
You can make your manufacturing work better by using five steps in the lean manufacturing process:
Identify value
Map the value stream
Create flow
Establish pull
Pursue perfection
Lean manufacturing is about getting rid of waste in the process. When you use lean principles, you remove waste, make more products, and work faster. Think about how each step helps you cut waste and get the most value in your work.
Key Takeaways
Lean manufacturing helps you get rid of waste. It lets you focus on what your customer wants most.
Mapping your process helps you see slow or extra steps. You can remove these steps to work faster.
Making a smooth flow and making products only when needed helps stop delays. This also saves resources.
Getting your team involved and listening to their feedback brings better ideas. It also leads to stronger improvements.
Always look for small ways to get better every day. This keeps your manufacturing efficient and reliable.
Lean Manufacturing Overview
What Is Lean?
You can think of lean as a way to make your manufacturing better by focusing on what matters most. Lean started with the Toyota Production System, which changed how people look at production. When you use lean, you look for steps in your process that do not add value. These steps often create waste. Lean helps you spot waste and remove it from your production.
Lean manufacturing uses simple ideas. You look at every part of your process and ask, “Does this help the customer?” If it does not, you find a way to change or remove it. Lean works in many types of manufacturing, not just cars. You can use lean in any production process where you want to make things better and faster.
Tip: Lean is not just a set of rules. You use it to build a culture where everyone looks for ways to improve the process and reduce waste.
Core Purpose
The main goal of lean manufacturing is to give your customer more value with less waste. You want to make your production flow smoothly. Lean helps you see where your process slows down or stops. When you fix these problems, you make your manufacturing more efficient.
You use lean to cut out steps that do not help your production. This means you use fewer resources, save time, and make better products. The Toyota Production System shows how lean can change a whole industry. When you follow lean, you focus on making your process better every day.
Lean manufacturing helps you:
Reduce waste in your production
Improve the flow of your process
Deliver products faster to your customers
Use your resources in the best way
Lean gives you a clear path to better manufacturing. You can see results when you make small changes and keep improving your process.
Lean Manufacturing Process Steps
Identify Value
You begin by finding out what your customer wants. Value is what your customer needs and will pay for. Look at each step in your process. Ask if it helps make value for the customer. If a step does not add value, it may cause waste. Focus on what is most important to your customer.
To do this, talk to your customers and ask for their thoughts. Study your products and services. Use facts to see which parts matter most. When you know what is valuable, you can get rid of waste. Then you use your time and money on what matters.
When you know what is valuable, you can make big changes. Companies that focus on value can work 15-20% better. They can cut costs by 12%. They can make 10-15% more products. They also find problems sooner, with a 32% better defect check. Downtime can go down by up to 45%.
Metric | Improvement Range | Impact Description |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency Improvement | 15-20% | Work gets better when you know what is valuable. |
Cost Reduction | 12% | You save money by making your work better. |
Production Throughput Increase | 10-15% | You make more products and earn more money. |
Defect Detection Improvement | 32% | You find mistakes sooner and fix them faster. |
Downtime Reduction | 35-45% | Machines stop less often and work better. |
You can see how finding value helps you work better, save money, and make better products. This step is the start of the lean manufacturing process.
Map Value Stream
After you find value, you map the value stream. The value stream is every step from raw material to finished product. Look at each step in your process. See which steps add value and which ones do not.
To map your value stream, draw a simple chart or picture. Write down each step in your process. Mark which steps help and which do not. Use facts from your shop, like dates, hours, and machine stops. This helps you find slow spots and places to fix.
Mapping the value stream helps you find and remove waste. You can see where things slow down or get stuck. When you fix these, your work moves faster. It is also easier to teach your team and make your process the same each time.
Create Flow
Once you know your value stream, you work to make flow. Flow means your product moves smoothly from one step to the next. You do not want waiting, slow spots, or piles of work. Good flow means less waste and faster work.
To make flow, put your machines and work areas in a good order. Take away things that slow down your work. Teach your team to find and fix problems fast. Use signs or floor marks to help guide the work.
