prototypes to save time. When you’re ready to test details, use high fidelity prototypes for better feedback. Using the right prototype at the right time makes your design process smoother and helps create a product users will love.
Steps in the prototyping process
Understanding what users need and want
Knowing your users is key to good product design. Start by finding out their needs, likes, and problems. Use surveys or questionnaires to gather this information. These tools help you collect numbers and facts about user preferences. For example, ask users about their daily routines or how they might use your product.
Another helpful method is A/B testing. This means showing users two designs and seeing which one they like more. It helps you check if your design choices match what users want. Using both methods gives you a clear idea of what users need. This helps you create a product that fits their expectations.
Picking features and drawing first ideas
After learning about your users, focus on features they need most. Brainstorm ideas and choose the most important ones. Draw simple sketches to show how the product might look and work.
For example, you can sketch a mobile app layout. Show where buttons, menus, and text will go. This step helps you quickly try out ideas and improve them. It also makes it easier to share your ideas with your team so everyone understands.
Using low fidelity prototypes to test early ideas
Low fidelity prototypes are cheap and easy to make. They include wireframes or simple sketches. These focus on the product’s basic structure and how users move through it.
These prototypes help you find big problems early without spending too much time or money. For example, test a website wireframe to see if users can navigate it easily. This lets you gather feedback and fix issues before creating detailed designs.
Tip: Low fidelity prototypes are great for testing ideas fast. Use them to improve your design and make sure it works for users.
Building high fidelity prototypes for detailed testing
High fidelity prototypes are detailed and work like the real product. They show how users will interact with your design. For example, an app prototype might let users press buttons and switch screens. This detail helps find problems that simpler prototypes might miss.
When making high fidelity prototypes, focus on key features. Use tools like Figma or Adobe XD to create interactive designs. These tools help you mimic real user experiences. Testing these prototypes gives helpful feedback. For instance, Spotify improved premium sign-ups by 46% by testing button designs during checkout.
Tip: High fidelity prototypes are great for showing ideas to stakeholders. They give a clear and realistic view of the final product.
Testing prototypes with users and collecting feedback
Testing prototypes with users is very important. It shows if your design meets their needs. Focus on these key metrics during testing:
Metric Type | What to Track | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Performance | Task time, error rates | Finds usability problems |
Behavioral | Navigation paths, hesitation | Shows where users get confused |
Emotional | Facial expressions, feedback | Measures user happiness |
To confirm your prototype works, aim for 95% accuracy in tests. Keep testing conditions the same for all users. Mix numbers, like task times, with user comments for better insights.
Note: 74% of companies use tools to study user behavior. These tools help you see how users interact with your prototype.
Improving and updating based on feedback
Prototyping is a process of improving over time. After testing, use feedback to fix problems and make features better. This lowers risks and ensures your product fits user needs.
For example, Bracey's Accountants used this method to create custom software. It saved time, reduced paperwork, and made work easier. By improving their prototype, they built the perfect solution.
Tip: Improving your prototype early finds problems faster. It also keeps stakeholders happy by showing progress and using their ideas.
Prototyping and improving your design lead to better results. You make a product that works well and makes users happy.
Tools for rapid prototyping
Figma: Team-friendly design and prototyping tool
Figma is great for team design work. It lets many people edit the same prototype at once. This is perfect for teams working remotely. You can make interactive prototypes directly in Figma. There’s no need to move files to other tools. This saves time and makes designing easier.
Figma helps teams work faster and better. Over 80% of users say it improves teamwork. About 70% say it speeds up design, and 60% see better user engagement. Teams using Figma create four times more ideas early on. They also cut down meetings by 60%.
Figma reduces the time needed to share designs by 75%. Its built-in tools for testing make it a top choice for quick prototyping.
Sketch: Simple tool for UI/UX design
Sketch is popular with designers for its easy-to-use features. It has many plugins and tools to fit your needs. Sketch is great for making detailed prototypes. It gives you control over every part of the design.
This tool is best for teams that want perfect designs. Its simple layout is easy for beginners to learn. While Sketch doesn’t allow real-time teamwork like Figma, it’s excellent for creating detailed designs and sharing them with developers.
