When deciding on a molding process, you should opt for liquid silicone rubber (LSR) molding over other methods if your product demands high precision, exceptional clarity, or complex shapes. Many engineers choose LSR for these specific reasons:
It offers precise control for tight burr management.
It provides exceptional clarity, ideal for medical components.
It can produce intricate and detailed parts.
It has faster cycle times compared to traditional thermoplastic molding.
Understanding the differences between liquid silicone molding vs other processes is crucial in selecting the most suitable molding process for your design and manufacturing needs.
Key Takeaways
Pick liquid silicone rubber (LSR) when you need very exact shapes or tricky designs in your products. LSR works well for medical and food items, so it is good for things that must be safe. LSR cures quickly and can be made fast, which helps you make more products in less time. Think about what your project needs, like if it must handle heat or be safe for the body, before you choose how to mold it. Make sure you plan your design well so you do not have problems with hard molds or mixing materials.
What Is Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)?
Definition of Liquid Silicone Rubber
You see liquid silicone rubber (LSR) in many safe and strong products. LSR is made from special man-made polymers. Factories use LSR because it moves easily and fills molds well. This helps make shapes with lots of small details. LSR gets hard fast and does not need extra chemicals. You find LSR in medical tools and food packages because it has no smell and is safe for skin and food.
Tip: LSR does not smell at all. Solid silicone can have a strong smell. This makes LSR better for things that need to be very clean.
Key Characteristics of LSR Material
LSR is special because of its strong and safe features. These features help when you need something to work well in tough places.
It gets hard fast, so making things is quick.
It flows well, so you can make tiny parts.
It is safer for the environment than other stuff.
It is safe for food use.
It does not bother your skin, so it is good for medical and wearable things.
You can look at this table to see how LSR and solid silicone rubber (SSR) are different:
Property | Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) | Solid Silicone Rubber (SSR) |
|---|---|---|
Chemical Structure | Inorganic-organic polymers | Mostly organic polymers |
Temperature Resistance | Handles more heat | Handles less heat |
Chemical Stability | Very stable | Somewhat stable |
Water Absorption | Takes in little water | Takes in more water |
Processing Method | Liquid injection molding | Solid molding |
Applications | Healthcare, food packaging | Consumer, industrial |
LSR is very clear, does not squish much, and stretches well. You can trust it for medical tools because it is safe for the body. It works well in hot or harsh places because it does not break down. If you need something safe, bendy, and strong, LSR is a smart pick.
LSR Material Properties
Mechanical Properties
Liquid silicone rubber makes parts strong and bendy. It does not change shape when you squeeze it. The surface is smooth, so it helps seals work well. You get both bendy and stiff parts with LSR. It is good for thin sensors and electric insulation. You can pick how hard or soft you want it. The durometer goes from 10 to 80 Shore A.
LSR does not lose its shape.
The surface is smooth and clean.
You get both bendy and strong parts.
LSR is great for seals and insulation.
You can choose the hardness you need.
Thermal Resistance
LSR works in very hot and cold places. It stays the same from -150°F to over 400°F. LSR is better than thermoplastic elastomers and solid silicone in heat and cold. You can use it for things that get hot or cold fast. This makes LSR good for cars, medical tools, and machines.
Note: LSR keeps working in heat and cold. You do not have to worry about it melting or cracking.
Chemical Resistance
LSR does not get ruined by chemicals. It stands up to wind, rain, steam, UV light, and oil. LSR does not rust or break down in tough places. The platinum-curing process makes it safe for food and medical things. LSR does not let bacteria grow and stays safe.
LSR does not rust or let bacteria grow.
It stays strong in bad weather and chemicals.
You can use it for food and medical products.
Biocompatibility
LSR is safe for skin, food, and medical tools. It passes hard tests for safety and chemical strength. You see LSR in hospitals and food packs because it is pure and safe.
Standard/Regulation | Description |
|---|---|
Checks for cell harm, allergies, and poison. | |
U.S. FDA Standards | 21 CFR 177.2600 checks silicone for food safety. |
USP Class VI | Tests if medical materials are safe for the body. |
EU Medical Device Regulation | Needs safety and chemical strength. |
REACH Regulation | Stops bad stuff in silicone materials. |
When you look at liquid silicone molding vs other processes, LSR is safer, lasts longer, and meets tough rules.