When you have flow, you work much faster. Products move quickly, and you use your tools better. You also cut down on wait time, so customers get orders sooner. Flow is a big part of lean manufacturing and can change how you work.
Establish Pull
The next step is to set up pull. Pull means you only make things when a customer asks. You do not make extra or keep too much in storage. This is called just-in-time production.
To set up pull, use signals like Kanban cards or alerts. These tell your team when to make more products. You match your work to what customers want. This keeps your storage low and cuts waste.
Pull helps you avoid making too much and saves space. You use your tools for what customers really need. This step helps you give value with every order.
Pursue Perfection
The last step is to try for perfection. You always look for ways to get better. Every day, you and your team find small ways to improve. This is called continuous improvement.
To do this, have meetings to talk about your process. Ask your team and customers for ideas. Use real-time tools, like MES or dashboards, to watch your progress. Set goals and check your results.
You can use numbers to see how you are doing. These include cycle time, yield rate, net output, on-time delivery, lead time, defect rate, and OEE. Good data helps you find problems and fix them fast.
Metric Category | Metric Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Operational Performance Indicators | Cycle Time | How long it takes to finish a job from start to end. | Making a car takes 8 hours from start to finish. |
Yield Rate | How many good parts you make compared to all parts. | 950 good items out of 1,000 parts = 95% yield rate. | |
Net Output | How much you make compared to what you could make. | Making 450 parts when you could make 500 = 90% net output. | |
On-Time Delivery (OTD) | How many orders you deliver on time. | 180 orders on time out of 200 = 90% OTD. | |
Lead Time | Time from order to delivery. | Order on Monday, deliver on Friday = 5 days lead time. | |
Quality Indicators | Defect Rate | How many bad parts you make compared to all parts. | 200 bad units out of 10,000 = 2% defect rate. |
Internal Non-Conformance Rate | How many items fail checks before delivery. | 50 failed units out of 1,000 = 5% non-conformance rate. | |
Scrap Rate | How many items you throw away after making them. | 500 thrown away out of 10,000 = 5% scrap rate. | |
Equipment and Resource Efficiency | Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | How well your machines work, including time, speed, and quality. | Machine runs 80% of the time, 90% speed, 95% quality = 68.4% OEE. |
Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) | How well your machines, team, and process work together. | Machine ready 90%, runs at 80%, makes 95% good parts = 68.4% TEEP. | |
Resource Utilization Rate | How well you use your tools, people, and materials. | Machine used 40 hours out of 50 = 80% use. | |
Downtime | Time when machines are not working. | 4 hours stopped out of 8-hour shift = 50% downtime. | |
Failure Frequency Rate | How often machines break down. | 5 breakdowns in 160 hours = 1 every 32 hours. | |
Financial and Economic Indicators | Cost per Unit Produced | How much it costs to make each item. | $50,000 cost for 5,000 units = $10 per unit. |
Return on Investment (ROI) | How much you gain from your projects compared to what you spend. | $10,000 spent gives $15,000 back = 50% ROI. |