Adobe XD: All-in-one design and prototyping tool
Adobe XD combines designing and prototyping in one place. It works well with other Adobe tools like Photoshop. This makes it easy to bring in images or designs. It saves time and keeps your work organized.
One cool feature of Adobe XD is Auto-Animate. It helps you make moving designs easily. This is great for showing how your product works. Adobe XD also supports voice commands, so you can design for voice-activated devices. These features make it a strong choice for modern design needs.
Tip: If you already use Adobe tools, try Adobe XD. It works well with them and makes designing easier.
InVision: Tool for interactive prototypes and teamwork
InVision helps make clickable prototypes from simple designs. These prototypes show how users will move through your product. You can share them with your team to get feedback. This makes it easier to improve your design.
A great feature of InVision is teamwork. Team members can leave comments on the prototype. This keeps communication clear and avoids confusion. InVision also works with tools like Slack and Trello, making work smoother.
For testing, InVision has hotspots and animations. These let you see how users interact with your design. For example, you can check how users move through an app and fix problems early.
Tip: Use LiveShare in InVision to show your prototype live. Talk about changes with your team right away to save time.
InVision is perfect for teams who want polished prototypes and easy teamwork. Its simple tools and features make it popular with designers and developers.
Axure RP: Tool for detailed and complex prototypes
Axure RP is great for making advanced and detailed prototypes. It’s useful for projects needing special features or tricky designs. With Axure RP, you can create prototypes that act like real products, such as forms or dashboards.
This tool works well for testing designs with users. Plugins like UXtweak help gather feedback and find problems. For example, Axure RP was used to test a calculator. User testing showed what needed fixing, proving it’s good for tough designs.
Axure RP helps test tricky features to ensure they work.
It saves time by making the switch from design to development easy.
Teams using Axure RP make fewer mistakes during development.
Note: Axure RP is best for projects needing detailed logic or special interactions.
Axure RP lets you test how things work, not just how they look. It helps improve designs and create products that users will love.
Prototyping is key in product design. It helps test ideas and improve results. You can fix problems early and save money. For instance, a team made nine prototypes of a medical device in 20 days. This quick testing helped them improve designs fast. They created a better product for users.
Using good tools and steps makes sure your product fits user needs. Prototyping saves time by solving problems early. Use it to try ideas and make them better step by step.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of prototyping?
Prototyping helps check ideas, find issues, and improve designs. It makes sure your product works for users and avoids big mistakes.
How do I choose the right prototyping tool?
Choose a tool based on your project’s needs. Use Figma for teamwork. Pick Sketch or Adobe XD for detailed designs. Axure RP is great for tricky prototypes.
Can I skip low fidelity prototypes?
It’s not a good idea to skip low fidelity prototypes. They help test ideas fast and cheaply. This step improves your plans before spending time on details.
How often should I test prototypes with users?
Test prototypes at every big step. Early tests with simple prototypes find major problems. Later tests with detailed prototypes show smaller usability issues.
Are prototypes only for digital products?
No, prototypes work for both physical and digital products. For example, you can make a 3D gadget model or a website wireframe. Prototyping fits any product type.

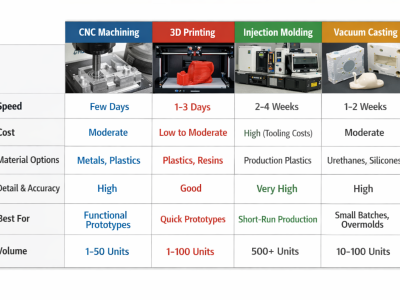
Start Your Next Project with LKprototype
LKprototype company simplifies procurement for custom manufacturing, Suitable for making your products or prototypes with a variety of materials, such as metal or plastic, silicone rubber, from 3D Printing to CNC Machined Parts and Vacuum Casting , with a focus on speed and efficiency. Our platform provides instant quotes. With LKprototype, You can connect with the team to communicate your project to ensure quality and on-time delivery.
Start with an instant quote and experience how our technology and expertise can make custom part procurement faster and easier.
 LKprototype
LKprototype