Molding manufacturing is a very common technique in operations such as that of automotive and even consumer goods. It consists of forming materials by introducing them into molds.
What Is Molding Manufacturing?
The Molding manufacturing process is the inverse of sheet metalworking in that it involves heating and pressuring a material into a molding cavity so as to achieve the desired shape. When cooled, the material sets in the shape of the cavity.
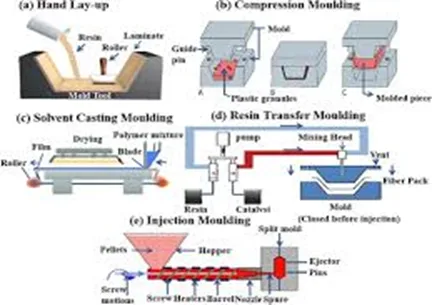
Different Types of Molding Processes
The term molding manufacturing includes a number of processes all aimed at working with different materials and responding to diverse product needs. These include:
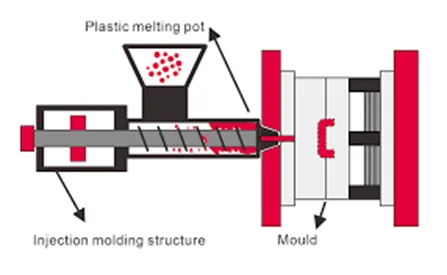
· Injection Molding:
Injection molded is the most extensively practiced molding processes. It consists of forcing molten material into a mold at high pressure. It is considered to be a good practice for creation of intricate shapes made out of the material that is in liquid form, but cools down to a solid, and is most often used for plastic parts injection across all verticals.
· Blow Molding:
Bottles or any hollow type of plastic component can be created out of Blow Molding. Using this technique, a form is made by blowing a molten plastic tube in a mold. The process makes it easier to produce numerous container types which are lightweight and strong as well as other hollow items.
· Compression Molding:
This type of molding is most of the times utilized in manufacturing thermoset materials. A certain amount of the material is already placed in an open mold cavity in its preformed state. After this, the mold cavity is closed and pressure and heat are applied to the material so as to shape it.
· Rotational Molding:
Rotational molding (or rotomolding) is primarily used to manufacture large, hollow parts such as tanks and playground structures. It consists of heating a mold and rotating it about two axis that are perpendicular to each other. The material inside is evenly distributed to create a uniform thickness.
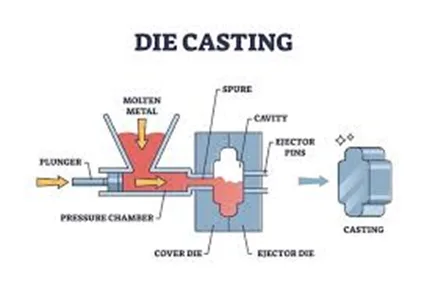
· Die Casting:
Die casting is ideal for manufacturing accurate metal components. In this procedure, molten metal is injected into a mold that has been subject to high pressure. It is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries to fabricate components that require specific tolerances and a finer finish.
· Thermoforming:
Thermoforming is the process of softening a plastic sheet by heating it, and then draping it over a mold, before cooling the sheet to hold the shape. This is an effective method for making shipping packages, a range of trays, and many automotive components.
No molding techniques will be ideal suited for all applications, however each technique will have particular areas of advantages over others across multiple industries.
Molding Manufacturing Process
Part manufacturing through molding manufacturing process guarantees the production of accurate and high quality components because it is performed in steps. These steps make sure the component is shaped, cured, and usable across different sectors.
· Preparing the Mold:
This process starts by designing and fabricating the mold which is constructed using sturdy metals such as steel or aluminum which can endure the mold’s conditions.
· Material Preparation:
The material, which can be in plastics, metals, or rubber form, is either melted or heated to the required temperature. In this way, the material can be heated enough to be molded into the respective shapes.
· Molding
The mold cavity is filled by the prepared material through injecting, pressing, or blowing it into the cavity. This process basically outlines the part with the material into the part geometry.
· Cooling/Hardening:
After the material is oriented in the geometry through the mold, the material is cooled down or is allowed to dry so that it sets in the required shape without changing its conformity.
· Demolding:
The cooling time is allowed after which the mold is separated so that the molded item can be taken out. The molded part needs to be handled carefully so that it is not damaged. This phenomenon is called demolding.
· Post-Processing:
The item might be subjected to processes such as trimming, painting, or polishing. This gives the final item a better aesthetic appeal and improves its operational qualities.