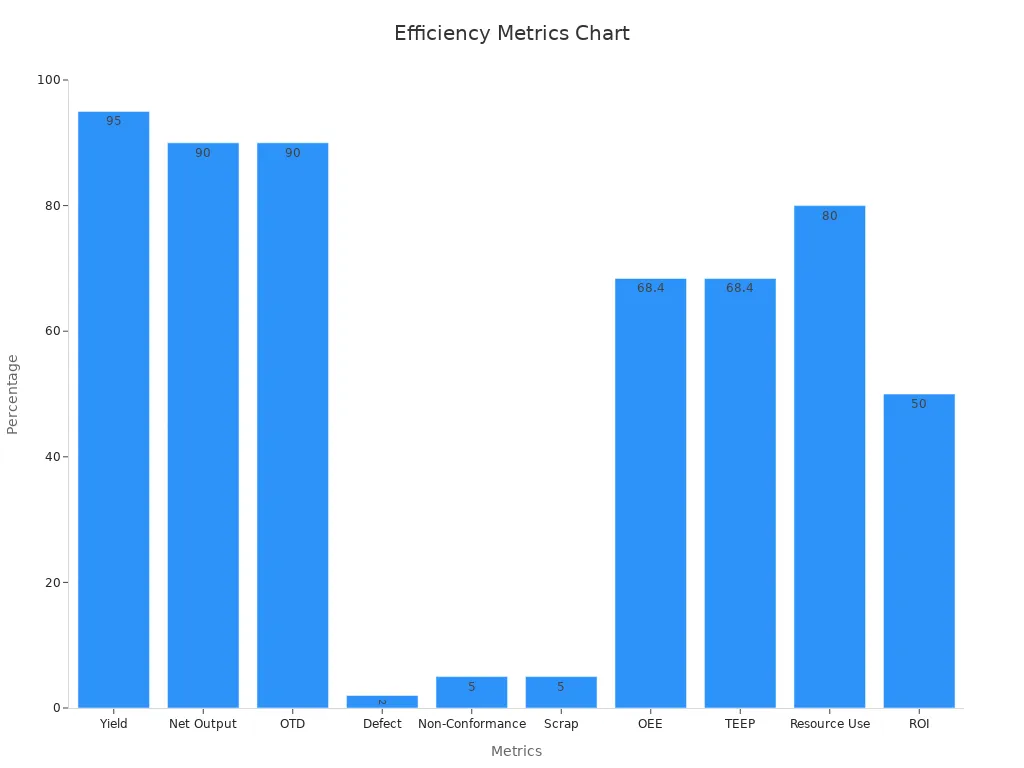
You can use these numbers to see how you are doing. When you follow all five steps, you build a team that always wants to get better. You find and remove waste, make better products, and give value to your customers. Lean manufacturing helps you work better and get great results.
Lean Production Flow

Stability in Lean Production
You need stability to make lean production work well. Stability means your process runs the same way every time. When you have stable production, you can spot problems quickly and fix them before they grow. You build stability by keeping machines in good shape, training your team, and following clear steps for each task.
Lean production uses data to keep your process steady. You can use control charts and other tools to watch for changes. These tools help you see patterns and catch issues early. When you use data, you do not guess. You make choices based on facts. This approach helps you cut waste and improve efficiency.
Tip: Stable lean production lets you deliver products on time and meet customer needs. You also lower costs and reduce mistakes.
Internal Logistics
Internal logistics means how you move materials and products inside your factory. Good internal logistics support lean production by making sure everything flows without stops. You want each part to arrive at the right place, at the right time. This helps you avoid piles of inventory and keeps your process smooth.
You can use just-in-time production to control your internal logistics. This method means you only bring in parts when you need them. You do not store extra items. You use signals, like Kanban cards, to tell your team when to move materials. This system supports just-in-time delivery and keeps your production lean.
Lean production flow works best when you:
Use data to track how materials move
Find and fix slow spots in your process
Train your team to spot and solve problems
Use simple tools to guide your work
When you use lean production and focus on internal logistics, you make your process faster and more reliable. You also improve customer satisfaction by meeting orders on time.
Practical Lean Implementation Tips
Value Identification Tips
You need to start by understanding what your customer values most. Talk to your customers and gather feedback. Use data to see which products or features matter most. You can collect numbers, look for patterns, and use charts to spot trends. Many companies use descriptive statistics, predictive modeling, and even machine learning to find hidden value in their operations. These methods help you make better decisions and focus on what really matters.
Ask your team to share ideas about what adds value.
Use surveys or interviews to learn from your customers.
Track which products sell best and why.
Apply tools like Six Sigma or root cause analysis to confirm your findings.
When you use these methods, you can see clear improvements in your manufacturing process. You reduce waste, increase value, and create customer value with every step.
Value Stream Mapping Tips
Draw a simple map of your entire production process. Show each step from raw material to finished product. Mark which steps add value and which steps create waste. Use real data, such as time spent at each stage or where delays happen. This helps you see where you can make improvements.
