Looking to bring your product idea to life? This guide on how to develop a product prototype breaks down the essential steps. From your initial concept to a refined, testable prototype, you’ll learn the process to create a tangible, user-ready product.
Key Takeaways
Prototyping helps visualize and test product ideas early, identifying potential flaws and saving time and money in development.
User testing and feedback during the prototyping process are crucial for refining products to better meet user needs and expectations.
Protect your intellectual property by using patents and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to secure your product ideas while collaborating with others.
Understanding Product Prototyping
The process of prototyping involves crafting an initial version of a product to evaluate and affirm design concepts. This early model, known as the product prototype, can vary from basic drawings to complex functional prototypes that emulate the final product in detail. The main goal of creating a prototype is to uncover potential problems before commencing mass production, which ultimately conserves both resources and finances.
Different kinds of prototypes fulfill distinct roles within the product development process. For example, feasibility prototypes are utilized to determine if a particular technical concept is practical, while high-fidelity prototypes provide an accurate representation of what the final product will look like for thorough user feedback evaluation. Conversely, low-fidelity prototypes act as preliminary outlines offering an elementary vision for how users will interact with the future product before moving forward into more sophisticated designs.
In essence, prototyping plays a pivotal role in bringing abstract ideas into physical existence by visualizing products ahead of full-scale manufacturing—facilitating progress from idea inception toward market introduction. By converting ideas into actual models through this practice facilitates validation against user expectations and contributes significantly towards refining functionality. Partaking in such iterative testing advances both design quality and marketplace viability—it stands crucial during any successful development journey.
Benefits of Developing a Prototype

The process of prototyping a product offers critical advantages that can substantially influence the ultimate success of your offering. A primary benefit is the early detection of design deficiencies within the development phase. By undergoing testing with a prototype, you can spot concerns regarding user-friendliness, robustness, and operational performance. This step allows for vital modifications to be made before initiating mass production.
Creating prototypes significantly contributes to minimizing production expenses. Through precise estimation of costs associated with manufacturing time and materials required, avoids exorbitant redesigns and postponements later on. Collecting feedback from users during testing phases enhances overall satisfaction by ensuring your product aligns with what your intended customers want and anticipate.
Possessing an advanced-stage prototype increases credibility among stakeholders and draws in prospective financiers as well. Showcasing how functional your concept is through a tangible prototype communicates that you have invested significant thought into it and are dedicated to launching it commercially, which may help sway investors’ confidence in its potential returns – ultimately aiding you in obtaining necessary financial backing for entering full-scale manufacturing stages.
Steps to Develop a Product Prototype
Beginning the journey of transforming your product concept into a physical prototype through the manufacturing process entails following essential steps pivotal to shaping an initial prototype from your idea. This includes forming your product concept, drafting preliminary sketches and designs, constructing a proof-of-concept model, crafting a functional prototype for demonstration purposes, carrying out testing with users to garner feedback, and making necessary adjustments to enhance the design.
During this development process, you will employ an assortment of prototyping techniques ranging from simple resources such as clay and cardboard to sophisticated digital platforms like computer-aided design (CAD) software. Adhering diligently to these stages allows you not only accurately capture the essence of what you envisioned, but also fulfills expectations pertinent to those who form your intended audience.
Conceptualize Your Product Idea
Initiating the prototype development process requires first establishing a clear concept of your product idea. This crucial stage entails extensive market research to grasp the demands and challenges faced by your intended customers. Recognizing what these potential users seek guarantees that your product will satisfy an authentic need in the marketplace.
It’s imperative to conduct a competitive analysis as part of this initial phase. Investigating competitors can reveal beneficial insights about their products’ strengths and weaknesses, which can inform how you position yours for success. By pinpointing areas ripe for innovation, you ensure that your prototype stands out from others on the market. Thorough groundwork during these preliminary steps assures that the foundation of your development process is informed by factual data instead of mere speculation.
Create Initial Sketches and Drawings
When you’ve solidified your product concept, the subsequent phase involves crafting initial designs and diagrams. Opt for either classical strategies like drafting with pen on paper or utilize modern resources such as CAD (Computer Aided Design) applications. Paper prototyping entails illustrating design concepts manually and may extend to employing tangible items to signify various components of the product. These rudimentary drawings act as preliminary visualizations that encapsulate both aesthetic appeal and functional considerations.
Incorporating digital instruments, for instance, AutoCAD can augment the exactitude in your design process by generating meticulous 2D and 3D representations via computer-aided design techniques. If these skills are outside your expertise, it’s advisable to engage a professional graphic designer or collaborate with firms specializing in digital prototype creation to materialize your vision.