LSR Injection Molding Process
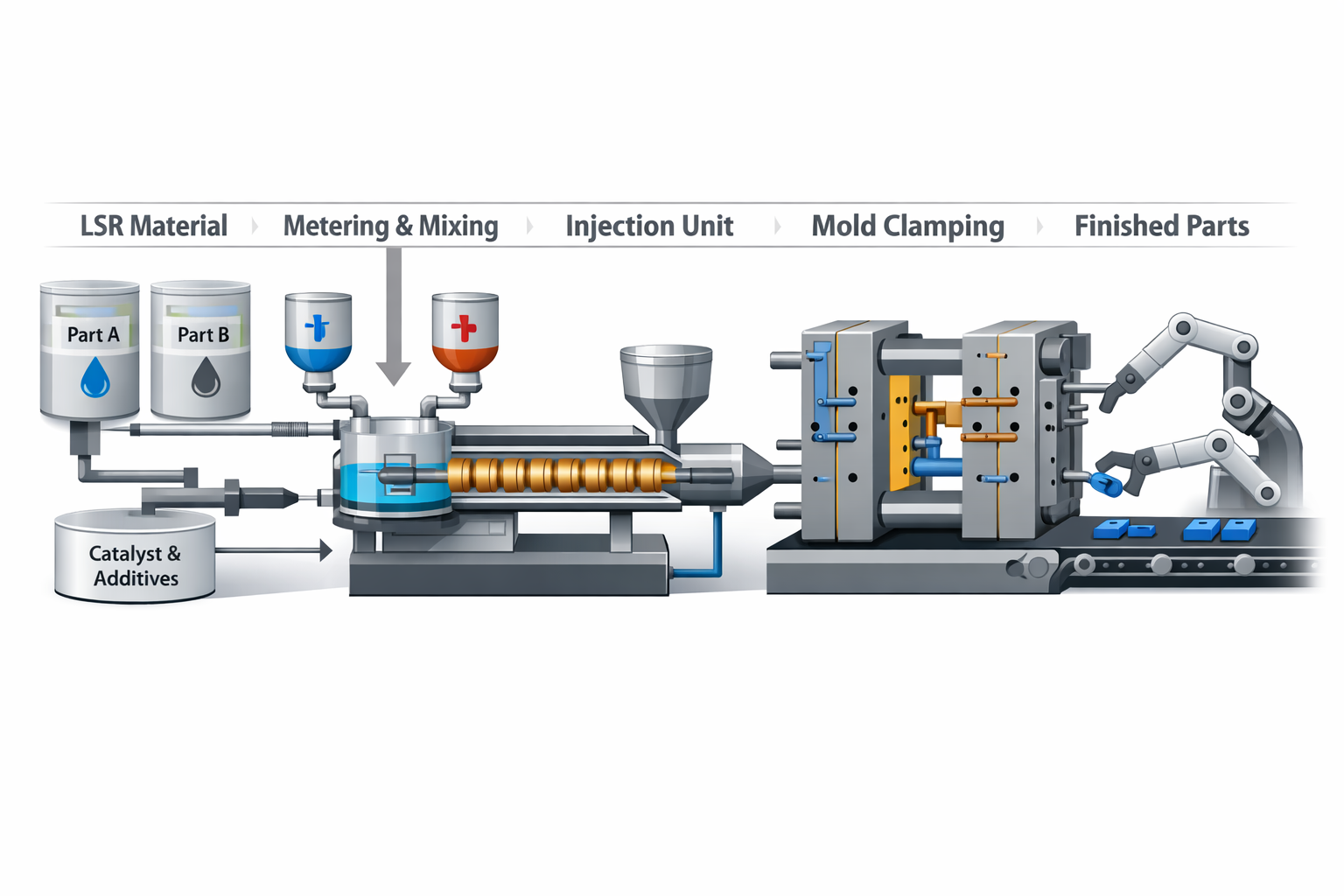
Process Steps
You can make good parts with the LSR injection molding process. This process has a few easy steps. Each step helps you get strong and clean parts fast. Here is a table that shows the main steps and how they help:
Step | Description | Impact on Production Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
1 | Preparation of the mixture, including homogenization and temperature stabilization. | Ensures optimal material properties and reduces defects during injection. |
2 | Closing the mold and starting the injection process under controlled conditions. | Affects the speed and quality of the injection, impacting overall cycle time. |
3 | Curing stage where the silicone transforms from liquid to solid. | Critical for product quality; improper curing can lead to defects and increased cycle time. |
4 | Cooling and demolding of the product. | Efficient cooling is essential to minimize cycle time and maximize throughput. |
Each step is important for speed and quality. When you compare liquid silicone molding vs other processes, you see that LSR molding is often faster. It also gives you fewer mistakes in the parts.