Involve your team in mapping the value stream.
Use sticky notes or software to make changes easy.
Review your map often to keep it up to date.
Creating Flow Tips
Set up your workspace so products move smoothly from one step to the next. Remove anything that blocks or slows down production. Train your team to spot problems early and fix them fast.
Arrange machines and tools in the order you use them.
Use signs or floor markings to guide the flow.
Keep work areas clean and organized.
Good flow in lean manufacturing means less waiting, fewer mistakes, and faster delivery.
Pull System Tips
Only produce what your customer needs, when they need it. Use signals like Kanban cards to control production. This keeps inventory low and reduces waste.
Set clear limits for how much you produce at each step.
Use visual signals to show when to start or stop work.
Check your system often to make sure it matches customer demand.
Continuous Improvement Tips
Always look for ways to get better. Hold regular meetings to discuss what works and what does not. Encourage your team to share ideas for improvement. Use data to measure your progress and celebrate small wins.
Set simple goals for each week or month.
Track key numbers like defect rate or lead time.
Reward your team for finding ways to reduce waste.
Continuous improvement helps you optimize lean manufacturing systems and keep your production strong.
Common Lean Pitfalls

Employee Involvement
You need your team to take part in every step of lean manufacturing. If you leave employees out, you miss ideas and slow down improvement. Many workers see problems before managers do. When you ask for their input, you find better ways to cut waste and add value. Hold regular meetings and encourage everyone to share feedback. Give training so each person understands the process and feels confident to help.
Tip: When you involve your team, you build trust and make your manufacturing stronger.
Process Updates
You may face problems when you update your process. Changes can bring confusion if you do not plan well. After COVID-19, many companies saw new steps and rules change often. This made it hard to measure results or compare progress. Without a simple way to collect data, you cannot track your improvement. Sometimes, teams do not get enough training in lean tools, which causes delays. You need clear goals that are specific and easy to measure. Keep checking your progress and adjust your plan as needed.
Common challenges with process updates:
Frequent changes make it hard to see what works.
Lack of easy data tools slows down tracking.
Not enough training leads to mistakes.
Missing feedback from workers and customers leaves gaps.
Goals that are not clear or realistic cause confusion.
Set clear targets and use simple tools to track your process. Train your team so everyone knows how to use lean methods.
Value Misunderstanding
You must know what your customer values. If you guess or make wrong assumptions, you waste time and resources. Some teams focus on features that do not matter to the customer. This creates extra work and adds waste. Always ask your customers what they need. Use surveys or direct talks to learn what brings value. Review your findings often to stay on track.
Ignoring Feedback
Ignoring feedback from your team or customers can hurt your manufacturing process. Workers often spot problems early. Customers can tell you if your product meets their needs. If you do not listen, you miss chances for improvement. Set up ways for people to share ideas. Thank them for their input and act on good suggestions.
Note: Feedback helps you find waste and improve your process. Make it easy for everyone to speak up.
You can make your manufacturing work better by using five lean steps.
Find out what is valuable.
Draw a map of your process.
Make sure work moves smoothly.
Only make things when needed.
Always try to get better.
Begin with small changes. Every step helps you waste less and do more. Keep using lean ideas. If you keep going, you will see things get better. Lean manufacturing works best when you keep making small improvements each day.
FAQ
What is the main goal of lean manufacturing?
You aim to reduce waste and deliver more value to your customers. Lean manufacturing helps you improve efficiency, cut costs, and make better products by focusing on what matters most.
How do you start implementing lean in your factory?
Begin by identifying what your customers value. Map your process, look for waste, and involve your team. Start with small changes. Track your progress and keep improving each step.
Can lean manufacturing work in small businesses?
Yes, you can use lean principles in any size business. Small teams often see results quickly because they can adapt faster. Focus on simple steps and involve everyone in the process.
What tools help you track lean improvements?
You can use charts, dashboards, and key metrics like cycle time, defect rate, and on-time delivery. These tools help you see progress and find areas to improve.
 LKprototype
LKprototype