It is imperative at this juncture to solicit evaluative input since it presents an opportunity to incorporate diverse viewpoints into refining your prototype—a vital step before proceeding towards actual manufacturing stages.
Build a Proof of Concept
Creating a proof of concept is crucial for confirming that the mechanisms of your product function properly prior to progressing toward more intricate prototyping stages. During this phase, you develop a rudimentary prototype which showcases your product’s fundamental capabilities, providing an opportunity to evaluate critical components and uncover any early-stage problems.
Ensuring that your product idea is viable and can be evolved into a functional prototype is facilitated by having a proof of concept. It allows you to validate the technical elements of your design thoroughly so that you may proceed with certainty, secure in the knowledge that your idea has been rigorously examined and stands ready for additional development.
Develop a Functional Prototype
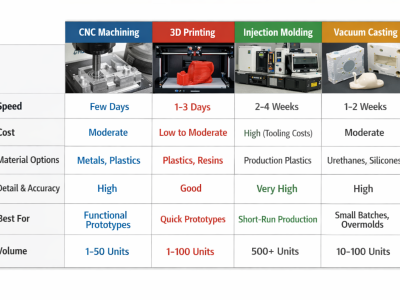
Creating a functional prototype entails the production of a physical model that accurately represents what the final product will look like. This process can employ various techniques, such as 3D printing, for rapid and precise creation of mechanical or industrial design prototypes.
Additional methods for fabricating functional prototypes include CNC machining and vacuum casting. CNC manufacturing commonly utilizes materials such as aluminum, copper, and ABS plastic. Whereas in vacuum casting processes, polyurethane and silicone are often used to mimic different types of plastics.
By using these approaches, one can generate detailed virtual prototypes that are subject to testing and iterative refinement through feedback gathered from users.
Conduct User Testing
The process of user testing plays a vital role in the prototyping phase, enabling you to collect feedback from genuine users to enhance your design. Presenting them with a functioning prototype for testing garners essential insights into how the product performs in practical scenarios.
Engaging in user testing allows for continuous refinement through iterative design adjustments informed by real-life use cases. By soliciting feedback directly from your intended audience, you can ensure that the final version of your product aligns with their requirements and anticipations, paving the way for its ultimate success.
Refine and Finalize Your Design
In the final phase of the prototype development process, your task is to perfect and complete your design. This entails incorporating essential modifications in response to user feedback and resolving all potential problems before proceeding to mass production. By continually assessing and enhancing your prototype’s performance, you guarantee that the final product meets top-quality standards.
Constructing a product roadmap can be instrumental in monitoring continuous enhancements and anticipated upgrades. Employing project management tools aids in orchestrating different stages of prototyping effectively. Through successive refinements across multiple iterations of the prototype, you achieve a product ready for manufacturing that corresponds with both your objectives and consumer anticipations.
Cost Considerations in Prototyping
Taking into account the financial aspect is paramount during the prototyping process, as it can lead to substantial future cost reductions by averting costly errors and subsequent redesigns. The expenses associated with creating a prototype can vary significantly, often ranging between $100 and upwards of $30,000 based on the design’s intricacy.
At the onset of prototyping lies the concept design stage, which typically incurs costs around $1,000. Progressing to more intricate stages such as design engineering prototypes. Sees starting costs at about $5,000. Following this is the prototype and test phase where developers craft a working alpha prototype. This particular step usually requires an investment exceeding $10,000. Setting up manufacturing for these prototypes can begin at a steep price point of approximately $30,000 depending heavily upon both complexity levels and material requisites.
To effectively control expenditures throughout each stage of prototyping without compromising your financial limitations, it’s crucial to determine an appropriate budget beforehand—and adhere strictly to it—ensuring that you deliver your product in a financially savvy manner.
Protecting Your Intellectual Property
Ensuring the security of your intellectual property is paramount throughout the process of prototyping to prevent the unauthorized replication of your product concept. Initiating a provisional patent application stands as a critical measure in shielding your design prior to advancing with the creation of a prototype. The laws surrounding intellectual property offer essential defense mechanisms for both your inventions and product designs.
The implementation of non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) establishes a legally binding framework that keeps sensitive data from falling into unapproved hands. There are primarily two forms: unilateral NDAs, which involve one party divulging confidential material, and mutual NDAs, where confidentiality is reciprocated between parties exchanging information. Adopting standard NDA templates can facilitate an efficient method for securing private details.
In engagements with external parties who assist in fabricating prototypes, it’s imperative to ensure that protections over your intellectual property rights are firmly in place by legal means.