Tooling and Automation
You need special tools and machines for LSR molding. Automation helps you work faster and make fewer mistakes. Here are some common types of automation and their benefits:
Type of Automation | Impact on Cycle Time and Quality |
|---|---|
Precise metering pumps | Ensures exact ratios of materials, enhancing consistency and quality. |
Specialized injection molding machines | Reduces cycle time by efficiently filling molds and maintaining temperature. |
Automated demolding processes | Minimizes human error and speeds up the removal of parts, improving quality. |
You need less work from people.
You make fewer mistakes.
You get the same results every time.
Automation makes the process smooth. It helps you keep up when you need to make many parts.
Quality Control
You want every part to be good. Quality control in LSR molding uses different ways to check for problems. Here is a table that shows some of the best ways:
Quality Control Method | Description |
|---|---|
Embed Quality Tools into Project Timeline | Develop a mutual understanding of the blueprint and establish critical dimensions and features. |
Visual Inspections | Create Visual Standards to define various defect modes for effective inspection. |
Dimensional Measurements | Utilize dimensional measurements to complement visual inspections. |
Material and Functional Tests | Conduct tests such as Shore hardness, tensile, and pressure/leak testing to meet control plan needs. |
Tip: You should use both looking and measuring to find problems early.
If you follow these steps, your LSR parts will be safe, strong, and ready to use.
Advantages and Limitations of LSR Molding
Advantages of LSR Molding
You get many good things when you use LSR molding. The process is simple and has fewer steps. You do not need workers with special skills. You can make parts faster and with fewer mistakes. This means you get more parts in less time. Machines do most of the work, so there are fewer errors.
LSR molding is better than other methods in many ways. It can handle high heat and strong chemicals. LSR is very tough and does not tear easily. It is safe for food and medical uses because it is biocompatible. You can make thin and tricky shapes with LSR. The material does not bend or change shape much.
Here is a table that shows how LSR and TPE are different:
LSR Advantages | TPE Advantages |
|---|---|
Very high temperature resistance | Compatible with standard injection machines |
Biocompatibility for medical and food | Re-moldable and recyclable |
High tear strength | Fast, simple, and less expensive molding |
Superior chemical resistance | Easy to add color with pigments |
Minimal warping | Heat sealable |
Superior compression set | Pellets easy to handle |
Tip: LSR injection molding helps you make safe and strong parts quickly.
Limitations of LSR Molding
There are some problems you should know about LSR molding. Sometimes, LSR does not stick well to other materials. You might need special steps to help it stick. Some plastics do not work well with LSR, so you must choose carefully.
You have to design molds the right way to stop mistakes. Curing LSR needs careful control. If you do not watch the process, you can waste material or get bad parts. LSR can shrink when it cures, which can change the size of your parts. Making hard shapes can cost more money, so you need to plan well.
Problems sticking to other materials
Some materials do not work with LSR
Mold design can be tricky
Curing needs careful control
Shrinking can change part size
Hard shapes can cost more
Note: You can fix many of these problems by planning and asking LSR experts for help.
Overview of Other Molding Processes
Thermoplastic Injection Molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is used in many places. This process melts plastic pellets. Machines push the hot plastic into metal molds. The plastic cools and gets hard fast. You get parts that are strong and light. There are many kinds of plastics to pick from. This method is good for making lots of parts. You can make toys, car parts, and boxes. The parts look smooth and fit together well.
Tip: You can use leftover thermoplastic again. This helps cut down on waste.
Compression Molding
Compression molding uses heat and pressure to shape things. You put a set amount of material in a hot mold. The mold closes and squeezes the material. Heat and pressure make the part. This method works for rubber, thermosets, and some plastics. Compression molding is good for big and simple shapes. You see it in car gaskets and electric insulators. It takes longer than injection molding. The finished parts may not have much detail.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding mixes ideas from compression and injection molding. You put the material in a chamber. A plunger pushes it into the mold. The mold shapes the part with heat and pressure. You use transfer molding for rubber and thermoset plastics. This process makes parts with metal pieces or tricky shapes. You see it in electronic parts and seals. Transfer molding gives more detail than compression molding.