Key Benefits of Molding Manufacturing
Molding has its own fair share of advantages which is why it is widely adopted across various industries. Here are the key benefits:
· Cost-Effectiveness:
Molding manufacturing becomes automatable so the cost of human labor is further reduced which makes mass production affordable. Moreover it is extremely economized especially for round about the same production over and over again since once the mold is made, the cost per each item drastically lowers down.
· Precision and Consistency:
Products manufactured via injection molding are astounding in regards to precision and accuracy. Each part made is of the identical dimensions because of pre-fabricated molds which is crucial for industries such as automotive and electronics which are impossible to operate in without having fairly strict tolerances.
· Design Flexibility:
This type of manufacturing can mold parts of a complex design, having various products in accordance with the requirements of the clients. That is why this is preferred in a broad spectrum of industries such as consumer goods and industrial equipment.
· Material Efficiency:
Molding processes are resource-consuming however it is also resource efficient. Injections create excessive amounts of waste but it does allow for further injection making it a lower marginal cost in the end which makes the process environmentally friendly.
· Speed and Scalability:
The molding manufacturing process combines efficiency and high-volume production due to its ability to encase complex designs. In time, as the mold is designed, a larger volume of parts can be produced with ease. This go hand in hand with industries which are time sensitive and require large quantities to be produced efficiently.
· Customization:
A wide range of industries use molding as it allows the companies to change parameters in their production designs. This includes altering the textures, colors, and the material used for molding.
Due to the advantages molding as a process does not only stand in the scale but also in the quality it can produce, molding will continue to be an efficient process in the manufacturing sector.
Applications of Molding Manufacturing
Molding doesn’t only serve the purpose of producing goods, components or parts, it also requires skill hence it not only focuses on achieving high efficiency results but also precision in the results. So where does molding find use? Here are a few key industries that make use of molding:
· Automotive Industry
Molding is extensively used within the automotive industry with parts like bumpers, dashboards, and even engine components being manufactured using this particular type of molding. With injection molding parts that are large in volume and intricate and designed with low weight can all be mass produced.
· Consumer Electronics:
One of the processes that is vital within the consumer electronics industry is molding. The molding process can be used to create enclosures, buttons and connectors. Molding processes are so precise that parts are always fitted and function perfectly.
· Medical Devices:
Syringes, surgical instruments and other medical diagnostic devices are parts that are readily made and created through molding in hospitals and medical environments. The why the industry is able to make sterile, precise and complex parts is because they are able to use molding.
· Packaging:
Containers, bottles and caps for packaging are developed using the molding process. Moreover, in the food and beverage industries as well as the pharmaceutical industries blow molding is used for packaging. This results in an efficient way to mass produce lightweight yet strong packaging.
· Aerospace:
Lightweight parts such as housings and ducts are produced through the molding method is the aerospace industry. Therefore, composites and high strength polymers are able to meet the strength and operational requirements for the aviation industry.
Molding manufacturing can be implemented in many sectors while being quick, effective and cost efficient.
Challenges in Molding Manufacturing
As a form of production, molding has its limitations that companies need to be able to establish controls for.
· Initial Mold Costs:
A common issue in molding is the costs associated with developing and carving. These costs tend to be high for metal parts since their requirements are very complex. These costs serve as a good deterrent especially for small scale runs.
· Material Limitations:
For molding techniques to work, certain materials are always a must. Sometimes materials do not melt and instead burn out of the pressure and heat being applied. This is true when dealing with advanced composite materials or even other metals since they require different molding procedures and equipment.
· Complexity in Mold Design:
There are times where developing the mold for some parts is troublesome. This is because their structural requirements such as exact geometries involve the need for very precise tools which increases the amount of time and resources spent on the production.
· Quality Control:
Another problem with molding as a whole is the evenness in quality of the parts. Parts would become slightly defective due to subtle changes in material consistency, pressure, and temperature. Meeting this challenge of the desired standard rigidity would require a lot of undertakings hence quality control measures being extremely demanding.
Molding still has great importance even in the wake of the issues that are faced during the production process. In order to manufacture components in a cost effective and a top quality way, it is paramount to comprehend and solve such restrictions.
Conclusion
Molds can be manufactured using different techniques. It is worth noting that, although there are a number of certain challenges like high mold costs and materials constraints, the molding processes offer cost-effectiveness, precision, and scalability making it ideal for mass production which explains why molding manufacturing is popular across multiple industries.
 LKprototype
LKprototype