Tools and Resources for Prototyping
A myriad of instruments and assets are crucial for the construction of prototypes, including CAD software and 3D printers. With 3D printing technology, one can swiftly bring CAD models to life, enabling rapid alterations and refinements. Utilizing power tools in fabrication processes can lead to the creation of stronger prototypes that include functional elements.
Prototype workshops offer access to an array of tools and machinery which may not be readily accessible on-site. For individuals working within a limited financial scope, there are affordable prototype manufacturing solutions available. Services offered by product prototype designers as well as full-service prototyping firms can greatly enhance the scope of prototyping projects.
Companies specializing in electronics prototyping play a pivotal role in integrating electronic features into prototypes thereby augmenting their overall functionality.
Collaborating with Experts
Involving specialists in the prototyping process can greatly improve your product’s quality and feasibility. Collaborating with engineers and designers leads to precise sketches and representations that guarantee both production readiness and visual attractiveness. Prototypes offer a concrete basis for dialogue among collaborators, resulting in more enlightened choices.
Starting as a unified team helps pinpoint and tackle possible impediments swiftly, reducing postponements. Collective testing and validation efforts bolster the end product’s caliber, securing adherence to rigorous benchmarks of quality assurance and customer satisfaction.
Encouraging teamwork between design and engineering personnel allows for the honing of concepts into market-ready innovations.
Real-World Examples of Successful Prototypes

Examples from the real world underscore the critical role that prototyping plays in introducing new products to consumers. For example, a prominent soft drink brand employed 3D printing technology during their prototyping process to create an innovative beverage dispensing system prototype. This design received positive feedback from focus groups and was later transitioned into mass production.
In another case, a pharmaceutical company developed a prototype for tamper-evident blister packaging that made any interference apparent while maintaining user-friendliness.
These instances demonstrate how product prototypes evolve from initial concepts into market-ready solutions throughout the prototyping process, often incorporating unforeseen improvements that refine the end product.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
In the development process, it is crucial to avoid certain traps that can impair progress when utilizing prototyping. A common mistake is to proceed with the initial workable idea without considering superior alternatives, which can result in missed opportunities. Ensuring that prototypes are created with a clear purpose helps prevent squandering resources and keeps the prototyping aligned with intended objectives.
Becoming overly attached to any one prototype can inhibit an unbiased assessment of its value. It’s important to embrace failed prototypes as part of a learning curve necessary for ongoing advancement. Over-explaining design concepts might distract from efficient prototyping activities and harboring the notion that prototyping is frivolous risks foregoing critical insights pivotal for product triumphs.
Summary
Creating a product prototype is an intricate procedure that includes numerous phases, starting with the initial concept and progressing through to the enhancement of the ultimate design. The act of prototyping serves not only to pinpoint and rectify any design shortcomings, but also aids in diminishing production expenses while drawing in prospective investors. By adhering to this guide’s outlined steps, you have the opportunity to produce a triumphant product prototype that caters perfectly to your target audience’s needs and distinguishes itself within the marketplace.
Keep in mind that transforming a concept into a market-ready item is repetitive by nature and demands ongoing refinement at every stage. Embrace each aspect of this journey, absorb knowledge from every version produced, and maintain focus on your intended goal. With unwavering commitment paired with an appropriate strategy, your creative concepts can be actualized successfully as you materialize them into tangible products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a product prototype?**?
The primary purpose of a product prototype is to identify issues early, helping you save time and money while ensuring the product aligns with user expectations.
It’s all about validating your ideas before diving into production!
How can prototyping reduce production costs?**?
Prototyping cuts production costs by enabling precise predictions of expenses, time, and materials, which helps avoid expensive redesigns and delays.
This way, you save money and streamline the whole process.
What are the common methods used to develop a functional prototype?**?
To develop a functional prototype, you can use common methods like 3D printing, CNC machining, and vacuum casting, each providing unique advantages in speed, materials, and cost.
Just choose the one that best fits your project’s needs!
Why is user testing important in the prototyping process?**?
User testing is essential in prototyping because it lets you collect valuable feedback from real users, helping you refine designs and ensure the final product truly meets the needs of your target audience.
By incorporating this feedback, you can create a product that’s more likely to succeed.
How can I protect my intellectual property during the prototyping process?**?
To safeguard your intellectual property during prototyping, file a provisional patent application and use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with anyone involved.
Don’t forget to ensure that third-party prototype makers also have protections in place for your designs.
Still, need help? Contact Us: [email protected]
Need a PROTOTYPE or PARTS machining quote? Quote now
 LKprototype
LKprototype