Solid Silicone Molding
Solid silicone molding uses solid silicone rubber. You mix and shape the rubber before putting it in the mold. The mold heats up and cures the silicone. You get parts that bend and last a long time. This method is good for making a small or medium number of parts. You use it for seals, gaskets, and medical tools. Solid silicone molding takes more time than liquid silicone molding. You may get more waste and less exact parts.
When you look at liquid silicone molding vs other processes, you see changes in speed, detail, and what materials you can use. Each process works best for certain jobs.
Liquid Silicone Molding vs Other Processes (Direct Comparison)
Process Flow and Cycle Time
You want to make parts quickly and with fewer mistakes. Each molding process has steps that affect how fast you finish a part. Look at this table to see how the cycle time breaks down:
Cycle Time Component | Description | Impact on Production Throughput |
|---|---|---|
Injection Time | Time taken to inject material into the mold. | Faster filling means more parts per hour. |
Cooling Time | Time for the material to cool and solidify. | Longest phase, keeps parts stable. |
Dwelling Time | Holding phase to prevent shrinkage. | Helps keep part size correct. |
Ejection Time | Time to remove the finished part. | Quick ejection boosts output. |
Mold Opening/Closing Time | Time for the mold to open and close. | Fast movement speeds up cycles. |
LSR molding often has shorter cooling and ejection times than other methods. You get more parts in less time.
Material Performance and Consistency
You need parts that last and work well. LSR stands out because it keeps its shape after many uses. It stays flexible and does not get brittle. Thermoplastics can bend or lose shape under pressure. LSR works better for seals and medical parts because it stays strong and safe.
LSR bounces back after being squeezed.
LSR stays flexible for a long time.
Thermoplastics may lose shape if pressed too much.
LSR also handles heat and cold better than other materials. You can trust it for tough jobs.
Design Flexibility and Tolerances
You want to design parts that fit together perfectly. LSR molding lets you make thin walls and detailed shapes. You can keep wall thickness between 0.5 mm and 5 mm for best results. Add draft angles of 1 to 2° to help remove parts from molds. LSR can reach tight tolerances, like 0.025 mm/mm. This means your parts will be accurate and reliable.
Tolerance Type | Value |
|---|---|
Linear Tolerance | 0.025 mm/mm |
Flash Allowance | Considered in design |
Tooling Cost and Mold Lifetime
You want to save money and use molds for a long time. Compression molding costs less and molds last longer. Injection molding, including LSR, costs more at first but works better for big runs. The mold for LSR may wear out faster than compression molds, but you get more parts quickly.
Molding Type | Mold Lifespan | |
|---|---|---|
Compression Molding | Lower; easy to maintain | Longer lifespan |
Injection Molding | Higher; good for large runs | Shorter than compression molds |
Production Volume Suitability
You need to pick the right process for your batch size. Injection molding fits high-volume jobs because you can use more cavities and lower the price per part. Transfer molding works better for small or medium batches. Silicone molding with vacuum casting is best for small runs. Silicone molds make 15–30 parts before wearing out, so they suit low-volume needs. The cost for silicone molds is lower than steel molds for injection molding.
When you compare liquid silicone molding vs other processes, you see that LSR is best for high-volume, precise, and flexible designs. Other processes may fit better for small batches or simple shapes.
Comparison Table – LSR vs Other Molding Processes
Precision and Tolerance Comparison
LSR molding makes parts with very tight tolerances. You get fine details in every part. This is important for medical seals and small parts. LSR molding gives you high precision every time. You can make complex shapes that fit well. LSR molds need careful design and special systems. Other molding processes may not give the same detail or quality.
Cost and Tooling Comparison
You need to think about tooling and production costs. LSR molds cost more to design and build. They need special features to work right. But you save money later with faster cycles and less labor. Compression molding may cost less for small runs. For big jobs, LSR saves more money over time.
Tip: Spending more on LSR tooling helps when you need many precise parts.
Cycle Time Comparison
Cycle time shows how fast you make parts. LSR molding is much quicker than other silicone processes. You can see the difference in this table:
Molding Process | Average Cycle Time |
|---|---|
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) | 30 seconds |
High Consistency Rubber (HCR) | 6 minutes |
Peroxide Cured Materials | 9 minutes |
Shorter cycle times help you finish jobs faster. You save on labor and meet deadlines more easily.
Material Compatibility Comparison
LSR works with many materials, especially for medical uses. Its low viscosity lets you add colorants or drugs easily. You can use LSR for high-precision, biocompatible parts. Other processes do not mix additives as well as LSR.
You can add many things without losing quality.
Automated LSR molding gives better results.
Typical Applications Comparison
LSR is used in many industries. Here is a quick look at where each process is used:
Application | Description |
|---|---|
Automotive | High-temperature seals and gaskets. |
Electronics | Durable, moisture-resistant components. |
Medical | Biocompatible implants and tubing. |
Consumer Goods | Flexible and safe household items. |
Industrial | Seals and insulators for machines. |
Building | Construction materials with added function. |
Healthcare uses LSR more because it is safe and flexible. When you compare liquid silicone molding vs other processes, LSR is best for precision, speed, and medical use.
Application Scenarios
Medical Devices and Healthcare
You can find liquid silicone rubber (LSR) in many medical tools. LSR helps make products that are safe and clean. Hospitals use LSR for tubing, seals, and bottle nipples. It is also in syringe parts and electric connectors. LSR does not cause allergies or let germs grow. It stays strong after you clean it. You can trust LSR for things that touch skin or go inside the body.
Tip: LSR passes hard safety tests. You can use it for medical implants and tools that must stay very clean.
Automotive Components
People use LSR to make car and truck parts. LSR can handle heat, cold, and chemicals. You find LSR in gaskets, seals, and electric connectors. Car makers use LSR for engine parts and sensors. LSR does not crack or lose its shape. It keeps water and dust out of car systems. You get parts that work well even in tough places.
Automotive LSR Uses | Why Choose LSR? |
|---|---|
Seals and gaskets | High temperature range |
Electric connectors | Chemical resistance |
Sensor covers | Flexible and durable |
Consumer Products
You see LSR in many things at home. LSR makes products that are safe and bendy. Kitchen tools like baking pans and spatulas use LSR. Baby bottle nipples and toys use LSR because it is soft and has no smell. LSR does not break in the dishwasher. You get things that last longer and are safe for your family.
Kitchen tools (baking pans, spatulas)
Baby items (bottle nipples, pacifiers)
Flexible things for the home
Industrial Uses
Factories use LSR for seals and membranes in machines. These parts must resist oil, steam, and sunlight. LSR works well for electric connectors and insulators. You get strong parts that last a long time. LSR helps machines run without leaks or problems.
LSR gives special benefits in many jobs. You get safe, strong, and bendy parts for medical, car, home, and factory needs.
Design and Cost Considerations
Part Geometry and Complexity
Think about your part’s shape before picking LSR molding. Simple shapes are easier to make. LSR can also make complex designs. Keep the wall thickness even, between 0.5mm and 2mm. This helps stop the part from warping. Small details, like micro-textures, need special molds. Features smaller than 0.2mm are hard to make. Good vents in the mold let air out. This helps the part fill all the way. If your part has tricky shapes, plan for easy removal. This stops bending or damage.
Design Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Wall Thickness Uniformity | Consistent wall thickness (0.5mm to 2mm) prevents warping and uneven curing. |
Micro-Features and Fine Details | High-precision molds are needed for micro-textures; features smaller than 0.2mm may be challenging. |
Venting and Gas Release | Adequate vents are necessary to avoid air entrapment, especially in complex geometries. |
Material Compatibility | Choose formulations based on the application environment (medical, food-safe, industrial). |
Mold Ventilation and Ejection | Proper venting ensures complete fill; ejection mechanisms must avoid part deformation. |
Material Certifications and Requirements
Check if your LSR part has the right certifications. For food contact, look for FDA approval. Medical devices need USP Class VI or ISO 10993. If your part touches drinking water, you need NSF certification. Electrical parts need UL certification. RoHS and REACH show your part is safe for the environment.
Certification | Application |
|---|---|
FDA (21 CFR 177.2600) | Food contact |
USP Class VI/ISO 10993 | Medical devices |
RoHS/REACH | Environmental compliance |
UL certification | Electrical components |
NSF | Drinking water applications |
Always check the rules for your industry before you start making parts.
Cost Analysis and ROI
You want to know how much your project will cost. Sample LSR tools cost less, from $3,000 to $20,000. They work slower and cost more to run. These tools help you test your design. Production molds cost more, from $50,000 to $150,000 or more. They save money when you make many parts. The price for each part goes down as you make more.
Type of Tool | Capital Expenditure (Capex) | Operational Expenditure (Opex) | Justification for Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
Sample LSR Tool | $3,000 – $20,000 | Higher due to inefficiency | Lower financial barrier for design validation |
Production Mold | $50,000 – $150,000+ | Lower due to efficiency | Justified by lower cost per part at high volumes |
Prototyping vs Mass Production
Use sample tools for prototyping. These tools let you test ideas without spending too much. For mass production, buy a full production mold. This mold costs more at first. You save money on each part when you make a lot. Prototyping helps you find problems early. Mass production gives you the best price for thousands of parts.
Start with a prototype to check your design. Move to mass production when you need lots of parts.
Choosing the Right Process
When to Use LSR
You should choose liquid silicone rubber (LSR) molding when your project needs high precision and strong material properties. LSR works well for parts with thin walls, complex shapes, or fine details. You get excellent clarity and flexibility. LSR is a smart choice for medical devices, baby products, and food-contact items. The material is safe for skin and does not cause allergies. You can trust LSR for parts that need to last in hot, cold, or harsh environments. LSR also resists chemicals and keeps its shape after many uses.
Tip: Pick LSR if you need biocompatibility, easy cleaning, or parts that must pass strict safety tests.
When to Choose Other Processes
You may want to use other molding processes if your project does not need the special features of LSR. Thermoplastic injection molding is good for simple shapes and high-volume production. Compression molding works well for large, basic parts. Transfer molding helps when you need to add metal pieces or make medium-sized batches. Solid silicone molding fits small runs and less detailed parts. These methods often cost less for small projects or when you do not need tight tolerances.
Process Type | Best For |
|---|---|
Thermoplastic Injection | Simple, high-volume parts |
Compression Molding | Large, basic shapes |
Transfer Molding | Metal inserts, medium batches |
Solid Silicone Molding | Small runs, less detail |
Practical Selection Guidelines
You need to look at several factors before you decide. Check if the material matches your project needs. Make sure the surface activation and conditioning steps will help your parts stick together and stay strong. This is very important for medical products that need sterilization and must last in tough environments. Think about your budget, the number of parts you need, and how fast you want to finish. Ask yourself these questions:
Does your part need to be safe for skin or food?
Will your part face heat, chemicals, or cleaning?
Do you need very fine details or tight tolerances?
Is your batch size small or large?
Can you meet the cost and tooling needs?
You make the best choice when you match your design, material, and production goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between LSR and compression molding?
LSR molding uses liquid silicone that flows into molds. It makes parts with small details and tight fits. Compression molding uses solid or thick silicone. You put it in a hot mold and press it. This works for simple and bigger shapes. LSR molding is faster and gives more even results. Compression molding costs less for small batches but is not as exact.
When should I choose liquid silicone injection molding?
Pick liquid silicone injection molding for high precision or strong parts. LSR is good for thin walls and tricky shapes. You do not need draft angles because LSR stretches out of molds. LSR’s tear strength lets you remove big or hard parts without breaking them. If your part needs to handle heat or touch skin, LSR is a smart pick.
Tip: LSR injection molding stops parts from bending when you take them out, even if they are complex.
Is LSR molding more expensive than thermoplastic injection molding?
LSR molding costs more at first. You pay extra for special molds and machines. Later, you save money because cycles are faster and there is less waste. Thermoplastic molding costs less for tools and works for simple, big batches. If you need flexible, medical, or heat-safe parts, LSR is worth the higher starting price.
What industries benefit most from LSR?
Many industries use LSR because it has special features. You find LSR in:
Medical tools and healthcare items
Car seals and connectors
Kitchenware and baby products
Factory machines and electronics
LSR can handle very hot or cold places. It is strong and safe for people. Engineers pick LSR for parts that must last and stay safe.
When you pick a molding process, think about what your product needs. LSR is great if you need to make many parts or shapes with lots of detail. You should learn about LSR’s material properties before you start designing. Make your part’s shape simple and smart to help it work better. Always think about how you will use the part and how it connects to other pieces.
LSR is good for making lots of detailed parts.
Knowing about the material helps you choose well.
A smart design makes it easier to make your part.
Tip: If your project is tricky, ask experts for help or read more to find the best way.
 LKprototype
LKprototype